A colossal asteroid slammed into Jupiter’s largest moon Ganymede with a lot energy it dramatically and completely reoriented the moon roughly 4 billion years in the past, new analysis suggests. Scientists say the pivotal affect additionally considerably influenced the geological and inside evolution of the moon, which is bigger than Mercury.
Laptop simulations by planetary scientist Naoyuki Hirata of Japan’s Kobe College predict the asteroid should have been about 186 miles (300 kilometers) vast, or 20 occasions greater than the fateful one which worn out the dinosaurs from the face of our planet about 66 million years in the past.
Solely an affect of this scale can be highly effective sufficient to destabilize Ganymede and trigger the tidally-locked moon to whirl on its axis, based on a examine printed by Hirata on Tuesday (Sept. 3) within the journal Scientific Studies.
“It is a neat try to rewind the clock by way of laptop simulations, looking for an evidence for the distribution of scars throughout Ganymede,” Leigh Fletcher, a planetary scientist on the College of Leicester within the U.Ok. who was not concerned with the brand new examine, instructed The Guardian.
Hirata estimates the consequential course of unfolded over roughly 1,000 years following the asteroid affect. The house rock seemingly crashed into Ganymede at an angle of 60 to 90 levels and produced a crater someplace between 870 to 990 miles vast (1400 to 1600 km), the brand new examine finds.
The proof for Ganymede’s reorientation is rooted in its floor, which is pockmarked with intensive furrows, or concentric rings of troughs regarded as fragmented remnants of bowl-shaped basins created by asteroid impacts. A recent evaluation of Ganymede’s largest furrow system, which scars the moon just under its equator, means that the asteroid strike brought on the moon to spin such that the affect crater faces away from Jupiter.
The asteroid strike would have “utterly eliminated the unique floor” of Ganymede, due to the crater reaching a whopping 25 p.c of the moon’s dimension, the researcher mentioned in a latest assertion. The affect would have considerably affected the moon’s geology and inside, the place scientists suppose a hidden saltwater ocean containing extra water than all of Earth’s oceans mixed exists.
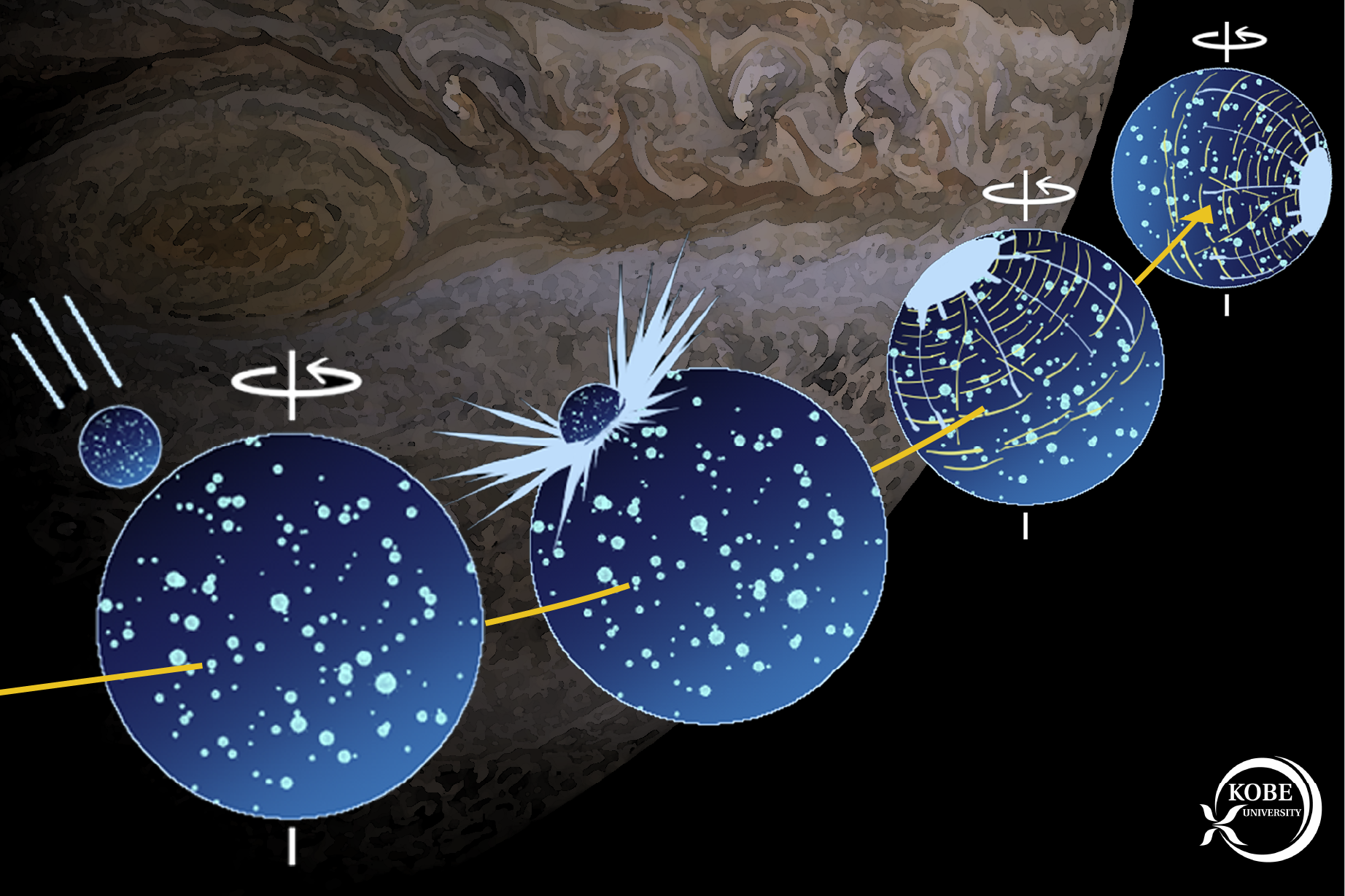
Though each Voyager spacecraft in addition to the Galileo probe took photographs of Ganymede within the late 1900s, many areas of the moon haven’t but been imaged with enough decision, limiting scientists’ understanding of its historical past and evolution. As an example, Ganymede’s dramatic reorientation might have spurred fractures and different tectonic landforms throughout its floor that have not been found but, Hirata mentioned.
Forthcoming photographs of Ganymede from the European House Company’s JUICE spacecraft may reveal extra about how the asteroid strike formed the moon’s evolution. JUICE pulled off tough gravitational slingshots previous our moon and Earth simply final month, and is about to reach on the Jupiter system in 2031.
Over the next 2.5 years, the solar-powered JUICE will orbit the gasoline big whereas swinging previous Ganymede, Europa and Callisto a number of occasions, cataloging their floor options in addition to potential for habitability by flying inside 120 to 620 miles (200 to 1,000 kilometers) of their surfaces.
JUICE will return to Ganymede in December 2034 for a devoted nine-month examine, which might mark the primary time a spacecraft orbits a moon aside from our personal.




