The James Webb House Telescope (JWST) has been no stranger to taking issues to the intense since its launch on Christmas day 2021, observing early galaxies billions of light-years away that existed when the universe was at a fraction of its at the moment 13.8 billion-year life.
Now, the highly effective house telescope has pushed it to the sting nearer to dwelling in our very personal galaxy, the Milky Approach. A workforce of astronomers has pointed the JWST on the outskirts of the Milky Approach, observing a area scientists name the “Excessive Outer Galaxy.”
This space is about 58,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Approach, or “Galactic Middle.” For comparability, the photo voltaic system is situated slightly below midway between the Galactic Middle and the very fringe of the Milky Approach. That distance is simply 26,000 light-years, so after we say “excessive edge” for these new observations, that is greater than hyperbole! The results of this galactic envelope-pushing train is a surprising picture of star clusters within the midst of a “starburst” and an intense interval of fast star start.
“Previously, we knew about these star-forming areas however weren’t capable of delve into their properties,” steam chief Natsuko Izumi of Gifu College and the Nationwide Astronomical Observatory of Japan mentioned in a press release. “The JWST knowledge builds upon what we’ve got incrementally gathered through the years from prior observations with totally different telescopes and observatories. We will get very highly effective and spectacular pictures of those clouds with the JWST.”
The Milky Approach star birthing areas seen by the workforce utilizing the JWST’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) and Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) are enveloped inside dense and huge conglomerations of fuel referred to as “molecular clouds.” The 2 molecular clouds in query are designated Digel Cloud 1 and Digel Cloud 2, that are many light-years lengthy and at the moment are imaged in unprecedented element.
Among the many components of those clusters seen within the pictures are extraordinarily younger protostars. These are stellar our bodies that have not but gathered sufficient materials from the prenatal cocoons of fuel and dirt to pile on mass to set off the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium of their cores, the method that defines what an grownup or “fundamental sequence” star is.
As any father or mother who has ended up with child meals of their hair will let you know, all infants are liable to tantrums, and these protostars aren’t any totally different. However these ejections aren’t Gerber strawberry and banana puree (tasty and nice for the hair); they’re jets and outflows of superheated fuel referred to as “plasma.” Proof of those stellar tantrums can also be seen within the new JWST picture.
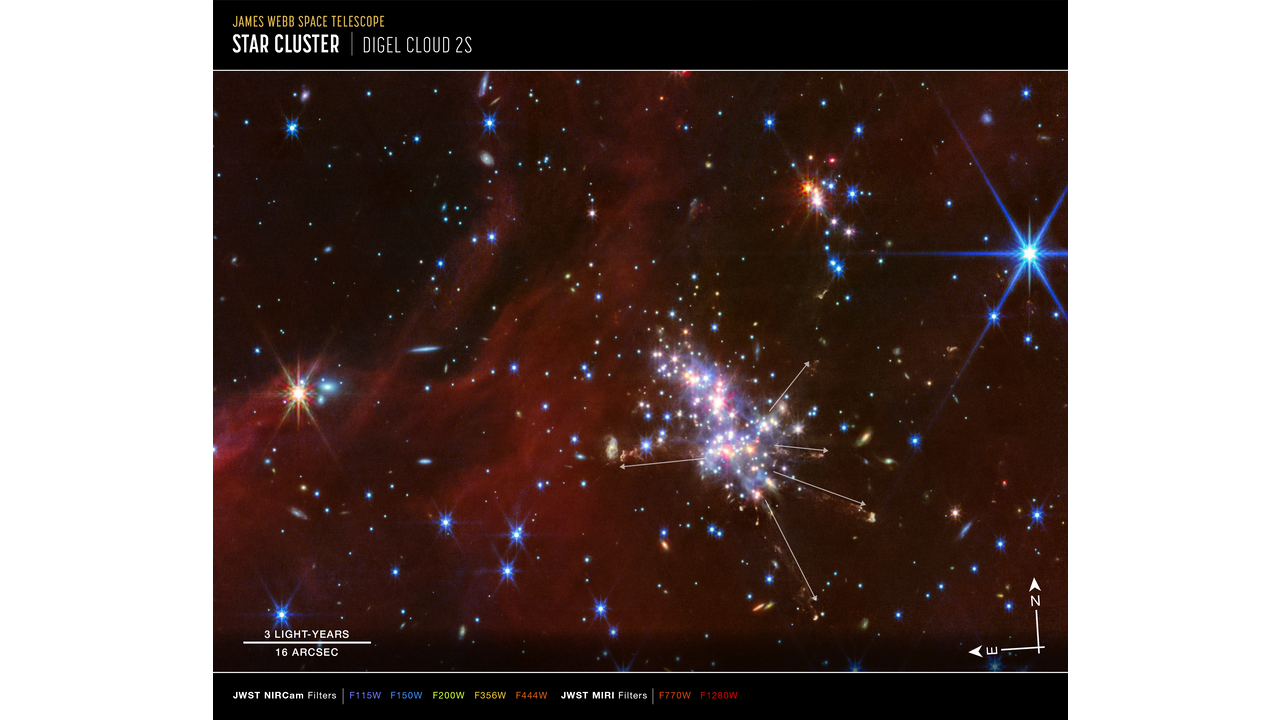
“Within the case of Digel Cloud 2, I didn’t count on to see such lively star formation and spectacular jets,” Izumi added.
The Digel Clouds have a barely totally different composition than different areas of the Milky Approach. They lack components heavier than hydrogen and helium, which astronomers considerably confusingly name “metals.”
This metal-poor nature makes the Digel Clouds proxy for learning dwarf galaxies and for understanding the Milky Approach’s earlier historical past earlier than dying stars elevated its metallic focus. This workforce regarded for exercise in 4 younger star clusters inside Digel Clouds 1 and a pair of, designated 1A, 1B, 2N, and 2S, respectively.
In 2S the astronomers noticed a dense and lively area of younger stars emitting lengthy jets of fabric from their poles. The workforce was additionally capable of distinguish the presence of a “sub-cluster” of stars in 2S.
“We all know from learning different close by star-forming areas that as stars kind throughout their adolescence section, they begin emitting jets of fabric at their poles,” mentioned Mike Ressler of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, research workforce member and principal investigator of the observing program.
“What was fascinating and astounding to me from the JWST knowledge is that there are a number of jets capturing out in all totally different instructions from this cluster of stars. It is a bit bit like a firecracker, the place you see issues capturing this manner and that.”
That is just the start of the workforce’s research of the Digel Clouds and the Excessive Outer Galaxy with the JWST. They’ll proceed to push to the restrict of the Milky Technique to resolve puzzles such because the relative abundance of stars of assorted plenty inside Excessive Outer Galaxy star clusters.
This might assist scientists to higher perceive how totally different environments affect the formation of various star sorts.
“I am keen on persevering with to review how star formation is going on in these areas. By combining knowledge from totally different observatories and telescopes, we will look at every stage within the evolution course of,” Izumi concluded. “We additionally plan to analyze circumstellar disks inside the Excessive Outer Galaxy. We nonetheless do not know why their lifetimes are shorter than in star-forming areas a lot nearer to us. And, in fact, I might like to grasp the kinematics of the jets we detected in Cloud 2S.”
The workforce’s analysis is revealed in the Astronomical Journal.





