TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Abstract
- Half I: Introduction to Asset Location
- Half II: After-Tax Return—Deep Dive
- Half III: Asset Location Myths
- Half IV: TCP Methodology
- Half V: Monte Carlo on the Amazon—Betterment’s Testing Framework
- Half VI: Outcomes
- Half VII: Particular Issues
- Addendum
Abstract
Asset location is broadly considered the closest factor there’s to a “free lunch” within the wealth administration trade.1 When investments are held in at the very least two varieties of accounts (out of three attainable sorts: taxable, tax-deferred and tax-exempt), asset location gives the flexibility to ship extra after-tax return potential, whereas sustaining the identical stage of danger.
Usually talking, this profit is achieved by inserting the least tax-efficient property within the accounts taxed most favorably, and essentially the most tax-efficient property within the accounts taxed least favorably, all whereas sustaining the specified asset allocation within the combination.
Half I: Introduction to Asset Location
Maximizing after-tax return on investments will be advanced. Nonetheless, most buyers know that contributing to tax-advantaged (or “certified”) accounts is a comparatively easy approach to pay much less tax on their retirement financial savings. Tens of millions of People wind up with some mixture of IRAs and 401(okay) accounts, each out there in two sorts: conventional or Roth. Many will solely save in a taxable account as soon as they’ve maxed out their contribution limits for the certified accounts. However whereas tax issues are paramount when selecting which account to fund, much less thought is given to the tax influence of which investments to then buy throughout all accounts.
The tax profiles of the three account sorts (taxable, conventional, and Roth) have implications for what to spend money on, as soon as the account has been funded. Selecting properly can considerably enhance the after-tax worth of 1’s financial savings, when multiple account is within the combine.
Virtually universally, such buyers can profit from a correctly executed asset location technique. The thought behind asset location is pretty easy. Sure investments generate their returns in a extra tax-efficient method than others. Sure accounts shelter funding returns from tax higher than others. Putting, or “finding” much less tax-efficient investments in tax-sheltered accounts might improve the after-tax worth of the general portfolio.
Allocate First, Find Second
Let’s begin with what asset location isn’t. All buyers should choose a mixture of shares and bonds, discovering an applicable steadiness of danger and anticipated potential return, in step with their objectives. One frequent aim is retirement, during which case, the combination of property must be tailor-made to match the investor’s time horizon. This preliminary willpower is called “asset allocation,” and it comes first.
When investing in a number of accounts, it’s common for buyers to easily recreate their desired asset allocation in every account. If every account, irrespective of the dimensions, holds the identical property in the identical proportions, including up all of the holdings will even match the specified asset allocation. If all these funds, nonetheless scattered, are invested in the direction of the identical aim, that is the proper end result. The combination portfolio is the one which issues, and it ought to monitor the asset allocation chosen for the frequent aim.
Portfolio Managed Individually in Every Account
Enter asset location, which might solely be utilized as soon as a desired asset allocation is chosen. Every asset’s after-tax return is taken into account within the context of each out there account. The property are then organized (unequally) throughout all coordinated accounts to assist maximize the after-tax efficiency of the general portfolio.
