As Southern California swelters underneath its most punishing warmth wave of the yr, worldwide local weather officers have confirmed that summer season 2024 was Earth’s hottest on document.
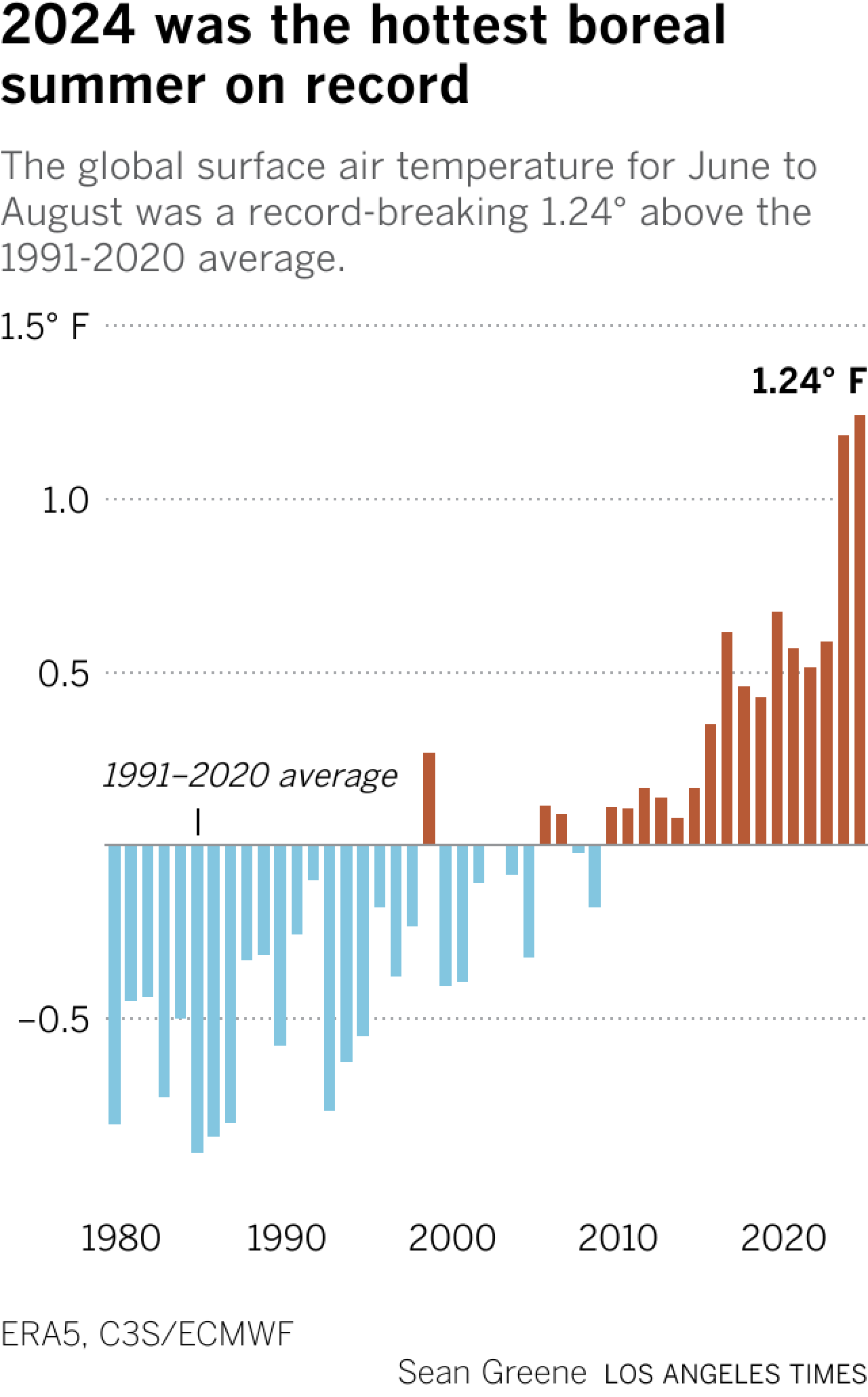
The worldwide common temperature in June, July and August — referred to as the boreal summer season within the Northern hemisphere — was a record-breaking 62.24 levels, in accordance with the European Union’s Copernicus Local weather Change Service. The season was marked by explosive wildfires, scorching warmth waves and heat-related deaths in California and plenty of different elements of the world.
“In the course of the previous three months of 2024, the globe has skilled the most popular June and August, the most popular day on document, and the most popular boreal summer season on document,” learn an announcement from Samantha Burgess, Copernicus’ deputy director. “The temperature-related excessive occasions witnessed this summer season will solely turn into extra intense, with extra devastating penalties for individuals and the planet except we take pressing motion to cut back greenhouse gasoline emissions.”
Not solely was it a sizzling summer season, however August successfully tied 2023 because the planet’s hottest August on document with a worldwide common temperature of about 62.28 levels, the company mentioned.
Actually, the whole yr to this point has been so heat that even with 4 months to go, 2024 is now practically sure to surpass 2023 as Earth’s hottest yr on document.
That’s as a result of the worldwide common temperature anomaly from January to August was the very best on document for the interval — and 0.41 levels hotter than the identical interval final yr.
The typical anomaly would wish to drop by greater than half a level for 2024 to not be hotter than 2023, which has by no means occurred in the whole Copernicus knowledge set, the company mentioned.

