In letzter Zeit breitet sich ein dichter Nebel über den USA aus, der Besorgnis unter den Amerikanern hervorruft. Der seit mehreren Tagen anhaltende Nebel hat Alarm ausgelöst. Es handelt sich nicht um gewöhnlichen Nebel, sondern um einen mit einem seltsamen, chemischartigen Geruch.
Nebel in Florida

David Bamber aus Florida schilderte seine Erfahrungen. Er beschrieb den Nebel als so dicht, dass die Sicht auf den Straßen stark eingeschränkt war. Gleichzeitig lag ein merkwürdiger chemischer Geruch in der Luft. Der weißliche, dichte Nebel erzeugte eine gespenstische Atmosphäre.
Seltsamer Nebel in Montana
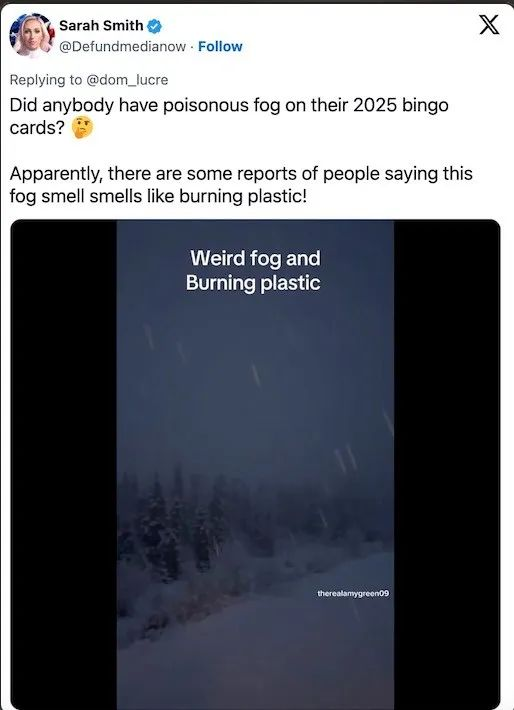
In Montana veröffentlichte Sarah Smith ein Video. Trotz Schneefalls war ein massiver, verschwommener Nebel zu erkennen, der nach verbranntem Plastik roch. Viele Anwohner berichteten von ähnlichen Erfahrungen.
Nebel in Massachusetts

Ein Bewohner von Massachusetts teilte ein Foto mit weißen Nebelpartikeln. Unter Lichteinfall wirkten sie wie in der Luft schwebende Regentropfen. Der seltsame Nebel schwebte knapp über dem Boden und erzeugte ein surreales Gefühl.
Beunruhigende Erfahrung in Florida

Ein Floridabewohner schilderte, wie er nach nur 10 Minuten in der Nähe einer Tankstelle zu husten begann und Fieber entwickelte. Kurz darauf folgten Niesanfälle mit geschwollenen Augen. Innerhalb einer Stunde traten grippeähnliche Symptome und Magenkrämpfe auf.
Besorgnis in Kansas

In Kansas äußerte eine Anwohnerin Verdacht: Seit fast einer Woche herrsche dichter Nebel, möglicherweise verursacht durch “Chemtrails” aus Experimenten oder unbekannten Quellen.
Ungewöhnlicher Nebel in Kalifornien

Ein Kalifornier beschrieb auf Social Media anhaltenden, ungewöhnlichen Nebel mit seltsamem Geruch, der seit Monaten auftrete. Es fühle sich wie ein Angriff aus der Luft an.
Nebel in Kanada und Großbritannien
Nicht nur in den USA, sondern auch in Teilen Kanadas und Großbritanniens kursierten Berichte über ähnliche Nebelphänomene. Dies weckte noch größere Besorgnis, da der Nebel einen deutlichen chemischen Geruch aufwies. Warum trat dieser seltsame Nebel sowohl in Großbritannien als auch in Nordamerika auf?
Öffentliche Skepsis

Trotz einer Nebelwarnung des National Weather Service (NWS) waren viele Menschen nicht überzeugt. Eine verbreitete Theorie unter Internetnutzern besagte, der Nebel stehe in Verbindung mit einer geheimen Militäroperation. Sie fragten sich, ob US-Bürger als “Versuchskaninchen” für ein Chemieexperiment missbraucht würden.
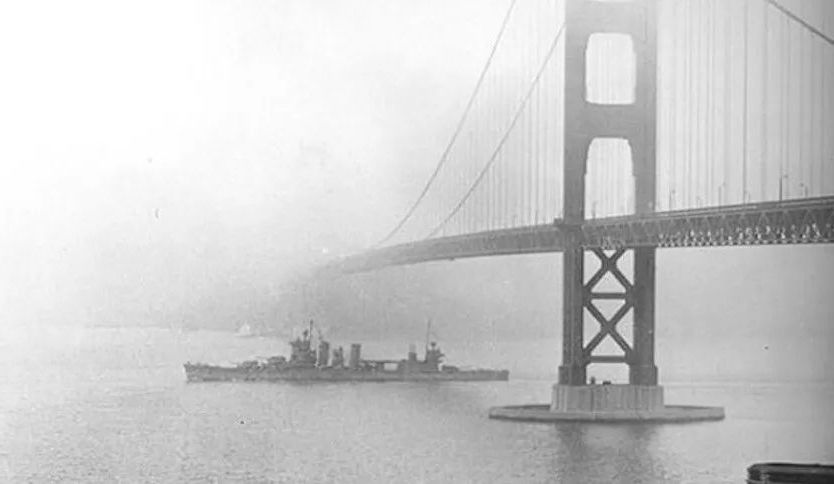
Der „Operation Sea-Spray“-Vorfall