Similar Portfolio General—With Asset Location
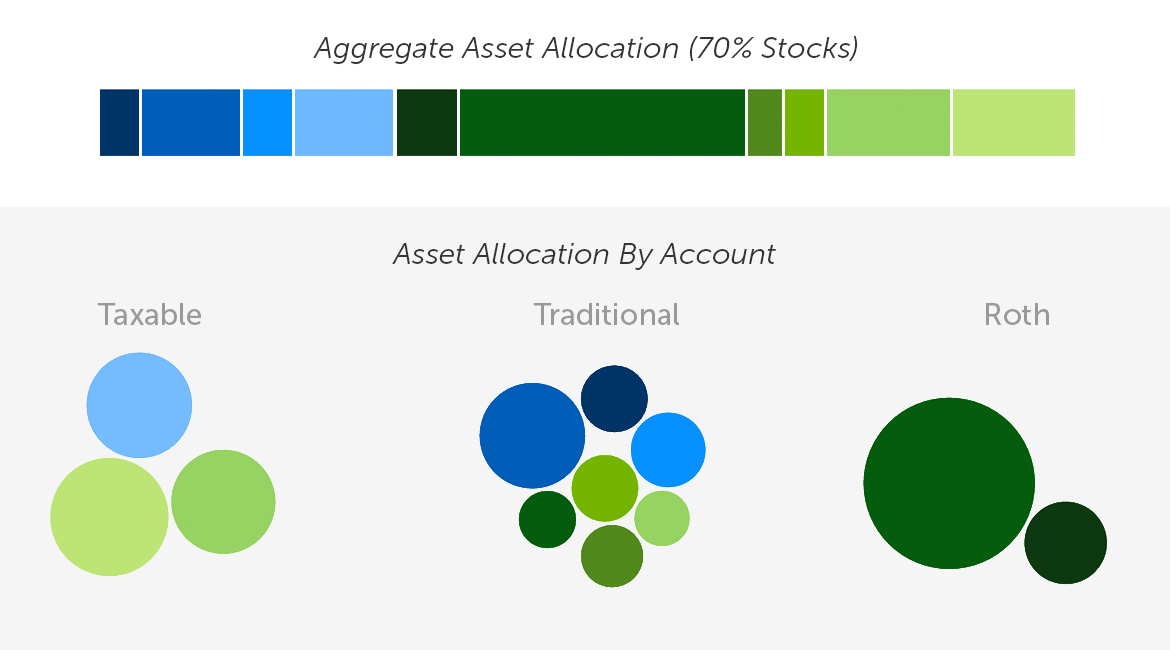
To assist conceptualize asset location, think about a crew of runners. Some runners compete higher on a monitor than a cross-country filth path, as in comparison with their extra versatile teammates. Equally, sure asset lessons can profit greater than others from the tax-efficient “terrain” of a certified account.
Asset allocation determines the composition of the crew, and the general portfolio’s after-tax return is a crew effort. Asset location then seeks to match up asset and surroundings in a manner that maximizes the general end result over time, whereas preserving the composition of the crew intact.
TCP vs. TDF
The first attraction of a target-date fund (TDF) is the “set it and neglect it” simplicity with which it permits buyers to pick out and preserve a diversified asset allocation, by buying just one fund. That simplicity comes at a value—as a result of every TDF is a single, indivisible safety, it can not inconsistently distribute its underlying property throughout a number of accounts, and thus can not ship the extra after-tax returns of asset location.
Specifically, members who’re locked into 401(okay) plans with out automated administration could discover that an affordable TDF remains to be their finest “arms off” possibility (plus, a TDF’s capacity to fulfill the Certified Default Funding Different (QDIA) requirement below ERISA ensures its baseline survival below present regulation).
Automated asset location (when built-in with automated asset allocation) replicates what makes a TDF so interesting, however successfully quantities to a “TDF 2.0″—a repeatedly managed portfolio, however one that may straddle a number of accounts for tax advantages.
Subsequent, we dive into the advanced dynamics that must be thought of when looking for to optimize the after-tax return of a diversified portfolio.
Half II: After-Tax Return—Deep Dive
An excellent place to begin for a dialogue of funding taxation is the idea of “tax drag.” Tax drag is the portion of the return that’s misplaced to tax on an annual foundation. Specifically, funds pay dividends, that are taxed within the yr they’re obtained.
Nevertheless, there isn’t any annual tax in certified accounts, additionally generally generally known as “tax-sheltered accounts.” Subsequently, inserting property that pay a considerable quantity of dividends into a certified account, moderately than a taxable account, “shelters” these dividends, and reduces tax drag. Decreasing the tax drag of the general portfolio is a method that asset location improves the portfolio’s potential after-tax return.
Importantly, investments are additionally topic to tax at liquidation, each within the taxable account, and in a standard IRA (the place tax is deferred). Nevertheless, “tax drag”, as that time period is usually used, doesn’t embody liquidation tax. So whereas the idea of “tax drag” is intuitive, and thus place to start out, it can’t be the only focus when seeking to assist reduce taxes.
What’s “Tax Effectivity”
A intently associated time period is “tax effectivity” and that is one that the majority discussions of asset location will inevitably give attention to. A tax-efficient asset is one which has minimal “tax drag.” Prioritizing property on the premise of tax effectivity permits for asset location choices to be made following a easy, rule-based strategy.
Each “tax drag” and “tax effectivity” are ideas pertaining to taxation of returns in a taxable account. Subsequently, we first think about that account, the place the foundations are most elaborate. With an understanding of those guidelines, we will layer on the influence of the 2 varieties of certified accounts.
Returns in a Taxable Account
There are two varieties of funding earnings, and two varieties of relevant tax charges.
