August 27, 2024
4 min learn
Why Getting older Is available in Dramatic Waves in Our 40s and 60s
A brand new examine means that waves of aging-related modifications happen at two distinct factors in our life
Bob_Bosewell/Getty Pictures
As an individual enters their 60s, it’s frequent for them to begin actually feeling the well being results of ageing. Many individuals may want glasses or listening to aids, or their medical doctors might warn them a couple of sharply elevated danger of diabetes or coronary heart illness. However new analysis printed this month means that our physique tends to bear a dramatic wave of age-related molecular modifications not solely in our 60s but additionally in our mid-40s.
For a examine in Nature Getting older, researchers tracked the degrees of greater than 135,000 molecules and microbes, all reflective of exercise in cells and tissues, in 108 wholesome volunteers aged 25 to 75. Every volunteer contributed organic specimens, together with blood and stool samples, each three to 6 months for a median of 1.7 years. Outcomes confirmed that variations within the ranges of many molecules and microbes clustered round two distinct time factors: age 44 and 60. The findings counsel that ageing may speed up round these intervals—and sign to specialists that our 40s and 50s could also be a major interval to intently monitor well being.
The examine additionally helps many individuals’s anecdotal studies of noticing modifications that vary from extra muscle accidents to worse hangovers of their 40s—and the info give clues as to why, says senior examine writer Michael Snyder, a genetics researcher at Stanford Medication.
On supporting science journalism
For those who’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world at the moment.
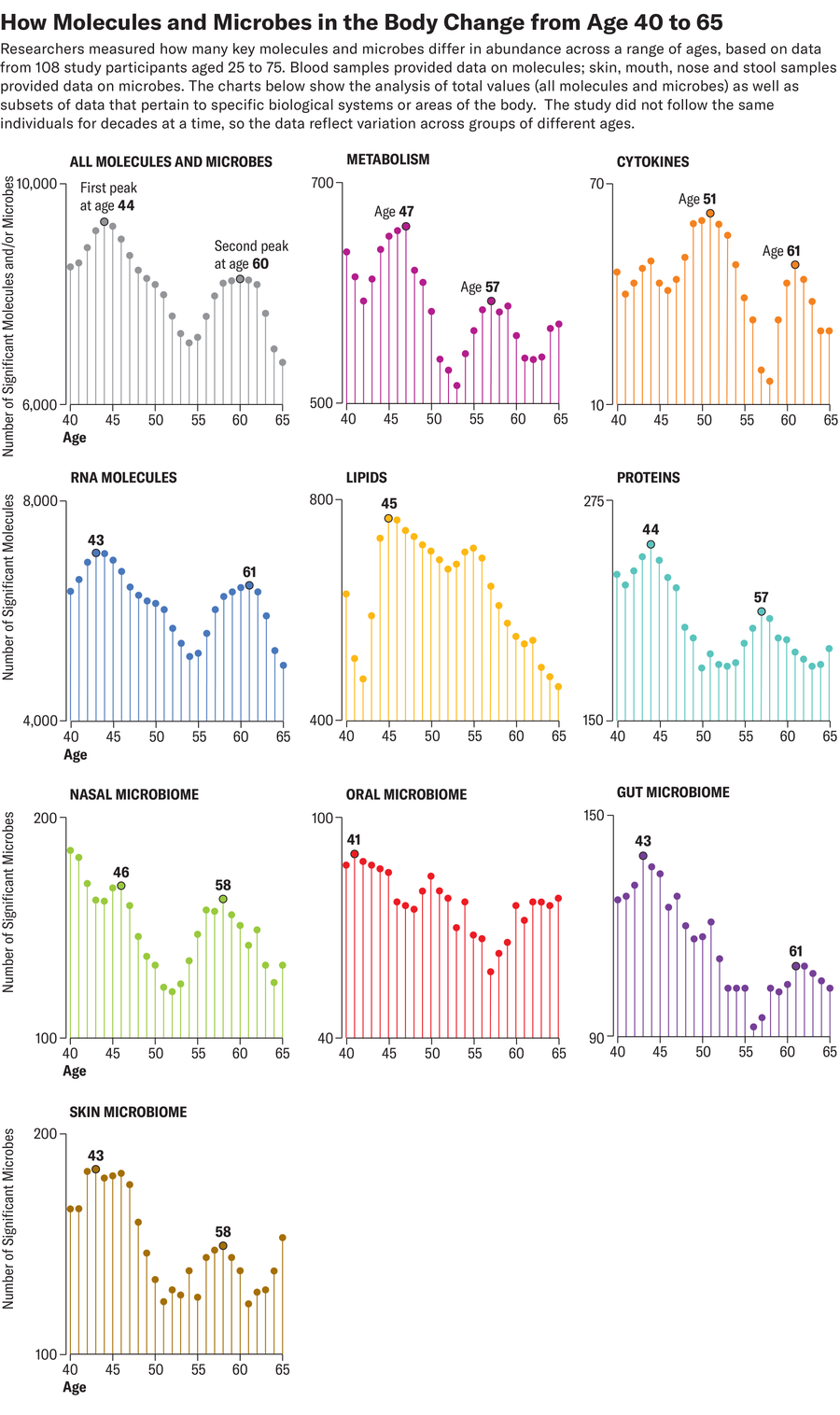
In contrast with youthful individuals, folks of their 40s and 60s displayed organic variations that seemed to be linked to muscle weak spot and loss, declines in coronary heart well being and inefficient caffeine metabolism. These of their 40s additionally had much less exercise in mobile pathways accountable for breaking down alcohol and fat—probably an indication that individuals might begin to digest these compounds extra slowly round this age. Individuals of their 60s, in the meantime, had decrease ranges of varied immune system molecules, corresponding to inflammatory cytokines, which corresponded to a weakened immune response. Additionally they confirmed vital variations in ranges of sure molecules related to carbohydrate digestion and coronary heart and kidney operate, suggesting that the older individuals had been extra inclined to kind 2 diabetes, heart problems and kidney points.
The brand new examine’s time factors are much like these recognized in a separate 2020 examine that discovered that the immune techniques of individuals grew markedly much less adept at preventing off pathogens round age 35 and once more round age 65. However the newest examine’s findings should not ironclad; it sampled a comparatively small variety of folks, all residing in California’s Palo Alto space. The ensuing lack of geographic variety within the individuals makes the info much less consultant of the broader public, notes Aditi Gurkar, who conducts aging-related analysis on the College of Pittsburgh and was not concerned within the current examine. Examine individuals probably had some life-style components in frequent, corresponding to eating regimen, train and environmental exposures, which might have swayed the outcomes, she says.
