There continues to be guesswork relating to sources out there on the moon.
Clearly, a number one sizzling subject is whether or not or not super-chilly water ice on the lunar south pole is really ripe for the selecting and processing into oxygen, hydrogen and different necessities wanted for all times assist, even rocket gasoline.
Certainly, exploitable water ice is on NASA’s Artemis agenda, a prospect considered as enabling a “sustainable” human presence on that bleak and cratered world. Lunar water ice is believed to reside inside “chilly traps,” permanently-shadowed areas, or PSRs. That elixir for all times, together with a bountiful wellspring of different moon sources, might assist shore up a self-sustaining area financial system. However maintain that thought. There is a want for first issues first.
Marketing campaign path
What’s urgently wanted is a moon prospecting effort to indicate the “reserve” potential of the lunar south pole.
It is a energetic election yr in the USA. Additionally on the marketing campaign path, so to talk, is Clive Neal, an knowledgeable in lunar exploration and professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences on the College of Notre Dame.
Final month, the celestial campaign has Neal detailing an preliminary Worldwide Lunar Assets Prospecting Marketing campaign on the 2024 Worldwide Geological Congress, that was held Aug. 25-31 in Busan, South Korea.
“We have to formalize this marketing campaign by way of getting individuals onboard, to take it critically. It is time for collaboration and cooperation,” Neal tells House.com. To realize this, a devoted coordinated marketing campaign of lunar missions is required. The moon’s useful resource potential have to be quantitatively evaluated, he argues.
Like water ice, there are different sources that might be helpful, Neal advises, and good science, exploration and business interactions await. The Worldwide Lunar Assets Prospecting Marketing campaign (ILRPC) is achieved by coordination, he stated.
Useful resource and reserve
Neal flags the truth that the time period “useful resource” in a lunar context has been used interchangeably with “reserve.” Doing so has precipitated confusion.
Primarily based upon present information and sure customers, the one potential lunar reserve is oxygen from regolith as it’s current in about the identical proportion anyplace on the moon. Defining it as a reserve, nevertheless, requires financial and authorized points but to be absolutely addressed.
Neal stated {that a} reserve — as framed by the U.S. Geological Survey — defines the time period “as that portion of an recognized useful resource from which a usable mineral or vitality commodity may be economically and legally extracted on the time of dedication.”
Between now and the top of the last decade, 30 robotic lunar missions are funded and below improvement; 16 extra have been proposed, however not but funded, Neal notes. “The entire level of the marketing campaign is that we do not have to create new missions, they’re both there, have gone, or are going.”
Lunar missions are actually and might be churning out various knowledge units. An entity is required to coordinate between completely different moon missions, together with these of China and Russia, stated Neal. Implementing the ILRPC requires a non-governmental group, finest representing a community-driven endeavor, he contends.

Worldwide curiosity
Ongoing and scheduled missions reveal the worldwide curiosity within the south pole area of the moon.
As an illustration, the veteran NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter is now dutifully finishing up prolonged science targets, together with a deal with volatiles on the polar areas.
Then there’s the Korean Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter now in operation across the moon. So, too, is the orbital element of India’s Chandrayaan-2 mission from 2019.
There is a chance to combine these completely different mission datasets and future spacecraft outputs to derive helpful merchandise for the nice of all lunar polar volatiles, Neal stated.
On the books
Upcoming and focused for the moon contains NASA’s Lunar Trailblazer, an orbiter geared to gauge the shape, abundance, and distribution of water on the moon and the lunar water cycle by way of thermal and infrared mapping of the lunar floor.
Apparently nonetheless caught in lunar limbo is the NASA Artemis lunar rover, the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER. The area company canceled VIPER on account of price range considerations. However it appears to be nonetheless rolling ahead as business and/or worldwide companions could also be fascinated about flying the moon machine to the lunar south pole.
Additionally, lawmakers in Congress are taking a budgetary hard-look on the scenario, prodded partially by a save the VIPER letter-writing marketing campaign now involving 4,800-plus supporters. Within the interim, VIPER not too long ago entered thermal vacuum chamber testing to be accomplished by October.
