The largest and strongest rocket ever constructed now has a half-dozen launches below its belt.
SpaceX’s 400-foot-tall (122 meters) Starship megarocket lifted off for the sixth time ever at present (Nov. 19), rising off the orbital launch mount on the firm’s Starbase website in South Texas at 5:00 p.m. EST (2200 GMT; 4:00 p.m. native Texas time).
SpaceX landed Starship’s large first-stage booster, referred to as Tremendous Heavy, again on the launch tower on the car’s most up-to-date flight, which occurred on Oct. 13. The corporate aimed to repeat that feat — which the tower achieved with its “chopstick” arms — at present, however the flight information did not help an try.
“We tripped a commit standards,” SpaceX’s Dan Huot mentioned through the firm’s Flight 6 webcast. So Tremendous Heavy ended up coming down for a managed splashdown within the Gulf of Mexico as an alternative, hitting the waves seven minutes after liftoff.
Anticipation for Flight 6 was excessive, partially due to the deliberate booster-catch try. For instance, President-elect Donald Trump made the journey to South Texas to observe Flight 6 in individual.
Associated: Starship and Tremendous Heavy defined
Trump’s help for Musk and Starship is not terribly shocking; the 2 billionaires have apparently grown fairly shut over the previous few months.
Musk campaigned exhausting for Trump’s election and put greater than $100 million of his personal cash towards that effort. And Trump has appointed Musk to co-lead the “Division of Authorities Effectivity.” This advisory group, Trump mentioned, will assist his administration “dismantle Authorities Forms, slash extra rules, lower wasteful expenditures and restructure Federal Companies.”

An action-packed flight
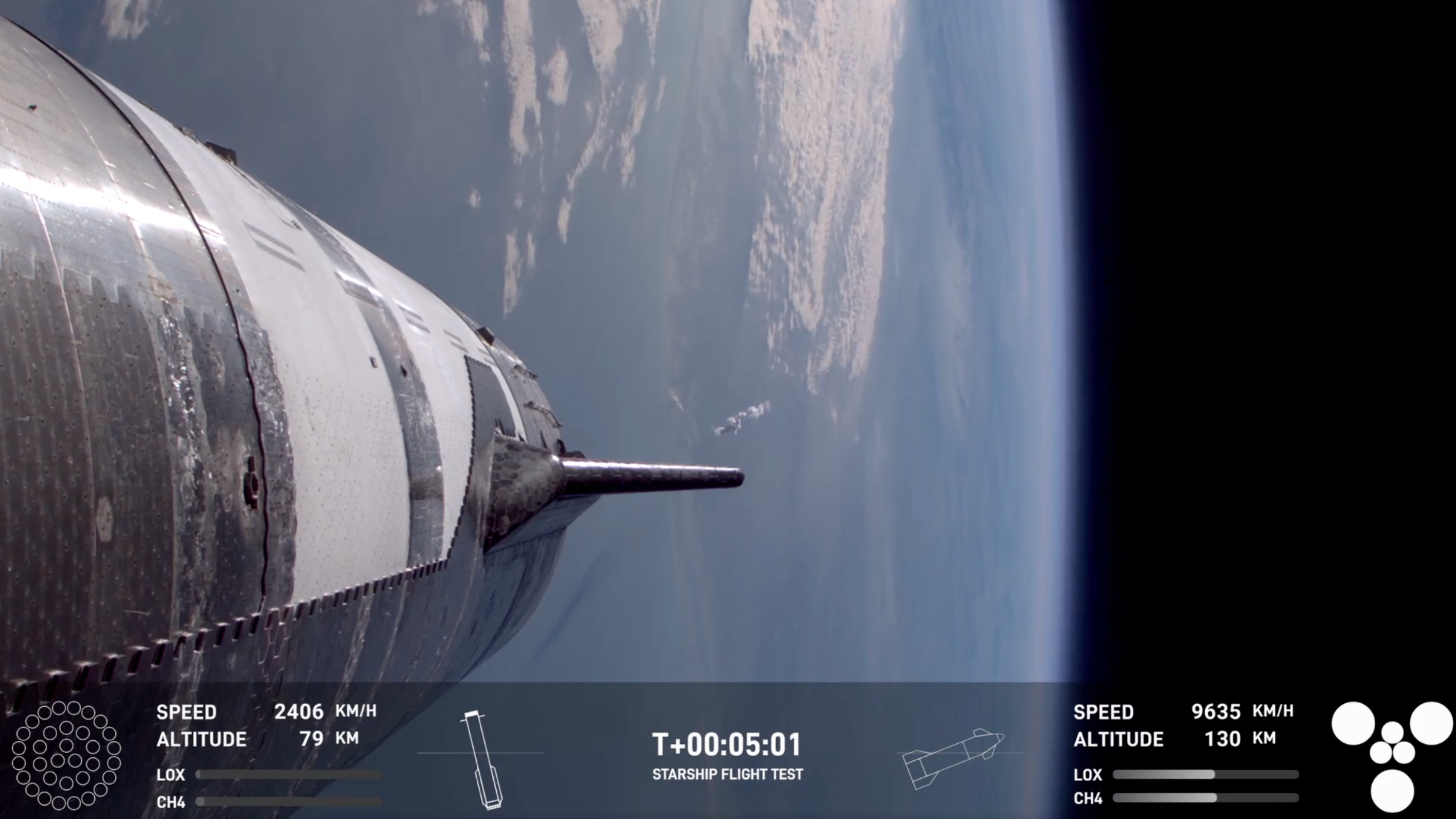
In the present day’s mission aimed to do way over simply convey Tremendous Heavy again to Earth in a single piece. SpaceX additionally needs to place Starship’s higher stage — a 165-foot-tall (50 m) spacecraft known as Starship, or just “Ship” — via its paces.