Two varieties of funding tax charges. All funding earnings in a taxable brokerage account is topic to considered one of two price classes (with materials exceptions famous). For simplicity, and to maintain the evaluation common, this part solely addresses federal tax (state tax is taken into account when testing for efficiency).
- Peculiar price: For many, this price mirrors the marginal tax bracket relevant to earned earnings (primarily wages reported on a W-2).
- Preferential price: This extra favorable price ranges from 15% to twenty% for many buyers.
For particularly excessive earners, each charges are topic to an extra tax of three.8%.
Two varieties of funding returns. Investments generate returns in two methods: by appreciating in worth, and by making money distributions.
- Capital positive aspects: When an funding is offered, the distinction between the proceeds and the tax foundation (usually, the acquisition value) is taxed as capital positive aspects. If held for longer than a yr, this acquire is handled as long-term capital positive aspects (LTCG) and taxed on the preferential price. If held for a yr or much less, the acquire is handled as short-term capital positive aspects (STCG), and taxed on the abnormal price. Barring unexpected circumstances, passive buyers ought to be capable of keep away from STCG solely. Betterment’s automated account administration seeks to keep away from STCG when attainable,4 and the remainder of this paper assumes solely LTCG on liquidation of property.
- Dividends: Bonds pay curiosity, which is taxed on the abnormal price, whereas shares pay dividends, that are taxed on the preferential price (each topic to the exceptions under). An exchange-traded fund (ETF) swimming pools the money generated by its underlying investments, and makes funds which might be referred to as dividends, even when some or the entire supply was curiosity. These dividends inherit the tax therapy of the supply funds. Which means that, usually, a dividend paid by a bond ETF is taxed on the abnormal price, and a dividend paid by a inventory ETF is taxed on the preferential price.
- Certified Dividend Revenue (QDI): There’s an exception to the overall rule for inventory dividends. Inventory dividends get pleasure from preferential charges provided that they meet the necessities of certified dividend earnings (QDI). Key amongst these necessities is that the corporate issuing the dividend have to be a U.S. company (or a certified international company). A fund swimming pools dividends from many firms, solely a few of which can qualify for QDI. To account for this, the fund assigns itself a QDI proportion annually, which the custodian makes use of to find out the portion of the fund’s dividends which might be eligible for the preferential price. For inventory funds monitoring a U.S. index, the QDI proportion is usually 100%. Nevertheless, funds monitoring a international inventory index may have a decrease QDI proportion, generally considerably. For instance, VWO, Vanguard’s Rising Markets Inventory ETF, had a QDI proportion of 38% in 2015, which signifies that 38% of its dividends for the yr have been taxed on the preferential price, and 62% have been taxed on the abnormal price.
- Tax-exempt curiosity: There’s additionally an exception to the overall rule for bonds. Sure bonds pay curiosity that’s exempt from federal tax. Primarily, these are municipal bonds, issued by state and native governments. Which means that an ETF which holds municipal bonds pays a dividend that’s topic to 0% federal tax—even higher than the preferential price.
The desk under summarizes these interactions. Notice that this part doesn’t think about tax therapy for these in a marginal tax bracket of 15% and under. These taxpayers are addressed in “Particular Issues.”
The influence of charges is clear: The upper the speed, the upper the tax drag. Equally vital is timing. The important thing distinction between dividends and capital positive aspects is that the previous are taxed yearly, contributing to tax drag, whereas tax on the latter is deferred.
Tax deferral is a robust driver of after-tax return, for the easy cause that the financial savings, although short-term, will be reinvested within the meantime, and compounded. The longer the deferral, the extra invaluable it’s.
Placing this all collectively, we arrive on the foundational piece of typical knowledge, the place essentially the most primary strategy to asset location begins and ends:
- Bond funds are anticipated to generate their return solely by dividends, taxed on the abnormal price. This return advantages neither from the preferential price, nor from tax deferral, making bonds the traditional tax-inefficient asset class. These go in your certified account.
- Inventory funds are anticipated to generate their return primarily by capital positive aspects. This return advantages each from the preferential price, and from tax deferral. Shares are due to this fact the extra tax-efficient asset class. These go in your taxable account.
Tax-Environment friendly Standing: It’s Difficult
Actuality will get messy moderately shortly, nonetheless. Over the long run, shares are anticipated to develop sooner than bonds, inflicting the portfolio to float from the specified asset allocation. Rebalancing could periodically understand some capital positive aspects, so we can not anticipate full tax deferral on these returns (though if money flows exist, investing them intelligently can doubtlessly cut back the necessity to rebalance through promoting).
