Newly Released Epstein Files Reveal Andrew’s Involvement
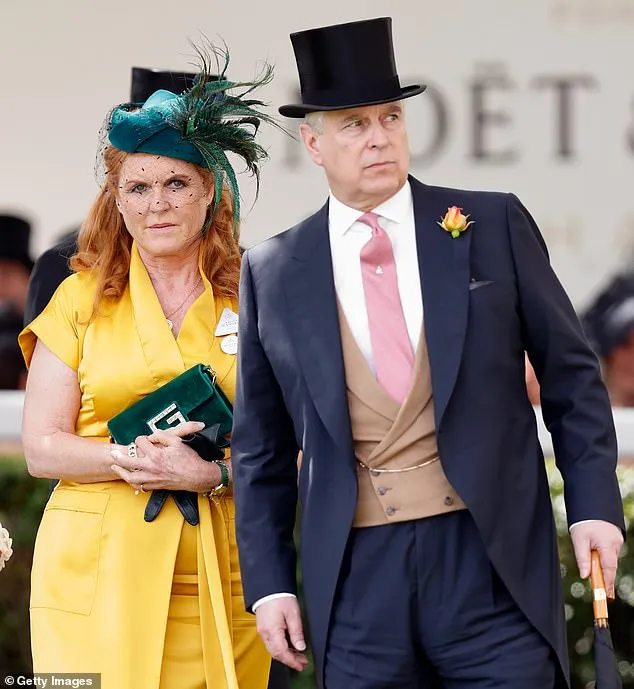
The United States Department of Justice recently released a fresh batch of Jeffrey Epstein investigation files, sparking renewed scrutiny over Prince Andrew, Duke of York. Among the documents, Andrew appears repeatedly, drawing intense media attention.
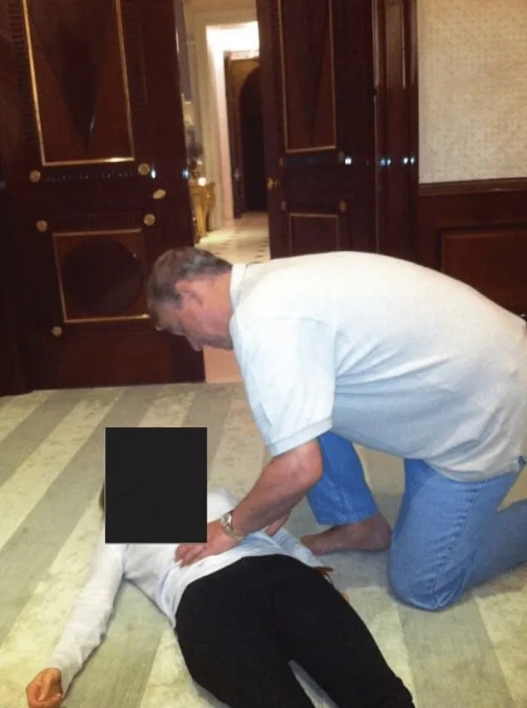
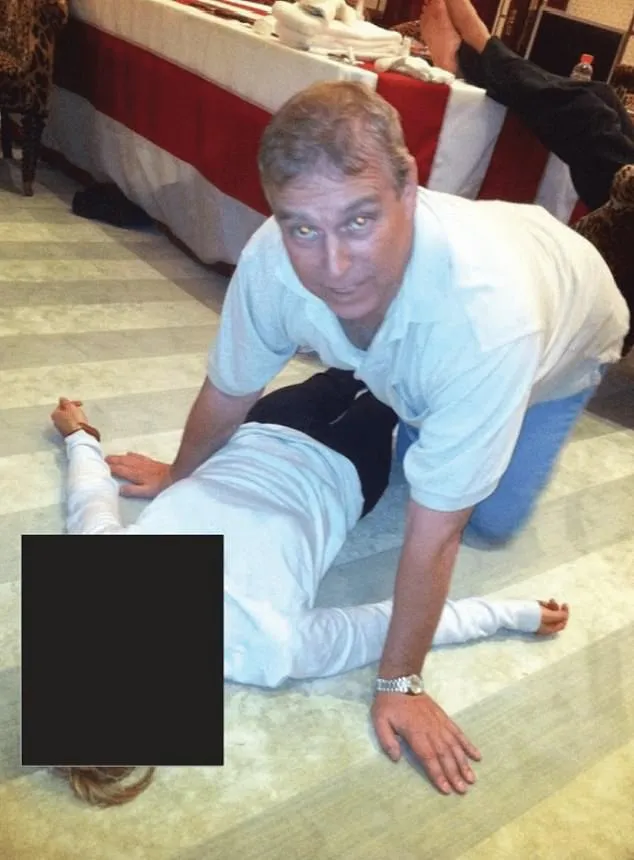
Three key photographs were highlighted. One shows him half-kneeling beside a woman lying on the floor, dressed in a white long-sleeve shirt and black pants, her face blacked out to protect her identity, while Andrew touches her stomach.
Another shows him kneeling with a table in the background stacked with towels. He looks directly at the camera, appearing unbothered.
A third photo captures him with his head down, adding to the mysterious nature of the release.
The photos provide no context—no dates, locations, or explanations. They were simply included in the public files.
Revealing Email Correspondence

