The Occasion Horizon Telescope (EHT), which is a collaboration of radio telescopes all world wide that function in unison to picture supermassive black holes, has achieved its most interesting decision but. Sooner or later, this accomplishment might result in pictures of the ring of sunshine round a black gap’s occasion horizon which can be 50% sharper, resolving hitherto unseen particulars and producing films of how the black holes change as they spin.
The EHT works on the precept of “very lengthy baseline interferometry,” or VLBI for brief. This includes tapping right into a community of telescopes throughout continents that each one work collectively to look at the identical object, combining their information within the course of. The broader the space between the 2 farthest telescopes within the community, the larger the decision, and the extra telescopes there are within the community, the larger the sensitivity.
The EHT managed to picture the black gap within the middle of our Milky Manner galaxy, Sagittarius A*, in addition to the black gap within the middle of the elliptical galaxy M87, M87* — marking the primary two black gap pictures captured by humanity — as a result of it has an enormous baseline. Consider the baseline as being the telescope’s aperture. The EHT’s most southern telescope is the South Pole Telescope, whereas its most northern station is the Greenland Telescope, which implies the community spans virtually prime to backside of the planet.
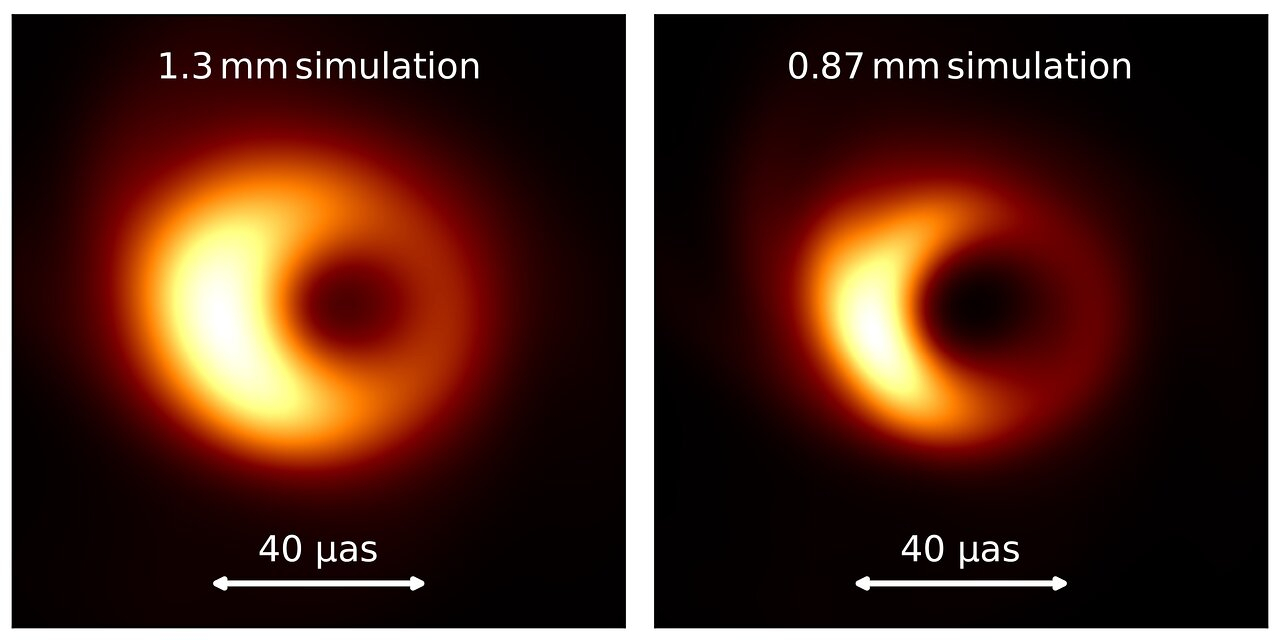
Together with the baseline issue, wavelength has a job to play, with decrease wavelengths reaching greater decision. The historic pictures of the black gap on the middle of our galaxy and M87 had been captured at a radio wavelength of 1.3mm. At this wavelength, the “photon ring,” which is the torus of emission across the occasion horizon with the black gap’s darkish shadow inside it, seems blurred — notably within the case of Sagittarius A*. It is because the radio emission coming from the black gap is being partially scattered by ionized gasoline within the interstellar medium between us and the article itself. This leads to the sunshine turning into smeared throughout an angular scale, corresponding to the decision of the EHT at 1.3mm. The smearing impact could be drastically much less obvious at shorter wavelengths.