Moreover, shares do generate some return through dividends. The anticipated dividend yield varies with extra granularity. Small cap shares pay comparatively little (these are progress firms that are inclined to reinvest any income again into the enterprise) whereas giant cap shares pay extra (as these are mature firms that are inclined to distribute income). Relying on the rate of interest surroundings, inventory dividends can exceed these paid by bonds.
Worldwide shares pay dividends too, and complicating issues additional, a few of these dividends won’t qualify as QDI, and might be taxed on the abnormal price, like bond dividends (particularly rising markets inventory dividends).
Returns in a Tax-Deferred Account (TDA)
In comparison with a taxable account, a TDA is ruled by easy guidelines. Nevertheless, incomes the identical return in a TDA includes trade-offs which aren’t intuitive. Making use of a unique time horizon to the identical asset can swing our desire between a taxable account and a TDA.Understanding these dynamics is essential to appreciating why an optimum asset location methodology can not ignore liquidation tax, time horizon, and the precise composition of every asset’s anticipated return.Though progress in a standard IRA or conventional 401(okay) shouldn’t be taxed yearly, it’s topic to a liquidation tax. All of the complexity of a taxable account described above is decreased to 2 guidelines. First, all tax is deferred till distributions are made out of the account, which ought to start solely in retirement. Second, all distributions are taxed on the identical price, irrespective of the supply of the return.
The speed utilized to all distributions is the upper abnormal price, besides that the extra 3.8% tax won’t apply to these whose tax bracket in retirement would in any other case be excessive sufficient.2
First, we think about earnings that may be taxed yearly on the abnormal price (i.e. bond dividends and non-QDI inventory dividends). The good thing about shifting these returns to a TDA is obvious. In a TDA, these returns will ultimately be taxed on the identical price, assuming the identical tax bracket in retirement. However that tax won’t be utilized till the top, and compounding because of deferral can solely have a constructive influence on the after-tax return, as in comparison with the identical earnings paid in a taxable account.3
Specifically, the danger is that LTCG (which we anticipate loads of from inventory funds) might be taxed like abnormal earnings. Beneath the essential assumption that in a taxable account, capital positive aspects tax is already deferred till liquidation, favoring a TDA for an asset whose solely supply of return is LTCG is plainly dangerous. There isn’t any profit from deferral, which you’d have gotten anyway, and solely hurt from a better tax price. This logic helps the traditional knowledge that shares belong within the taxable account. First, as already mentioned, shares do generate some return through dividends, and that portion of the return will profit from tax deferral. That is clearly true for non-QDI dividends, already taxed as abnormal earnings, however QDI can profit too. If the deferral interval is lengthy sufficient, the worth of compounding will offset the hit from the upper price at liquidation.
Second, it’s not correct to imagine that each one capital positive aspects tax might be deferred till liquidation in a taxable account. Rebalancing could understand some capital positive aspects “prematurely” and this portion of the return might additionally profit from tax deferral.
Putting shares in a TDA is a trade-off—one which should weigh the potential hurt from destructive price arbitrage in opposition to the good thing about tax deferral. Valuing the latter means making assumptions about dividend yield and turnover. On prime of that, the longer the funding interval, the extra tax deferral is price. Kitces demonstrates {that a} dividend yield representing 25% of whole return (at 100% QDI), and an annual turnover of 10%, might swing the calculus in favor of holding the shares in a TDA, assuming a 30-year horizon.4 For international shares with lower than excellent QDI, we’d anticipate the tipping level to come back sooner.
Returns in a Tax-Exempt Account (TEA)
Investments in a Roth IRA or Roth 401(okay) develop tax free, and are additionally not taxed upon liquidation. Because it eliminates all attainable tax, a TEA presents a very invaluable alternative for maximizing after-tax return. The trade-off right here is managing alternative price—each asset does higher in a TEA, so how finest to make use of its treasured capability?
Clearly, a TEA is essentially the most favorably taxed account. Standard knowledge thus means that if a TEA is offered, we use it to first place the least tax-efficient property. However that strategy is incorrect.
Every part Counts in Massive Quantities—Why Anticipated Return Issues
The highly effective but easy benefit of a TEA helps illustrate the limitation of focusing completely on tax effectivity when making location selections. Returns in a TEA escape all tax, regardless of the price or timing would have been, which signifies that an asset’s anticipated after-tax return equals its anticipated whole return.