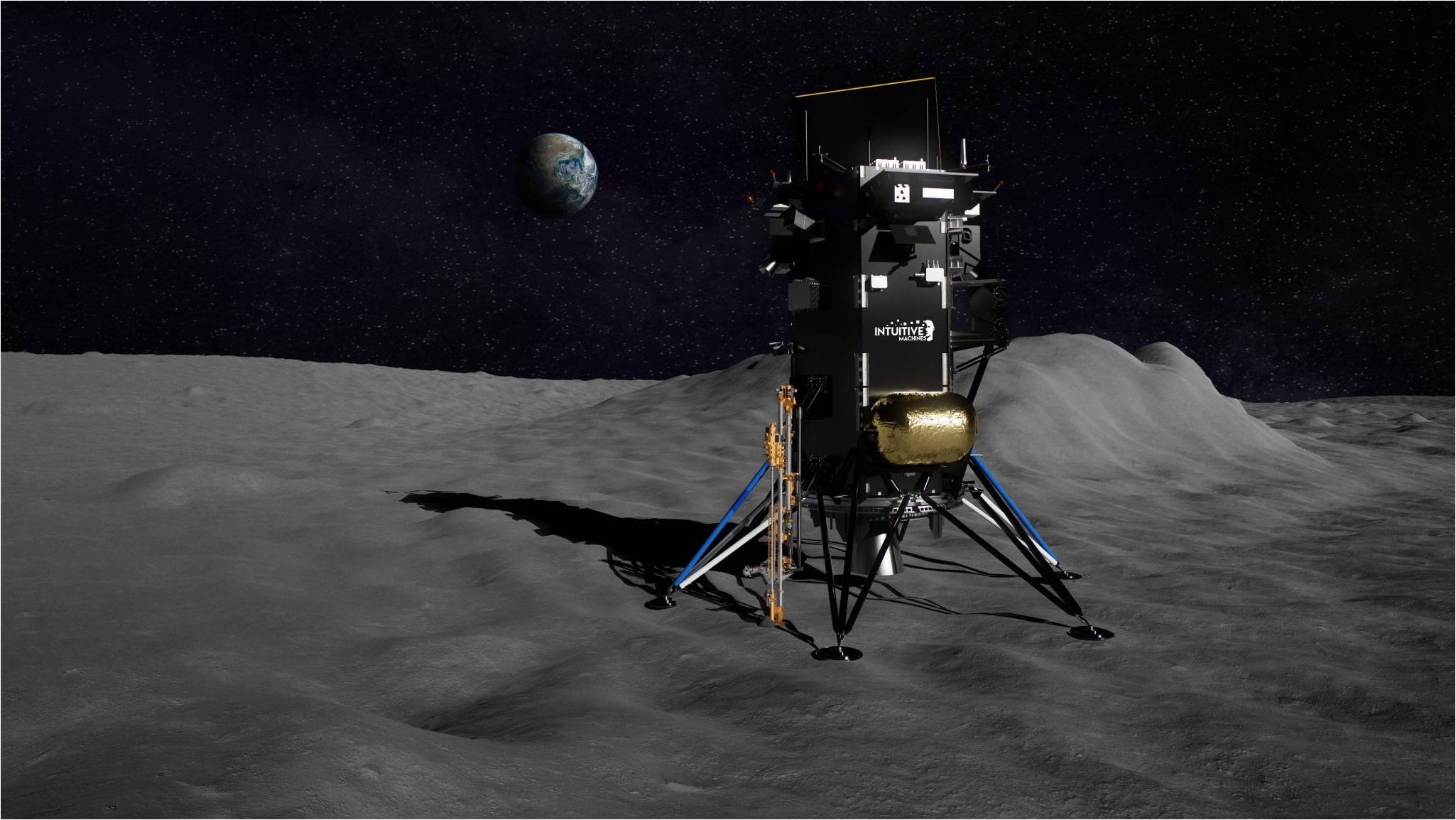
Later this yr is NASA’s Polar Assets Ice Mining Experiment-1, slated to fly on the personal Intuitive Machines IM-2 moon lander as a part of the Industrial Lunar Payloads Companies endeavor.
If IM-2’s landing is achieved, a Micro Nova Hopper, a propulsive drone funded by NASA, is to be deployed and bounce throughout the lunar floor, even dive into the completely shadowed flooring of Marston crater. The hopper’s objective is to yield the primary direct floor measurement of hydrogen, a key indicator for the presence of water.
On the books is the LUnar Polar EXploration mission (LUPEX) mission from the Japanese House Company in collaboration with the Indian House Company to discover Shackleton — de Gerlache ridge for volatiles.
Add within the European House Company’s Package deal for Useful resource Statement and in-Situ Prospecting for Exploration, Industrial exploitation and Transportation (PROSPECT), constructed for lunar floor/subsurface probing to judge volatiles.
China and Russia are additionally engaged on robotic missions to analyze the south pole for unstable sources as a prelude to establishing an Worldwide Lunar Analysis Station.

Coping with Datasets
“That is an iterative method. Whereas companies and organizations are placing cash into ISRU [in-situ resource utilization], we do not even know if we will extract the water ice. We do not know if that is an economically viable useful resource on the moon,” stated Neal. “With out taking elementary steps, investments in ISRU know-how might all be vaporware.”
Neal is aware of that coordinating this marketing campaign of cooperation and collaboration is not going to be straightforward.
Any lunar useful resource analysis or prospecting marketing campaign will have to be worldwide in nature, Neal concludes, as nobody area company can have the cash or mandate to conduct it alone.
“That is the place science and exploration come collectively. Everyone wins if science and exploration go collectively,” Neal stated.