Associated: Beautiful Pictures of Our Milky Manner Galaxy (Gallery)
To this finish, for the primary time ever, the EHT has been capable of conduct VLBI at a shorter wavelength of 0.87mm.
“With the EHT, we noticed the primary pictures of black holes by detecting radio waves on the 1.3mm wavelength, however the brilliant ring we noticed, fashioned by mild bending within the black gap’s gravity, nonetheless appeared blurry as a result of we had been on the absolute limits of how sharp we might make the photographs,” mentioned Alexander Raymond, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in a assertion. “At 0.87mm, our pictures shall be sharper and extra detailed, which in flip will possible reveal new properties, each those who had been beforehand predicted and perhaps some that weren’t.”
Attaining VLBI at 0.87mm shouldn’t be a straightforward factor, therefore why it hasn’t been completed earlier than. One of many difficulties has to do with water vapor within the ambiance tending to soak up radio waves at this brief wavelength, so climate must be very dry in any respect the EHT’s observing websites.
As for these observing websites, this explicit VLBI experiment concerned each the Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment in Chile, the Institute for Radio Astronomy within the Millimeter Vary (IRAM) 30-meter telescope in Spain, the Northern Prolonged Millimeter Array (NOEMA) in France, the Submillimeter Array (SMA) on Mauna Kea in Hawaii and the Greenland Telescope, all of that are stations for the EHT. Probing quite a few quasars at 0.87mm, they achieved a decision of 19 microarcseconds.
How small is nineteen microarcseconds? Nicely, the sky is split into 360 levels, with every diploma consisting of 60 arcminutes, and every arcminute is additional subdivided into 60 arcseconds. A microarcsecond is a millionth of an arcsecond, so 19 microarcseconds is like with the ability to resolve a bottle-top on the floor of the moon. It is the best decision for an astronomical picture ever achieved solely from the floor of the Earth (though combos of ground- and space-based telescopes have achieved comparable resolutions prior to now). Raymond and his colleagues really suppose the EHT might resolve down to simply 13 arcseconds when working at full capability (for instance, with the inclusion of the South Pole Telescope, which was not concerned within the 0.87mm check).