When each a taxable account and a TEA can be found, it might be price placing a high-growth, low-dividend inventory fund into the TEA, as a substitute of a bond fund, despite the fact that the inventory fund is vastly extra tax-efficient. Comparable reasoning can apply to placement in a TDA as properly, so long as the tax-efficient asset has a big sufficient anticipated return, and presents some alternative for tax deferral (i.e., some portion of the return comes from dividends).
Half III: Asset Location Myths
City Legend 1: Asset location is a one-time course of. Simply set it and neglect it.
Whereas an preliminary location could add some worth, doing it correctly is a steady course of, and would require changes in response to altering circumstances. Notice that overlaying asset location shouldn’t be a deviation from a passive investing philosophy, as a result of optimizing for location doesn’t imply altering the general asset allocation (the identical goes for tax loss harvesting).
Different issues that can change, all of which ought to issue into an optimum methodology: anticipated returns (each the risk-free price, and the surplus return), dividend yields, QDI percentages, and most significantly, relative account balances. Contributions, rollovers, and conversions can improve certified property relative to taxable property, repeatedly offering extra room for added optimization.
City Legend 2: Making the most of asset location means you must contribute extra to a specific certified account than you in any other case would.
Positively not! Asset location ought to play no function in deciding which accounts to fund. It optimizes round account balances because it finds them, and isn’t involved with which accounts must be funded within the first place. Simply because the presence of a TEA makes asset location extra invaluable, doesn’t imply you must contribute to a TEA, versus a TDA. That call is primarily a wager on how your tax price in the present day will examine to your tax price in retirement. To hedge, some could discover it optimum to contribute to each a TDA and TEA (that is referred to as “tax diversification”). Whereas these choices are out of scope for this paper, Betterment’s retirement planning instruments may also help purchasers with these selections.
City Legend 3: Asset location has little or no worth if considered one of your accounts is comparatively small.
It relies upon. Asset location won’t do a lot for buyers with a really small taxable steadiness and a comparatively giant steadiness in just one kind of certified account, as a result of many of the general property are already sheltered. Nevertheless, a big taxable steadiness and a small certified account steadiness (particularly a TEA steadiness) presents a greater alternative. Beneath these circumstances, there could also be room for less than the least tax-efficient, highest-return property within the certified account. Sheltering a small portion of the general portfolio can ship a disproportionate quantity of worth.
City Legend 4: Asset location has no worth in case you are investing in each varieties of certified accounts, however not in a taxable account.
A TEA gives important benefits over a TDA. Zero tax is best than a tax deferred till liquidation. Whereas tax effectivity (i.e. annual tax drag) performs no function in these location choices, anticipated returns and liquidation tax do. The property we anticipate to develop essentially the most must be positioned in a TEA, and doing so will plainly improve the general after-tax return. There’s an extra profit as properly. Required minimal distributions (RMDs) apply to TDAs however not TEAs. Shifting anticipated progress into the TEA, on the expense of the TDA, will imply decrease RMDs, giving the investor extra flexibility to regulate taxable earnings down the highway. In different phrases, a decrease steadiness within the TDA can imply decrease tax charges in retirement, if larger RMDs would have pushed the retiree into a better bracket. This potential profit shouldn’t be captured in our outcomes.
City Legend 5: Bonds at all times go within the IRA.
Presumably, however not essentially. This generally asserted rule is a simplification, and won’t be optimum below all circumstances. It’s mentioned at extra size under.
Present Approaches to Asset Location: Benefits and Limitations
Optimizing for After-Tax Return Whereas Sustaining Separate Portfolios
One strategy to rising after-tax return on retirement financial savings is to take care of a separate, standalone portfolio in every account with roughly the identical stage of risk-adjusted return, however tailoring every portfolio considerably to benefit from the tax profile of the account. Successfully, which means every account individually maintains the specified publicity to shares, whereas substituting sure asset lessons for others.
Usually talking, managing a totally diversified portfolio in every account signifies that there isn’t any approach to keep away from inserting some property with the very best anticipated return within the taxable account.
This strategy does embody a invaluable tactic, which is to distinguish the high-quality bonds part of the allocation, relying on the account they’re held in. The allocation to the part is identical in every account, however in a taxable account, it’s represented by municipal bonds that are exempt from federal tax , and in a certified account, by taxable funding grade bonds .
This variation is efficient as a result of it takes benefit of the truth that these two asset lessons have very comparable traits (anticipated returns, covariance and danger exposures) permitting them to play roughly the identical function from an asset allocation perspective. Municipal bonds are extremely tax-efficient because of their federal tax-exempt curiosity earnings, making them notably compelling for a taxable account. Taxable funding grade bonds have important tax drag, and work finest in a certified account. Betterment has utilized this substitution since 2014.