The launch despatched Ship on the identical semi-orbital trajectory that it took on Flight 5, focusing on a splashdown within the Indian Ocean off the coast of Australia about 65 minutes after liftoff. However there will likely be some new milestones alongside the best way this time, if all goes based on plan.
For instance, Flight 6 carries the first-ever Starship payload — an opulent banana onboard Ship, which serves as a zero-gravity indicator. (It is not going to be deployed into area.) As well as, Ship will rekindle one in all its six Raptor engines about 38 minutes into the flight. (Tremendous Heavy additionally employs Raptors — a whopping 33 of them.)
This burn will assist present that Ship can carry out the maneuvers wanted to come back again to Earth safely throughout orbital missions. Certainly, Ship is designed to be absolutely and quickly reusable, similar to Tremendous Heavy; SpaceX finally intends to catch it with the chopstick arms as properly, and can doubtless attempt to take action on a take a look at flight within the close to future. (Touchdown straight on the launch mount, relatively than on a ship at sea or a chosen landing pad, will allow faster and extra environment friendly inspection, refurbishment and reflight, SpaceX has mentioned.)
Flight 6 can also be testing modifications to Ship’s warmth protect, which protects the car throughout reentry to Earth’s environment.
“The flight take a look at will assess new secondary thermal safety supplies and can have total sections of warmth protect tiles eliminated on both facet of the ship in places being studied for catch-enabling {hardware} on future autos,” SpaceX wrote in a mission description. “The ship additionally will deliberately fly at the next angle of assault within the ultimate part of descent, purposefully stressing the boundaries of flap management to achieve information on future touchdown profiles.”
SpaceX additionally shifted the launch time for Flight 6, to permit for higher remark of Ship’s reentry and splashdown. Flight 5 (and all 4 of its predecessors) lifted off from Texas within the morning, and Ship got here down in darkness on the opposite facet of the world.
Associated: SpaceX’s epic Starship Tremendous Heavy rocket catch regarded similar to the corporate imagined (side-by-side video)

Ramping up the flight fee
SpaceX is creating Starship to assist humanity settle the moon and Mars, and to carry out all kinds of different spaceflight duties, comparable to constructing out its Starlink broadband megaconstellation in low Earth orbit.
NASA has a critical stake within the car, deciding on Starship to be the primary crewed lander for its Artemis program of moon exploration. If all goes based on plan, Starship will put NASA astronauts down on the moon for the primary time in late 2026, on the Artemis 3 mission.
SpaceX is working to get Starship up and operating as quickly as attainable, and take a look at flights are an enormous a part of this effort. The megarocket has now flown six instances — in April and November of 2023, and March, June, October and November of this 12 months — and the cadence is more likely to improve significantly within the close to future.
Musk is apparently focusing on 25 Starship launches in 2025 and 100 a number of years after that. These numbers could seem optimistic, however SpaceX has already launched 113 missions of its workhorse Falcon 9 rocket thus far in 2024. And the regulatory atmosphere — which Musk has railed in opposition to repeatedly in current months — might quickly calm down significantly, given Trump’s said objectives and his apparently closeness with the SpaceX founder and CEO.
These take a look at missions are designed to pave the best way for extra formidable jaunts — and shortly, if all goes based on plan.
“Each one in all these flights is a step nearer to a totally operational Starship that may take us past Earth orbit, and with our tempo of speedy iteration right here, the moon and Mars aren’t practically as far sooner or later as you might suppose,” Kate Tice, a senior high quality engineering supervisor at SpaceX, mentioned throughout at present’s launch webcast. “In reality, we’re planning to ship starships to Mars as quickly as 2026, which is when the subsequent Mars switch window opens.”





