En una operación encubierta que sorprendió a los analistas militares, Ucrania lanzó una huelga de drones que no fue solo audaz, sino que se ejecutó brillantemente. La misión dañó o destruyó docenas de aviones rusos, muchos de los cuales se usaban para aterrorizar a las ciudades ucranianas con ataques casi diarios.
UcraniaServicio de seguridad de Ucrania (SBU)Se afirmó la responsabilidad de la huelga, diciendo que 41 aviones rusos fueron golpeados. Estos incluyeron bombarderos estratégicos y planos de vigilancia. Si bien el número exacto de aviones completamente destruidos sigue sin estar claro, la operación se está aclamando como uno de los movimientos más atrevidos de la guerra de Ucrania.
Justin Bronk, un miembro principal en elRoyal United Services Institute, lo llamó “un éxito impresionante”. Hizo hincapié en que incluso si solo la mitad de las afirmaciones de daño resultan precisas, la huelga degradaría significativamente la capacidad de Rusia para llevar a cabo a largo plazomisil de cruceroataques, así como mantienen sus misiones de disuasión nuclear en Europa y Asia.
Golpear objetivos muy por detrás de las líneas enemigas
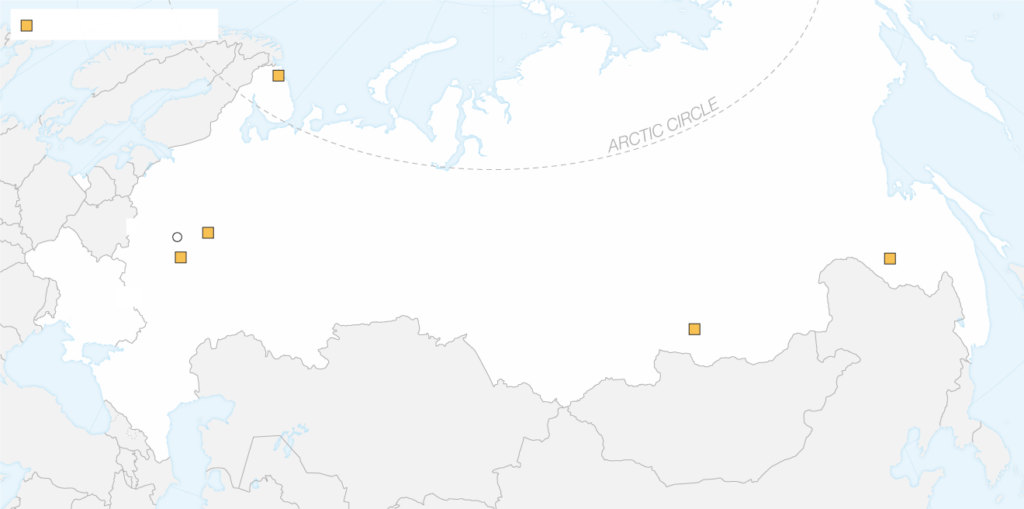
El ataque no se llevó a cabo en la frontera, llegó a lo profundo del territorio ruso. Uno de los golpes aéreos más alejados fueEn problemas, ubicado en elIrkutsk oblast, aproximadamente 4,500 kilómetros (2,800 millas) de Ucrania.
UcraniaSbutambién identificó una base en RusiaAcúdico amurcomo objetivo. No está claro si el ataque allí falló o fue cancelado.
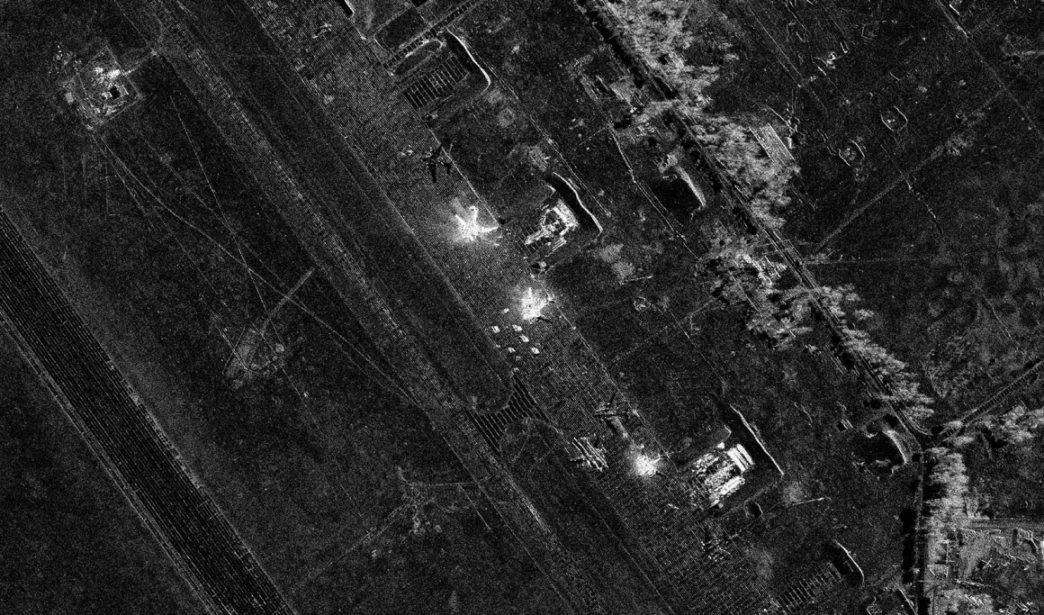
Muchas de estas bases tenían aviones estacionados a la intemperie, algunos incluso visibles enGoogle Maps. La complacencia rusa puede haber surgido de la creencia de que estos lugares eran seguros debido a la distancia sola.