The Primary Precedence Checklist
Gobind Daryanani and Chris Cordaro sought to steadiness issues round tax effectivity and anticipated return, and illustrated that when each are very low, location choices with respect to these property have very restricted influence.5 That research impressed Michael Kitces, who leverages its insights right into a extra refined strategy to constructing a precedence record.6 To visually seize the connection between the 2 issues, Kitces bends the one-dimensional record right into a “smile.”
Asset Location Precedence Checklist
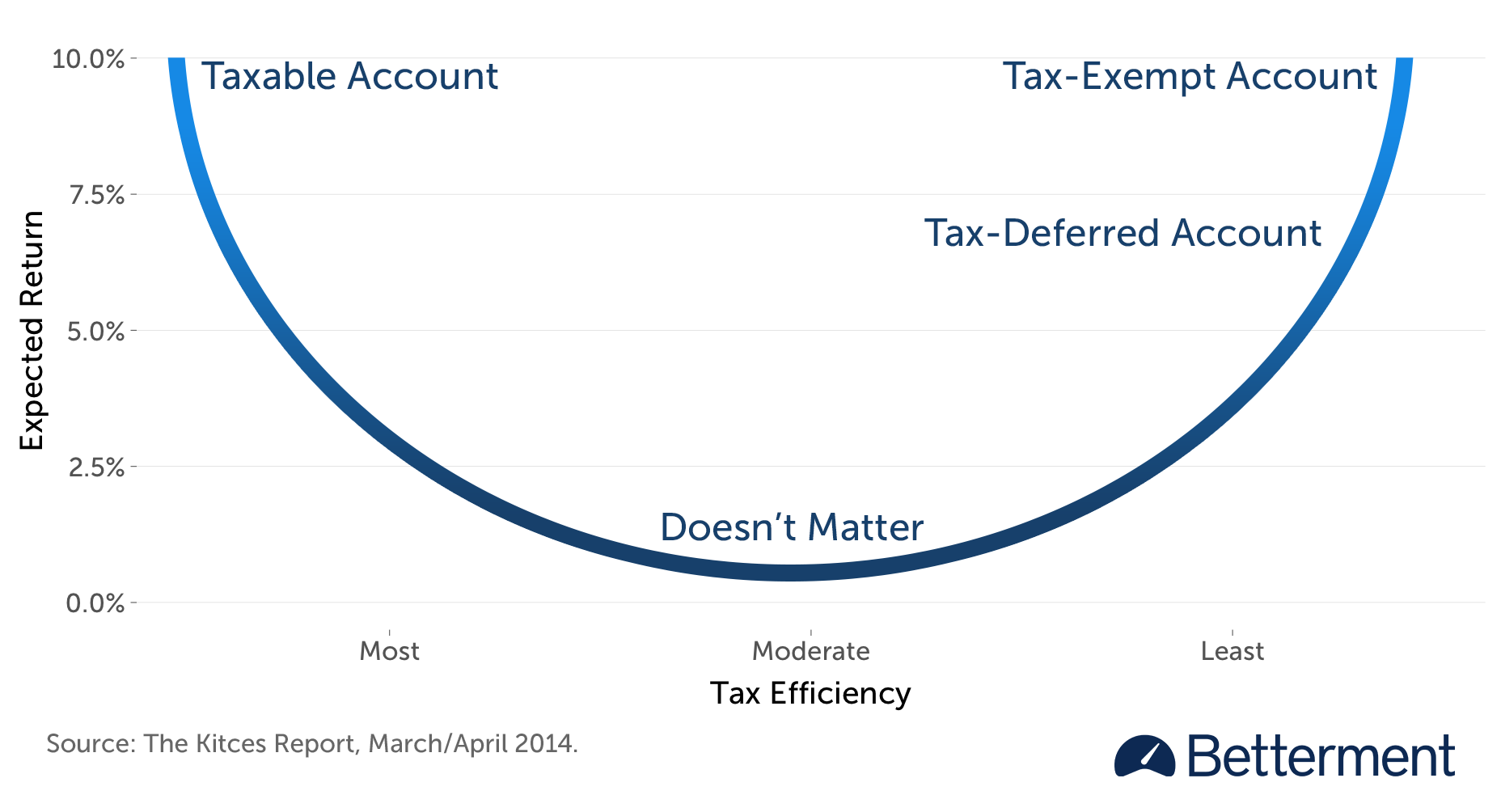
Belongings with a excessive anticipated return which might be additionally very tax-efficient go within the taxable account. Belongings with a excessive anticipated return which might be additionally very tax-inefficient go within the certified accounts, beginning with the TEA. The “smile” guides us in filling the accounts from each ends concurrently, and by the point we get to the center, no matter choices we make with respect to these property simply “don’t matter” a lot.
