In the age-old saying “You are what you eat,” there’s more truth than we often realize. Many chronic diseases, especially cognitive conditions like dementia, are directly linked to what we consume daily. A study spanning 22 years has confirmed that those who habitually consume an inflammatory diet face a significantly higher risk of developing dementia, and most are completely unaware of it.
The Link Between Inflammatory Diets and Dementia Risk
A recent 22-year-long study published in Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia found that those who frequently eat an inflammatory diet have a much higher risk of developing dementia. The study tracked 1,487 participants and concluded that the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) increased by a staggering 88% among those with the highest “dietary inflammation index” (DII).

Research Screenshot
Chronic, low-grade inflammation often goes unnoticed by individuals, making it even more dangerous. Inflammation in the body can be triggered by certain foods, and this inflammation is associated with a higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia. The study assigned a score to 36 dietary components, and the higher the score, the more pro-inflammatory the diet.
Foods were categorized into two groups: anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory. Anti-inflammatory foods include foods like Omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants, while pro-inflammatory foods include high-fat, high-sugar, and highly processed foods.

Pro-Inflammatory Foods: The Everyday Culprits
Studies have long shown that chronic inflammation plays a central role in conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. Below are five common pro-inflammatory foods that are part of the daily diet for many individuals:
1. Excessive Red Meat Consumption
Red meats, such as beef, pork, and lamb, have been shown to promote inflammation in the body. Overconsumption increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, colorectal cancer, and obesity. Red meat consumption has long been associated with increased inflammation markers.
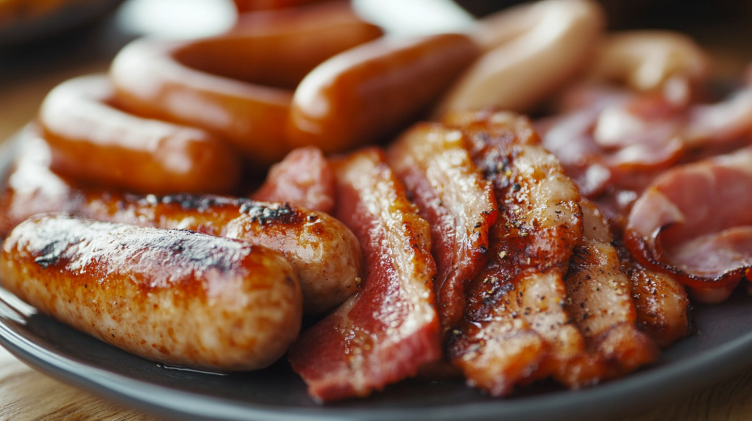
2. Processed Meats
Processed meats like bacon, sausages, and ham are known to contain harmful chemicals like N-nitroso compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons that trigger inflammation. These substances increase oxidative stress and inflammation. Processed meat includes meats that have been modified through curing, salting, or smoking.

3. High-Sugar Foods
Refined sugars disrupt the gut microbiota, leading to chronic inflammation. Foods like sugary beverages, pastries, and white bread are prime contributors. Sugar intake, particularly refined sugar, has been linked to inflammation and metabolic issues.

4. Trans Fats
Trans fats, commonly found in processed foods like cakes, cookies, and margarine, promote inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. Trans fats are artificial fats that are created through hydrogenation and can raise cholesterol levels and inflammation.
5. Fried Foods
Fried foods, especially those cooked in reused oil, contain high levels of saturated fats and trans fats. The frying process itself also generates harmful compounds that can aggravate inflammation. Fried food is associated with high calorie content and increased risk of metabolic diseases.

Anti-Inflammatory Foods: The Key to Better Health
On the other hand, certain foods help reduce inflammation and may help prevent diseases like Alzheimer’s. The China Anti-Cancer Association and other health organizations recommend the following anti-inflammatory foods for better health:
1. Whole Grains
Foods like brown rice, oats, and barley are rich in fiber and have a proven anti-inflammatory effect while also helping maintain stable blood sugar levels. Whole grains are an essential part of a healthy diet due to their high fiber and nutrient content.

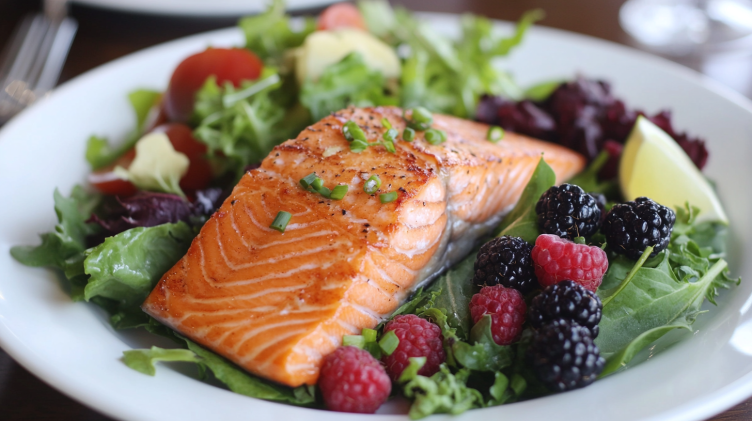
2. Healthy Fats
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon and tuna, as well as in walnuts and flaxseeds, play a key role in reducing inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties and heart health benefits.

3. High-Quality Proteins
Opt for lean proteins like fish, poultry, eggs, and plant-based proteins like tofu and legumes. Avoid processed meats to reduce inflammation. Protein is essential for bodily functions, but the source and quality are crucial for reducing inflammation.
4. Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
Vegetables and fruits, particularly those rich in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and tomatoes, are packed with vitamins and minerals that help fight inflammation. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables help neutralize free radicals that contribute to inflammation.

5. Tea
Drinking green or black tea has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Tea contains polyphenols, which are effective in reducing inflammation and preventing various cancers, including colorectal cancer. Tea is rich in compounds like catechins and flavonoids that are linked to numerous health benefits.

Conclusion
Diet plays a pivotal role in the body’s inflammation levels, which in turn affects overall health and well-being. By making simple changes—like reducing red and processed meats, cutting down on sugar, and adding more whole grains and healthy fats to your diet—you can significantly reduce your inflammation levels and lower your risk for dementia and other chronic diseases. It’s never too late to make healthier dietary choices, and doing so could help you live a longer, more vibrant life.