Lanzamiento de drones desde el interior de Rusia
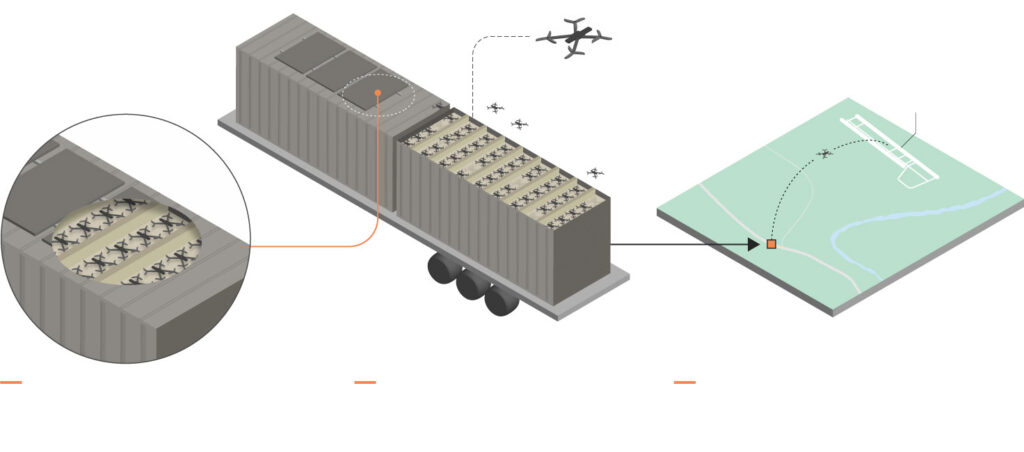
Ucrania no lanzó drones desde su propio territorio. En cambio, los agentes los contrabandearon profundamente en Rusia. Según el presidenteVolodymyr Zelenskyy, Se usaron 117 drones. Fueron transportados en cobertizos de madera forrados con techos de metal, escondidos en cavidades de aislamiento y montados en camiones.
Inteligencia ucranianalogró obtener los drones cerca de sus objetivos antes de lanzarlos. Una vez en posición, se abrió el techo de cada cobertizo móvil, y los drones tomaron vuelo.
ACNNInvestigación verificó imágenes de la escena. Muestra dos drones saliendo de un camión cerca de la base aérea de Belaya. En la distancia, el humo espeso de una huelga anterior las huelgas en el aire. Momentos después, el mismo camión parece explotar, un mecanismo de autodestrucción probable.
Las defensas aéreas rusas se sorprendieron
Los sistemas de radar de Rusia simplemente no estaban preparados. Las bases carecían de defensas capaces de interceptar drones de baja altitud volando a corta distancia. Ametralladoras pesadas: del tipo que Rusia usa contra los drones del mar en elMar Negro– O no estaban disponibles o se desplegaron demasiado tarde.
La estrategia de Ucrania evitó el rusosuperioridad aéreazonas. En cambio, se basaba en el contrabando local y el tiempo de precisión. Los informes de los canales de telegrama ruso Baza y Astra sugieren que un hombre ucraniano que vive en Rusia pudo haber comprado los camiones y los conductores pagados para entregarlos a las zonas objetivo.
Aunque ninguna de las partes ha confirmado estos detalles, elRia NovostiLa agencia de noticias informó que las autoridades de Irkutsk estaban buscando a un sospechoso cuyo nombre coincidiera con los mencionados en los informes.
Pilotos remotos de drones y redes de telecomunicaciones rusas
Un funcionario ucraniano familiarizado con la operación dijo a CNN que los pilotos de drones probablemente operaban desde centros remotos. Los drones se controlaron a través de las propias redes de telecomunicaciones de Rusia. Esto incluyó el uso de teléfonos celulares rusos estándar, que son más difíciles de detectar que los sistemas basados en satélite comoEnlace de estrellas.