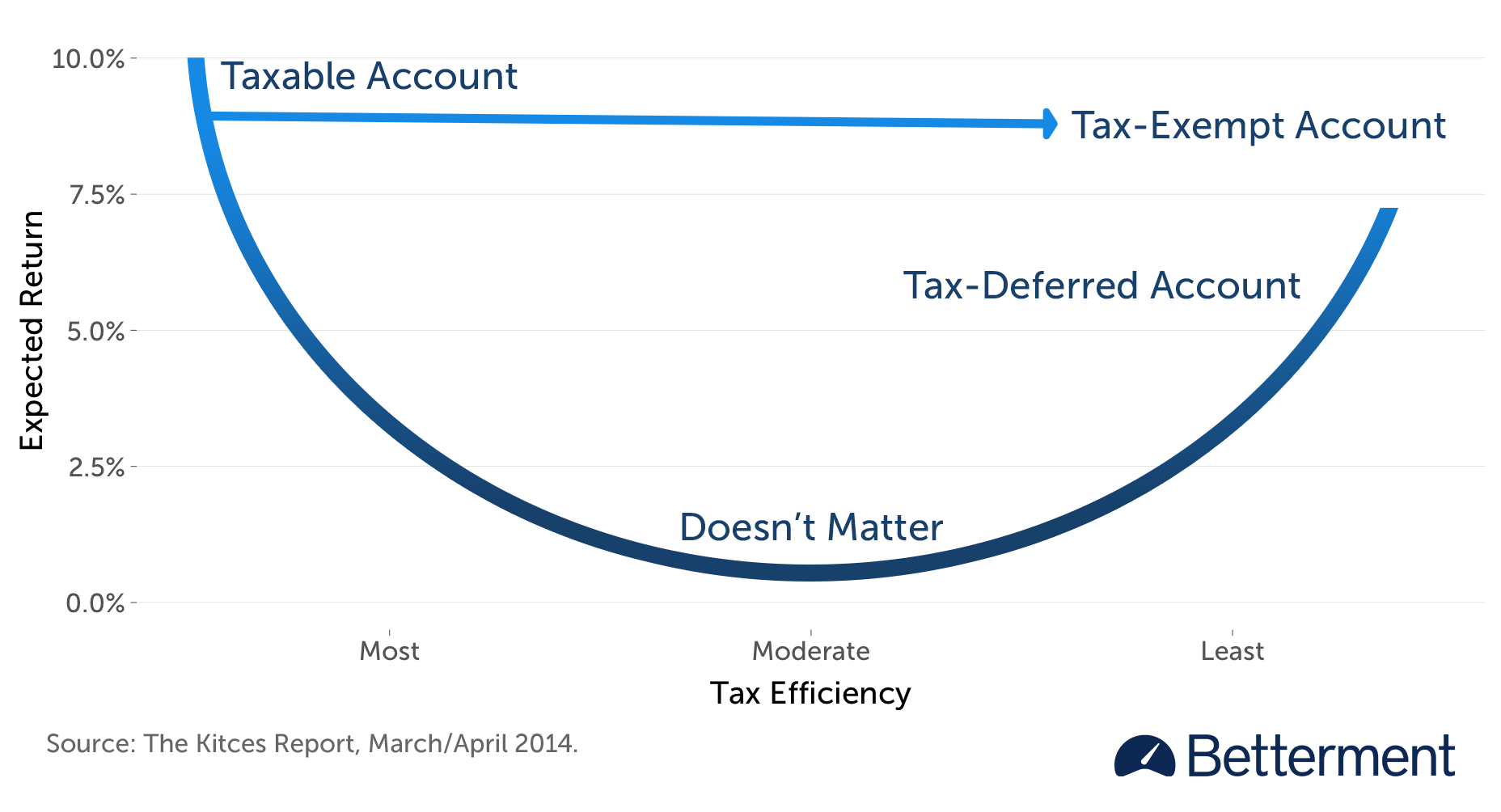
Nevertheless, Kitces augments the graph briefly order, recognizing that the essential “smile” doesn’t seize a 3rd key consideration—the influence of liquidation tax. As a result of capital positive aspects will ultimately be realized in a taxable account, however not in a TEA, even a extremely tax-efficient asset could be higher off in a TEA, if its anticipated return is excessive sufficient. The following iteration of the “smile” illustrates this desire.