The examine additionally didn’t comply with any particular person individuals for intervals longer than about seven years, so scientists can’t be sure that variations between folks in several age teams replicate common modifications. For instance, the 40- and 60-year-olds within the examine might have aged sooner relative to others of the identical age within the broader inhabitants, Gurkar cautions. She and others say one of the simplest ways to verify the outcomes—and to exactly hint age-related organic shifts—can be by means of a bigger examine that tracks the identical individuals over the course of a lifespan. Accumulating information on components corresponding to illness standing, bodily operate or incapacity might additionally assist higher assess the extent to which age-related shifts have an effect on an individual’s total well being. (The quantity of stress that cells and tissues bear—what researchers discuss with as “organic ageing”—varies broadly between folks of various races and socioeconomic courses, and it even differs between particular person organs in an individual’s physique.)
The the reason why the ages of 44 and 60 is likely to be turning factors in well being should not but obvious, however the examine authors hope to probe a number of hypotheses in future work. Snyder suspects that for folks of their 60s, declines in immune system operate may precipitate a extra widespread breakdown of organs. A midlife decline in bodily exercise, in the meantime, might clarify the variations seen amongst individuals of their 40s—however so may hormonal modifications, together with menopause. Menopause alone, nonetheless, couldn’t clarify the tendencies within the examine, Snyder says. Female and male individuals appeared to point out the identical diploma of age-related variations at each time factors.
Snyder thinks the brand new information can present actionable well being info. Individuals of their 40s may profit from getting blood exams that observe lipid ranges, as an illustration, or from exercising recurrently to take care of coronary heart well being. Snyder additionally underscores the significance of early and common screenings for coronary heart illness for folks on this age vary who’ve present well being situations.
The brand new examine might have limitations, however it’s nonetheless a robust reminder that life-style decisions corresponding to eating regimen and train can speed up ageing—or gradual it down, Gurkar says. Few research on ageing deal with middle-aged individuals or contain organic sampling as complete as that of this new paper, she provides. And along with figuring out potential waves of age-related modifications, the work supplies an important first step towards sooner or later constructing large-scale illness prediction fashions primarily based on organic information.