Es posible que los operadores nunca hayan estado cerca de los sitios de lanzamiento. AVista en primera persona (FPV)El sistema de drones les permitió apuntar a cada base una por una.
Toda la configuración subraya la creciente sofisticación de Ucrania envehículo aéreo no tripulado(UAV) Guerra.
Mascú minones, bloggers indignados
El Ministerio de Defensa de Rusia reconoció los ataques, pero los describió como “actos terroristas”. Las autoridades no afirmaron víctimas y dijeron que los incendios en las bases de Irkutsk y Murmansk se extinguieron. Sin embargo, su cuenta difería bruscamente de la de los bloggers militares pro-rusos.
Uno de los más influyentes,Achicar, llamó a las huelgas “una pérdida trágica” y acusó al ejército ruso de “negligencia criminal”.
UcraniaSbuestimó el daño en $ 7 mil millones. Afirmaron que el 34% de la flota de transportistas de misiles de cruceros de Rusia se dañó en sus bases aéreas primarias.
Bombarderos estratégicos: raro y difícil de reemplazar
Rusia comenzó 2025 con solo 55 Tu-22M3 y 57 TU-95 bombarderos, según elEquilibrio militarInforme delInstituto Internacional de Estudios Estratégicos. Estos bombarderos son esenciales para las capacidades de ataque de largo alcance de Rusia.
ElTu-95, introducido por primera vez en la década de 1950 durante elUnión SoviéticaERA, se ha modernizado para llevar misiles de crucero. Pero construir reemplazos es casi imposible ahora. Rusia ya no los produce a escala, y las sanciones limitan su capacidad de fabricación.
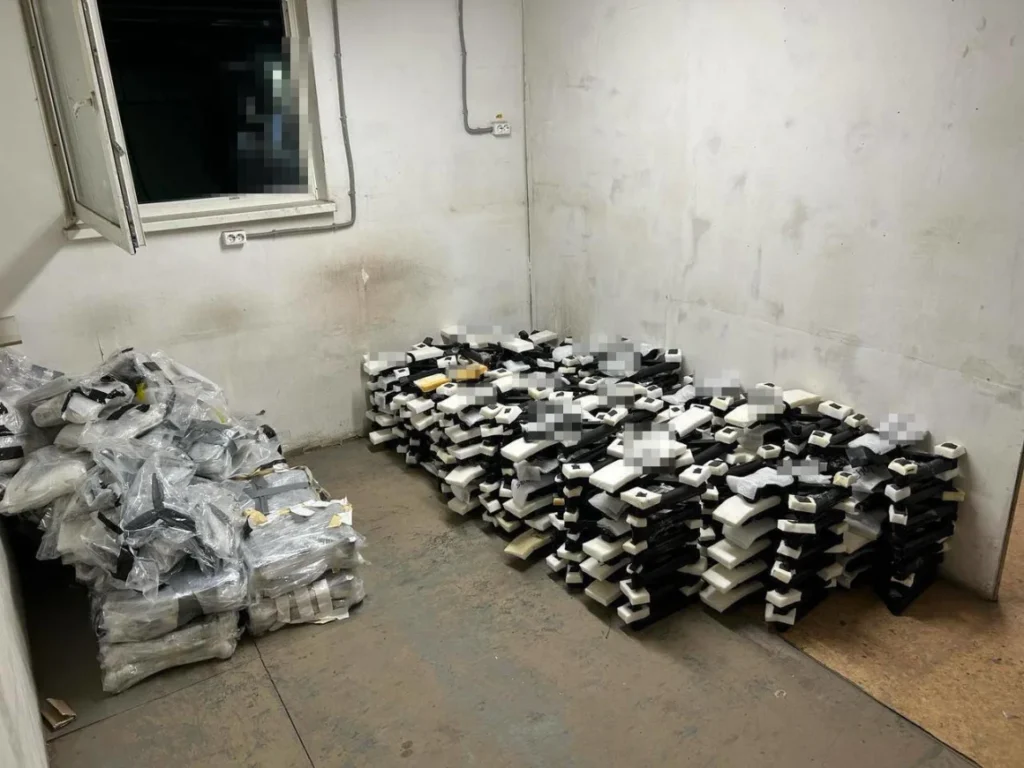

De acuerdo aJustin Bronk, reemplazar estos aviones sería un desafío masivo, y eso hace que su pérdida sea aún más devastadora.
Un nuevo capítulo en la guerra de drones
La huelga de Ucrania señala un cambio en cómo se pueden luchar futuras guerras. Los ataques profundos, precisos y sigilosos ya no se limitan a los estados con grandes fuerzas aéreas. Con la creatividad, la estrategia y la persistencia, Kiev demostró que podría perforar el corazón de las defensas estratégicas de Rusia, y alejarse ileso.



