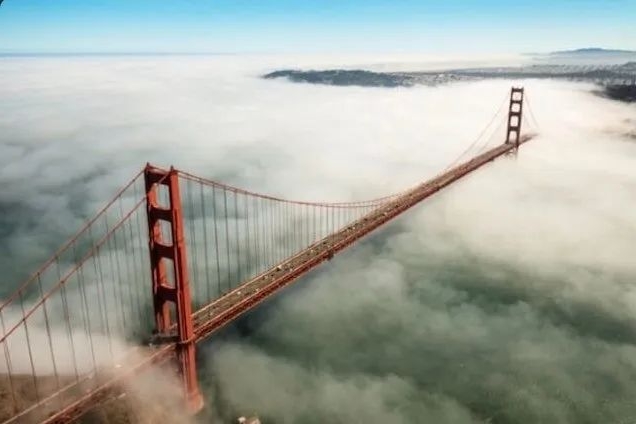
Diese Theorie verknüpfte man mit einem mysteriösen Ereignis aus dem Jahr 1950. Am 20. September überzog plötzlich ein seltsamer, chemisch riechender Nebel San Francisco. Selbst Teile der Golden Gate Bridge verschwanden im Dunst. Der Nebel hielt eine Woche an, und viele Anwohner erkrankten.
Am 11. Oktober suchten 11 schwer erkrankte Bewohner das Stanford Hospital auf. Die Diagnose lautete auf eine seltene Infektion durch das Bakterium Serratia marcescens. Nach der Behandlung genasen 10 Patienten, doch ein Mann namens Edward Nevin verstarb.
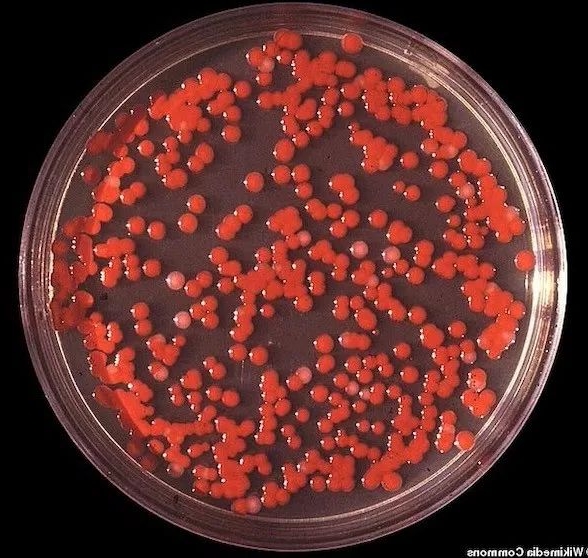
Das rätselhafte Bakterium

Das seltene Serratia marcescens-Bakterium war zwar nicht hochgefährlich, aber in Nordamerika praktisch unbekannt. Ärzte rätselten über seine Herkunft. Nach monatelangen Ermittlungen kam die Wahrheit ans Licht: Das US-Militär hatte das Bakterium absichtlich in die Luft freigesetzt.
Die Wahrheit hinter dem Nebel
1977 wurde bei einer Senatsanhörung enthüllt, dass die US Navy 1950 ein geheimes Biowaffenexperiment durchgeführt hatte. Unter dem Codenamen „Operation Sea-Spray“ setzte die Marine Serratia marcescens zusammen mit Anthrax-Simulantien in der Atmosphäre frei. Die Freisetzung erfolgte vor der Küste von San Francisco.
Das Militär überwachte 43 Stellen in der Stadt und stellte fest, dass über 800.000 Einwohner die Partikel eingeatmet hatten. Die “Vergiftungsaktion” dauerte mehrere Tage. Ob die 11 Erkrankungen und der Todesfall tatsächlich auf das Experiment zurückgingen, bleibt unklar.
<!– wp:Ein solches Experiment fand 1966 statt. Forscher setzten pathogene Bakterien in der New Yorker U-Bahn frei, um die Verbreitung von Bacillus-anthracis-Sporen zu testen. Während der Hauptverkehrszeit infizierten die Krankheitserreger viele Bewohner, und mehrere Menschen erkrankten oder starben. Ziel dieser Experimente war es, die Reaktion großer US-Städte auf biologische Angriffe zu bewerten.
Öffentliche Ängste und Skepsis
Aufgrund dieser Vorgeschichte, in der die Öffentlichkeit als „Versuchsobjekte“ genutzt wurde, sind Amerikaner zu Recht besorgt über den Nebel. Sie fragen sich, ob der aktuelle Nebel Teil eines neuen Experiments ist. Der National Weather Service reagierte jedoch schnell auf die Gerüchte. Man erklärte, die Nebelpartikel seien lediglich durch das Licht sichtbar gemachte Luftschadstoffe. Der „chemische Geruch“ entstand dadurch, dass der Nebel Schadstoffe wie Autoabgase und Industrieemissionen aufnahm.
Der NWS erläuterte, dass Schwefeldioxid, Stickoxide und andere Schadstoffe in den Wassermolekülen des Nebels eingeschlossen werden. Diese Schadstoffe bleiben in der Luft schweben und verursachen den von vielen bemerkten chemischen Geruch. Dies sei zwar ein seltenes Ereignis, aber der NWS betonte, es handle sich um ein natürliches Phänomen, keine Verschwörung.
Fazit
Obwohl der Nebel ein natürliches Ereignis sein könnte, bleibt die Sorge vor chemischen Ursachen groß. Es zeigt, dass die Öffentlichkeit geheimen Regierungsexperimenten immer noch misstraut. Bislang bleibt der Nebel für viele ein Rätsel, doch die Behörden fordern zur Ruhe auf. Es gibt keine Hinweise auf bösartige Aktivitäten hinter diesem ungewöhnlichen Wetterphänomen.



















