Meteorites have a reasonably dangerous status. The newest main influence with our planet was – to be honest – fairly devastating, wiping out a very good three-quarters of all animal species on the planet.
However a a lot, a lot bigger impactor, for much longer in the past, could have had the alternative impact.
Some 3.26 billion years in the past a large rock between 50 and 200 instances the dimensions of the Chicxulub dino-killer smacked into our planet. In accordance with a group led by geologist Nadja Drabon of Harvard College, the upheaval ensuing from this gobsmackingly-colossal influence would have churned up vitamins that gave a choose few early microbes a lift.
“Image your self standing off the coast of Cape Cod, in a shelf of shallow water,” Drabon says. “It is a low-energy setting, with out sturdy currents. Then hastily, you’ve a large tsunami, sweeping by and ripping up the ocean ground.”
We do not know, firsthand, what a large meteorite influence does to our planet. That is a very good factor, general. However we’re in a position to mannequin and simulate what occurs, reconstructing occasions primarily based on mineral deposition within the geological file.
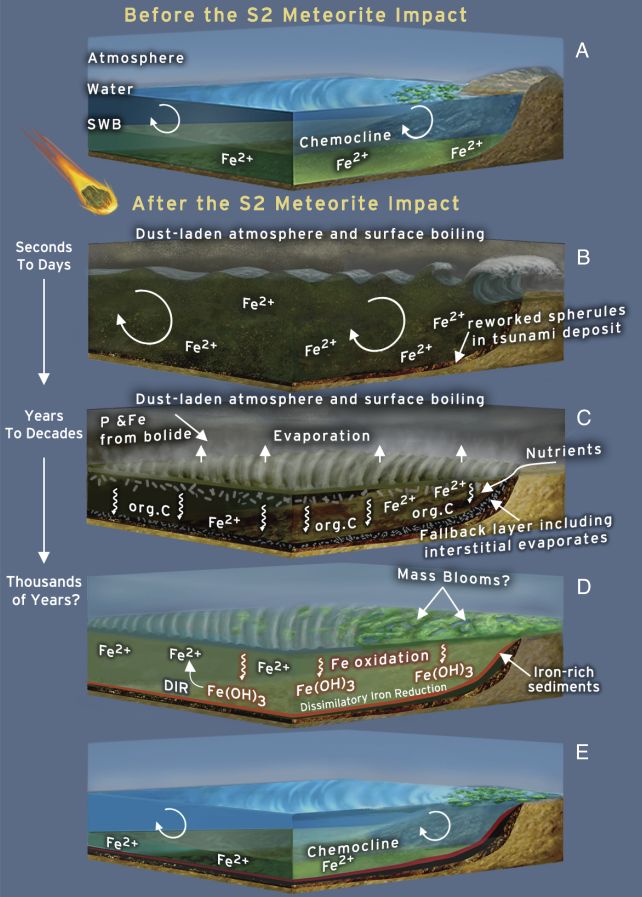
A formation generally known as the Barberton Greenstone Belt in South Africa comprises proof of a large influence that shook Earth 3.26 billion years in the past, an occasion generally known as S2. Drabon and her colleagues carried out a painstaking characterization of the minerals within the S2 rock layer, and devised a reconstruction of the sequence of occasions that adopted.
It nonetheless would have been fairly devastating. The warmth from the collision would have boiled off the highest layer of the ocean, whereas the influence itself is predicted to have sprayed mud and particles into the ambiance, making a thick haze that blocked the daylight and stymied photosynthetic microbes dwelling in shallow waters.
There additionally would have been an enormous tsunami that dredged the ocean ground, bringing materials often sequestered within the depths to the floor.
Though this could have harmed most of the burgeoning life varieties that had been eking out an existence for only a few hundred million years at this level, it will have been a boon to some.
The meteorite itself would delivered a burst of phosphorus, for instance, whereas the waters dredged up from the seafloor would have been wealthy in iron. Each parts would have fed any microbes able to metabolizing them, inflicting a short, however vital, spike of their numbers earlier than Earth settled again down right into a extra steady existence. This may particularly have been true for iron-metabolizing microbial blooms in shallow waters.
“We consider influence occasions as being disastrous for all times, however what this examine is highlighting is that these impacts would have had advantages to life, particularly early on,” Drabon says. “These impacts might need truly allowed life to flourish.”
It will be greater than 2.5 billion years earlier than multicellular organisms would emerge, introducing their very own vital adjustments to Earth’s biosphere. And dinosaurs did not seem till about 250 million years in the past, give or take, reigning till the Chicxulub meteorite triggered the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction 66 million years in the past.
Even that devastating influence – the one meteorite we have confidently linked to an extinction occasion – opened new avenues for all times to thrive. With the decline of the non-avian dinosaurs, mammals rose to fill the vacated ecological niches; with out that devastation, it is attainable that humanity would by no means have emerged.
So, whereas it’s true {that a} huge meteorite influence has vital deleterious results for some organisms, it could possibly profit others in sudden methods. In reality, it is totally attainable that repeated early impacts altered Earth in ways in which primed it for the evolutionary explosions that might comply with.
“Our work means that on a worldwide scale, youth could have benefitted from an inflow of vitamins and electron donors, in addition to new environments, because of main influence occasions,” the researchers write.
They plan to review the Barberton Greenstone Belt additional, to attempt to piece collectively this mysterious, however probably essential, interval within the historical past of life on Earth.
The analysis has been printed within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.





