It has been 20 years since a paper within the journal Science confirmed the environmental accumulation of tiny plastic fragments and fibres. It named the particles “microplastics”.
The paper opened a complete analysis area. Since then, greater than 7,000 printed research have proven the prevalence of microplastics within the surroundings, in wildlife and within the human physique.
So what have we discovered? In a paper launched at this time, a world group of consultants, together with myself, summarise the present state of data.
Briefly, microplastics are widespread, accumulating within the remotest elements of our planet. There may be proof of their poisonous results at each degree of organic organisation, from tiny bugs on the backside of the meals chain to apex predators.
Microplastics are pervasive in food and drinks and have been detected all through the human physique. Proof of their dangerous results is rising.
The scientific proof is now greater than enough: collective world motion is urgently wanted to deal with microplastics – and the issue has by no means been extra urgent.
Tiny particles, enormous drawback
Microplastics are typically accepted as plastic particles 5mm or much less in a single dimension.
Some microplastics are deliberately added to merchandise, equivalent to microbeads in facial soaps.
Others are produced unintentionally when greater plastic gadgets break down – for instance, fibres launched if you wash a polyester fleece jacket.
Research have recognized a few of the primary sources of microplastics as:
- beauty cleansers
- artificial textiles
- car tyres
- plastic-coated fertilisers
- plastic movie used as mulch in agriculture
- fishing rope and netting
- “crumb rubber infill” utilized in synthetic turf
- plastics recycling.
Science hasn’t but decided the speed at which bigger plastics break down into microplastics. They’re additionally nonetheless researching how shortly microplastics develop into “nanoplastics” – even smaller particles invisible to the attention.
Measuring the microplastic scourge
It is tough to evaluate the amount of microplastics within the air, soil and water. However researchers have tried it.
For instance, a 2020 research estimated between 0.8 and three million tonnes of microplastics enter Earth’s oceans in a 12 months.
And a current report suggests leakage into the surroundings on land might be three to 10 instances higher than that to oceans. If right, it means between ten and 40 million tonnes in whole.
The information will get worse. By 2040, microplastic releases to the surroundings may greater than double. Even when people stopped the move of microplastics into the surroundings, the breakdown of larger plastics would proceed.
Microplastics have been detected in greater than 1,300 animal species, together with fish, mammals, birds and bugs.
Some animals mistake the particles for meals and ingest it, resulting in hurt equivalent to blocked intestines. Animals are additionally harmed when the plastics inside them launch the chemical substances they include – or these hitch-hiking on them.
Invaders in our our bodies
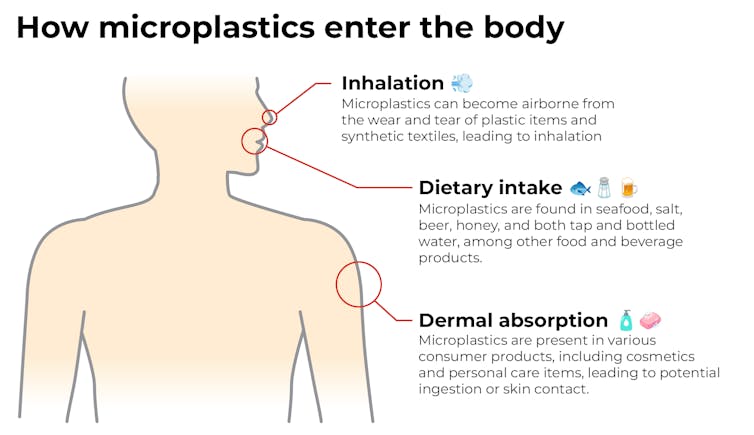
Microplastics have been recognized within the water we drink, the air we breathe and the meals we eat – together with seafood, desk salt, honey, sugar, beer and tea.
Typically the contamination happens within the surroundings. Different instances it is the results of meals processing, packaging and dealing with.
Extra information is required on microplastics in human meals equivalent to land-animal merchandise, cereals, grains, fruits, greens, drinks, spices, and oils and fat.
The concentrations of microplastics in meals differ extensively – which implies publicity ranges in people around the globe additionally varies. Nonetheless, some estimates, equivalent to people ingesting a bank card’s value of plastic each week, are gross overstatements.
As tools has superior, scientists have recognized smaller particles. They’ve discovered microplastics in our lungs, livers, kidneys, blood and reproductive organs. Microplastics have crossed protecting obstacles into our brains and hearts.
Whereas we get rid of some microplastics by means of urine, faeces and our lungs, many persist in our our bodies for a very long time.
So what impact does this have on the well being of people and different organisms? Through the years, scientists have modified the way in which they measure this.
They initially used excessive doses of microplastics in laboratory assessments. Now they use a extra reasonable dose that higher represents what we and different creatures are literally uncovered to.
And the character of microplastics differ. For instance, they include completely different chemical substances and work together otherwise with liquids or daylight. And species of organisms, together with people, themselves differ between people.
This complicates scientists’ capability to conclusively hyperlink microplastics publicity with results.
With reference to people, progress is being made. In coming years, anticipate higher readability about results on our our bodies equivalent to:
- irritation
- oxidative stress (an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants that damages cells)
- immune responses
- genotoxicity – injury to the genetic info in a cell that causes mutations, which might result in most cancers.
What can we do?
Public concern about microplastics is rising. That is compounded by our seemingly long-term publicity, given microplastics are nearly unattainable to take away from the surroundings.
Microplastic air pollution is the results of human actions and selections. We created the issue – and now we should create the answer.
Some international locations have carried out legal guidelines regulating microplastics. However that is inadequate to handle the problem. That is the place a brand new legally binding settlement, the UN’s International Plastics Treaty, affords an necessary alternative. The fifth spherical of negotiations begins in November.
The treaty goals to cut back world manufacturing of plastics. However the deal should additionally embody measures to cut back microplastics particularly.
In the end, plastics have to be redesigned to stop microplastics being launched. And people and communities have to be introduced on board, to drive help for presidency insurance policies.
After 20 years of microplastics analysis, there’s extra work to be accomplished. However now we have greater than sufficient proof to behave now.![]()
Karen Raubenheimer, Senior Lecturer, College of Wollongong
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.