A girl sunbathes in a park in Milan, Italy, throughout a July warmth wave.
(Luca Bruno / Related Press)
The near-relentless string of record-hot months has left local weather scientists and officers involved because the planet hurtles towards a harmful tipping level.
“We’re taking part in Russian roulette with our planet, and we’d like an exit ramp off the freeway to local weather hell,” António Guterres, secretary-general of the United Nations, mentioned throughout a speech initially of the record-hot summer season in June.
Whereas Earth’s rising temperatures are considerably in step with the upper finish of local weather mannequin projections, the warmth has additionally defied some expectations, in accordance with Zeke Hausfather, a local weather scientist with Berkeley Earth.
“The warmth in 2024 has endured longer than many people anticipated, with the previous few months tying the extremes we noticed within the latter half of 2023,” Hausfather mentioned in an e-mail.
That is significantly perplexing as a result of El Niño — a local weather sample related to hotter world temperatures — dissipated towards the top of Could however didn’t result in an anticipated decline in world temperatures. Sometimes, there’s a three-month lag between peak El Niño circumstances and the worldwide floor temperature response, “however even with that we should always have already began cooling off a bit,” Hausfather mentioned.
That circumstances have remained steadily heat with out El Niño could also be a sign that further elements are at work, he mentioned. Some theories embrace a change in aerosol delivery laws that allowed extra daylight to achieve Earth; an uptick within the 11-year photo voltaic cycle; and the 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha‘apai volcano, which can have trapped some warmth within the ambiance.
However even these elements “don’t appear to utterly add as much as what we’re seeing,” Hausfather mentioned.
Additionally regarding is the regular climb of temperatures past the worldwide restrict of two.7 levels, or 1.5 levels Celsius, which was established by practically 200 nations underneath the 2015 Paris local weather accord in an effort to forestall the worst results of world warming.
The restrict is measured in opposition to the pre-industrial period, or the interval earlier than people started to meaningfully alter the planet’s local weather by way of greenhouse gases and different fossil gas emissions, and customarily makes use of temperature knowledge from between 1850 and 1900.
August 2024 was the thirteenth month in a 14-month interval to exceed that benchmark, with the worldwide common temperature measuring roughly 2.72 levels — or 1.51 levels Celsius — above pre-industrial ranges, in accordance with Copernicus. The streak was damaged solely by the month of July, which got here in simply shy of the restrict for the primary time in a yr.
Consultants say a single yr of warming over the restrict doesn’t imply humanity has formally exceeded the boundary, however it’s a regarding pattern that’s transferring within the flawed path.
“It’s definitely a worrying signal that world temperatures have been persistently above 1.5 levels Celsius for thus lengthy,” Hausfather mentioned. He positioned the likelihood of 2024 exceeding 2023 as the most popular yr on document at better than 95%, and mentioned it is usually very prone to be the primary yr above 1.5 levels Celsius within the Copernicus knowledge set, though different knowledge units could disagree as a consequence of slight variations in measurements.

Vacationers stroll with an umbrella in entrance of the Parthenon on the historic Acropolis in central Athens, in June.
(Petros Giannakouris / Related Press)
And whereas summer season was marked by sweltering warmth on land, the planet’s oceans additionally simmered. Report-warm ocean waters contributed to a violent begin to the Atlantic hurricane season this yr, with Hurricane Beryl turning into the basin’s earliest Class 5 hurricane on document when it fashioned in late June.
August additionally noticed Arctic sea ice extent dip to 17% under common — the fourth-lowest for the month within the satellite tv for pc document and “distinctly additional under common than the identical month for the earlier three years,” Copernicus officers mentioned.
Antarctic sea ice extent was 7% under common, the second-lowest extent for August within the satellite tv for pc knowledge document.
The report comes as Southern California endures a number of consecutive days of triple-digit temperatures, together with highs over 110 levels in some elements of Los Angeles County.
Actually, the summer season was notably heat throughout practically all the Golden State, the place July went down as California’s hottest month on document.
Officers in Dying Valley Nationwide Park — the place two individuals died of heat-related sickness — confirmed that the park noticed its hottest-ever summer season with 9 consecutive days of 125 levels or hotter. The park’s common 24-hour temperature in June, July and August was 104.5 levels, beating the earlier document of 104.2 levels set in 2021 and 2018.

Aggressive and impactful reporting on local weather change, the surroundings, well being and science.
Daniel Swain, a local weather scientist with UCLA, mentioned the present warmth wave is prone to break some day by day data in Southern California, which has largely fared higher than the remainder of the state throughout this yr’s sizzling summer season.
“It’ll nearly definitely [bring] the most popular day of the yr in a number of Southern California, and maybe even the most popular day in a number of years in some elements of Southern California,” Swain mentioned throughout a briefing on Wednesday. “This can be a important warmth occasion.”
Giant swaths of the the area are additionally prone to see a few of their warmest nights on document for the time of yr, he mentioned.
“It could not sound as dramatic as, say, the most popular days on document or the most popular afternoon peak temperatures, however these nighttime temperatures are fairly consequential from a human well being affect perspective, an ecosystem well being perspective and in addition a wildfire perspective,” he mentioned.
Certainly, warmth is the deadliest of all local weather hazards, and a latest research confirmed that heat-related deaths are on the rise in the USA.
The newest seasonal outlooks from the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration point out that above-normal temperatures could persist throughout practically all the nation by way of at the very least November.
Already, residents in Phoenix, Arizona, have endured greater than 100 consecutive days of temperatures over 100 levels, shattering the earlier document of 76 days set in 1993, in accordance with the Nationwide Climate Service.