Within the constellation of Cygnus, some 7,800 light-years from Earth, lurks an actual house oddity. There, a black gap in a system named V404 Cygni repeatedly engages in conduct that has concurrently baffled and delighted scientists.
Now it is whipped a model new trick out of its seemingly limitless arsenal: an unseen binary companion, a star on a large orbit of round 70,000 years.
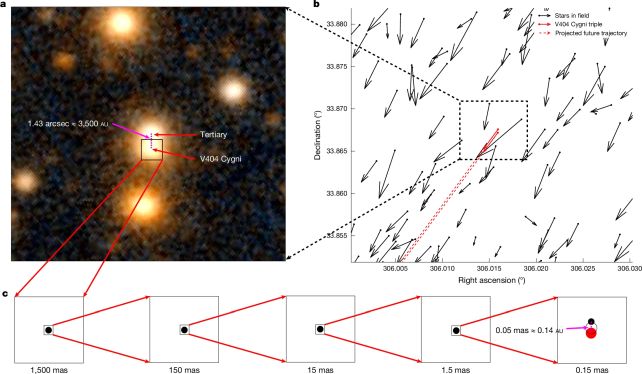
Since V404 Cygni already has a companion – a star on an in depth, 6.5-day orbit, on which the central black gap is leisurely feasting – the newly found third object makes the system a trinary.
It is the primary time we have seen a system with this configuration, and it may provide some insights into how black holes type. It is because a supernova explosion, regarded as the mechanism by which stellar-mass black holes type, ought to have snapped the tenuous gravitational bond of a large orbit.
“We expect most black holes type from violent explosions of stars, however this discovery helps name that into query,” says physicist Kevin Burdge of the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how.
“This method is tremendous thrilling for black gap evolution, and it additionally raises questions of whether or not there are extra triples on the market.”
We have identified in regards to the second star, in reality, for many years; astronomers thought it was only a star near V404 Cygni, which might be comparatively unremarkable.
However knowledge collected by the European Area Company’s Gaia mission revealed that there is undoubtedly extra occurring there than we thought. Gaia is mapping the three-dimensional positions of the objects within the Milky Approach galaxy; nevertheless it’s additionally mapping their route and velocity as they transfer via house.
V404 Cygni and the seemingly unrelated star are transferring via house in the identical route and on the identical pace. That reveals the objects are linked.
“It is virtually definitely not a coincidence or accident,” Burdge says. “We’re seeing two stars which might be following one another as a result of they’re connected by this weak string of gravity. So this needs to be a triple system.”
There’s proof on the market for the supernova mannequin of black gap formation. That is when a dying star erupts in a colossal explosion, ejecting its outer materials, whereas the core of the star collapses beneath gravity to type a black gap, the densest object within the Universe.
Scientists have seen supernovae, and disentangled the sunshine to gauge the mass of the item on the core to deduce the manufacturing of a black gap. However that does not imply {that a} supernova is the one formation mechanism. Another choice is the direct collapse mannequin. Right here, the large star merely implodes, utterly, right into a black gap, no mess, no fuss.
Right here, the proof is a bit more troublesome to return by. With no mess or fuss, there’s just about an absence of proof.
That is the place V404 Cygni abruptly turns into very attention-grabbing certainly – as a result of when a supernova explosion is asymmetrical, which they typically are, the imbalance in vitality can provide the nascent black gap a directional kick.
That is troublesome to resolve with such a large orbit as seen with the newly related star. The black gap and the star are separated by a distance of three,500 astronomical items, which makes their gravitational tether to one another comparatively weak. The disruption launched by a supernova ought to have damaged that tether like a wisp of cobweb.
The large orbital separation additionally makes gravitational seize between two passing objects difficult to clarify. Burdge and his colleagues carried out tens of 1000’s of simulations, and located that the perfect rationalization is that the three objects have been already gravitationally sure when the black gap fashioned; and that the formation mechanism was direct collapse.
“The overwhelming majority of simulations present that the best approach to make this triple work is thru direct collapse,” Burdge says.
It is the perfect proof but for the direct collapse mannequin of black gap formation, which bolsters the mechanism as a legitimate approach to interpret black holes whose formation historical past is troublesome to resolve with a supernova.
There could very effectively even be different large black hole-inclusive trinaries on the market that we now have missed because of black holes’ stealthiness; discovering them may assist us higher perceive how these objects type, and why a black gap would possibly collapse immediately fairly than exploding in a blaze of sunshine.
“Both we acquired very fortunate, or tertiaries are frequent,” says astronomer Kareem El-Badry of Caltech.
“If they’re frequent, which may remedy a few of the long-standing questions on how black gap binaries type. Triples open up evolutionary pathways that aren’t doable for pure binaries.
“Individuals have really predicted earlier than that black gap binaries would possibly type largely via triple evolution, however there was by no means any direct proof till now.”
The analysis has been revealed in Nature.