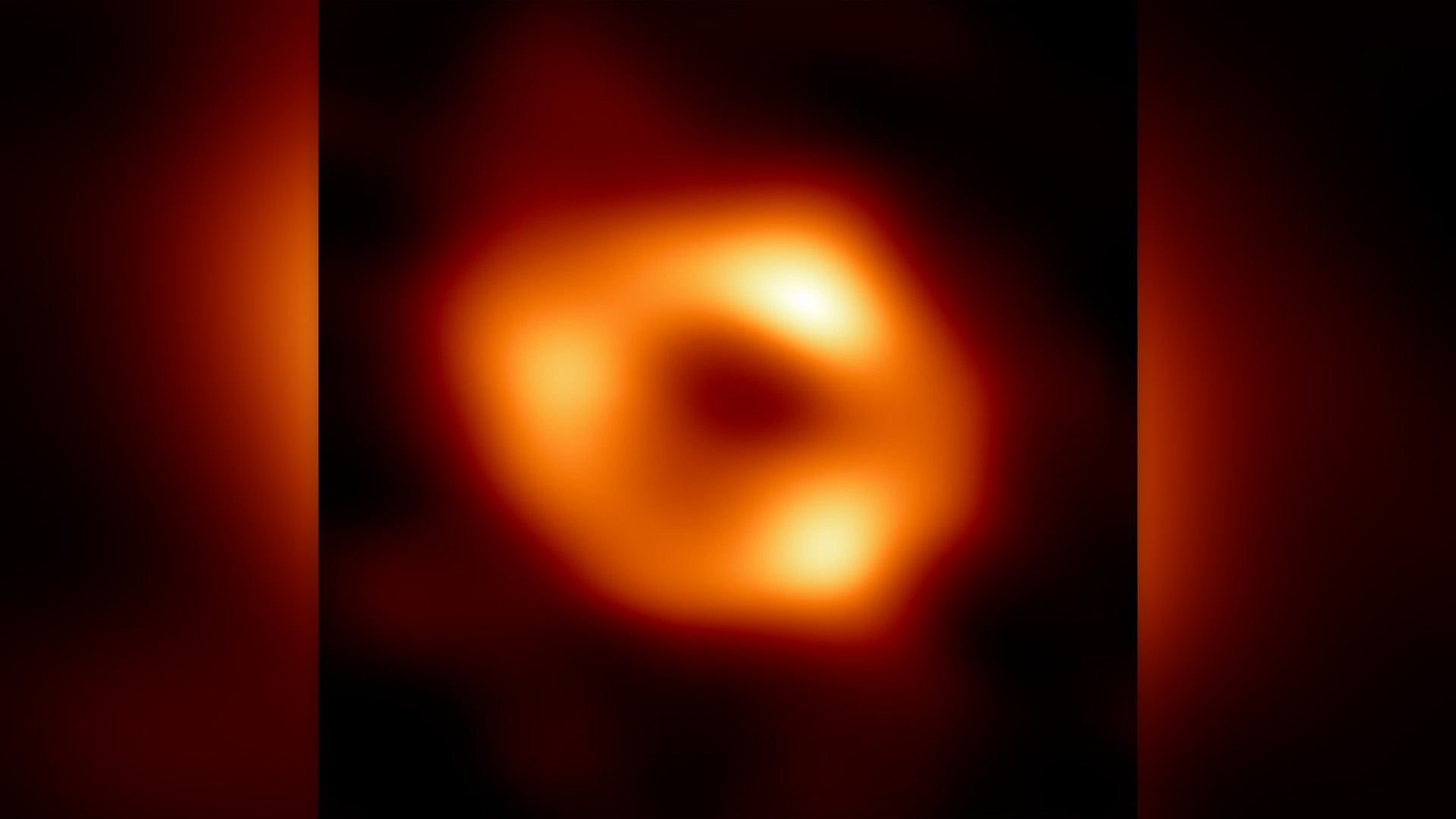

The intention now’s to use this breakthrough whereas taking new pictures of Sagittarius A* and the supermassive black gap in M87.
“The time is true, as the brand new detections show, to advance to 0.87mm,” mentioned Remo Tilanus of the College of Arizona, who’s the EHT’s Operations Supervisor.
The larger decision will not simply sharpen the picture of the photon ring round every black gap, but additionally extra exactly depict their form and dimension, permitting extra correct estimates of the black holes’ spin charges and angle to us. It’ll additionally deliver into vary supermassive black holes in different galaxies, and permit us to see nearer to the bottom of relativistic jets capturing out from energetic black holes corresponding to in quasars. This might present extra solutions into how a black gap’s magnetic area produces jets that transfer at virtually the velocity of sunshine and lengthen out into deep area for hundreds of light-years.
Along with now with the ability to function at a shorter wavelength, there are plans in place for main modifications to the EHT, in a program referred to as “subsequent era EHT,” or “ngEHT” for brief. This can add new telescopes to the prevailing EHT infrastructure at areas world wide optimized to offer the best baselines and sensitivity, in addition to enhance detector services on the current members of the collaboration to allow them to observe black holes at a number of wavelengths between 3mm and 0.87mm concurrently.
All in all, the following era EHT is anticipated to extend the sharpness and readability of black gap pictures by an element of 10, even perhaps enabling high-resolution films displaying modifications within the photon ring round a black gap’s occasion horizon over time because the black gap spins and accretes extra matter from the encompassing area.
“These VLBI sign detections at 0.87mm are groundbreaking since they open a brand new observing window for the research of supermassive black holes,” mentioned Thomas Krichbaum of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany in a assertion issued by the European Southern Observatory.
The outcomes of this groundbreaking VLBI experiment had been printed on Aug. 27 in The Astronomical Journal.