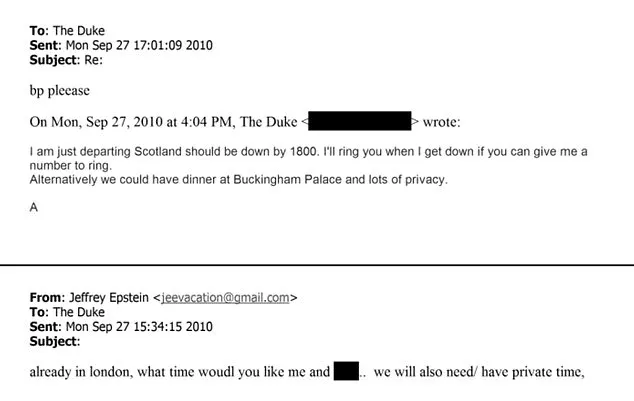
The files also contain a series of emails. In August 2010, Epstein invited Andrew to dinner in London, claiming he would introduce a friend. Andrew replied that he would be happy to meet her and asked whether the person had been informed about him, including her email.
At the time, Epstein had already been convicted in 2008 for sex offenses against minors. A royal frequently contacting a convicted sex offender raises serious questions about the nature of their correspondence.
By September, their emails detailed plans to meet in London. Andrew even suggested hosting dinner at Buckingham Palace, citing the privacy it could offer. Epstein responded positively, noting the need for private time.
Further emails revealed Epstein was in London with three women and asked Andrew if he wanted them to attend for “extra fun.” The correspondence demonstrates frequent and overtly suggestive interactions, contradicting Andrew’s 2019 BBC interview claim that he had cut ties with Epstein in 2010.
Sarah Ferguson’s Controversial Emails

Andrew’s former wife, Sarah Ferguson, also appears in the released documents. In April 2009, she wrote to Epstein using flattering and intimate language, praising him as “impressive” and a “legendary friend.”
By August, her emails grew even more effusive, expressing gratitude for his kindness in front of her daughters, Princess Beatrice and Princess Eugenie. She even shared a digital Christmas card featuring their daughters’ photos with Epstein.
Reports also suggested that Ferguson invited Epstein to Andrew’s 50th birthday party at St. James’s Palace, describing the event as “formal, mysterious, and playful.” Epstein declined.
These interactions highlight a dual dynamic: public opposition to Epstein contrasted with private familiarity, underscoring complex motives and mutual use of influence.
Historical Communications and Hidden Identities
Another set of released files traces correspondence back to 2001. A user signing as “Invisible” contacted Epstein’s associate Ghislaine Maxwell, mentioning attendance at the Balmoral Castle summer retreat and asking about finding “newly inappropriate friends.”
The Invisible account is linked to Andrew, who had just finished service in the Royal Navy in July 2001. Maxwell’s reply was playful, suggesting the selection of suitable friends was challenging.
In 2002, further email exchanges reference invitations to Epstein’s private U.S. island, with Andrew considering alternatives such as Spain’s Sotogrande alongside Sarah and the children. Subsequent correspondence included intentionally ambiguous and provocative language.
Ongoing Legal and Public Pressure

On January 31, the UK Prime Minister publicly called on Andrew to testify before the United States Congress. Andrew has yet to respond, signaling that the controversy is far from over.
Attorney David Boies, representing multiple victims, warned that the documents released are only the beginning. Andrew’s name recurs across flight logs, Epstein’s communications, and Maxwell’s planning records, appearing under various aliases including “Invisible” and “The Duke.”
Boies predicts more documents will be declassified, likely revealing far greater damaging details. While the current files alone cannot directly convict anyone, they offer a clearer glimpse into previously concealed interactions and raise serious questions about accountability.



