Asset Location Precedence Checklist with Restricted Excessive Return Inefficient Belongings
Half IV: TCP Methodology
There isn’t any one-size-fits-all asset location for each set of inputs. Some circumstances apply to all buyers, however shift by time—the anticipated return of every asset class (which mixes separate assumptions for the risk-free price and the surplus return), in addition to dividend yields, QDI percentages, and tax legal guidelines. Different circumstances are private—which accounts the shopper has, the relative steadiness of every account, and the shopper’s time horizon.
Fixing for a number of variables whereas respecting outlined constraints is an issue that may be successfully solved by linear optimization. This technique is used to maximise some worth, which is represented by a components referred to as an “goal operate.” What we search to maximise is the after-tax worth of the general portfolio on the finish of the time horizon.
We get this quantity by including collectively the anticipated after-tax worth of each asset within the portfolio, however as a result of every asset will be held in multiple account, every portion have to be thought of individually, by making use of the tax guidelines of that account. We should due to this fact derive an account-specific anticipated after-tax return for every asset.
Deriving Account-Particular After-Tax Return
To outline the anticipated after-tax return of an asset, we first want its whole return (i.e., earlier than any tax is utilized). The overall return is the sum of the risk-free price (identical for each asset) and the surplus return (distinctive to each asset). Betterment derives extra returns utilizing the Black-Litterman mannequin as a place to begin. This frequent trade technique includes analyzing the worldwide portfolio of investable property and their proportions, and utilizing them to generate forward-looking anticipated returns for every asset class.
Subsequent, we should cut back every whole return into an after-tax return.7 The instant drawback is that for every asset class, the after-tax return will be totally different, relying on the account, and for the way lengthy it’s held.
- In a TEA, the reply is straightforward—the after-tax return equals the entire return—no calculation obligatory.
- In a TDA, we undertaking progress of the asset by compounding the entire return yearly. At liquidation, we apply the abnormal price to the entire progress.8 We use what’s left of the expansion after taxes to derive an annualized return, which is our after-tax return.
- In a taxable account, we have to think about the dividend and capital acquire part of the entire return individually, with respect to each price and timing. We undertaking progress of the asset by taxing the dividend part yearly on the abnormal price (or the preferential price, to the extent that it qualifies as QDI) and including again the after-tax dividend (i.e., we reinvest it). Capital positive aspects are deferred, and the LTCG is absolutely taxed on the preferential price on the finish of the interval. We then derive the annualized return based mostly on the after-tax worth of the asset.9
Notice that for each the TDA and taxable calculations, time horizon issues. Extra time means extra worth from deferral, so the identical whole return may end up in a better annualized after-tax return. Moreover, the risk-free price part of the entire return will even rely upon the time horizon, which impacts all three accounts.
As a result of we’re accounting for the potential for a TEA, as properly, we even have three distinct after-tax returns, and thus every asset successfully turns into three property, for any given time horizon (which is restricted to every Betterment buyer).
The Goal Perform
To see how this comes collectively, we first think about an especially simplified instance. Let’s assume now we have a taxable account, each a standard and Roth account, with $50,000 in each, and a 30-year horizon. Our allocation calls for less than two property: 70% equities (shares) and 30% fastened earnings (bonds). With a complete portfolio worth of $150,000, we’d like $105,000 of shares and $45,000 of bonds.
1. These are constants whose worth we already know (as derived above).
req,tax is the after-tax return of shares within the taxable account, over 30 years
req,trad is the after-tax return of shares within the conventional account, over 30 years
req,roth is the after-tax return of shares within the Roth account, over 30 years
rfi,tax is the after-tax return of bonds within the taxable account, over 30 years
rfi,trad is the after-tax return of bonds within the conventional account, over 30 years
rfi,roth is the after-tax return of bonds within the Roth account, over 30 years
2. These are the values we are attempting to unravel for (referred to as “determination variables”).
xeq,tax is the quantity of shares we are going to place within the taxable account
xeq,trad is the quantity of shares we are going to place within the conventional account
xeq,roth is the quantity of shares we are going to place within the Roth account
xfi,tax is the quantity of bonds we are going to place within the taxable account
xfi,trad is the quantity of bonds we are going to place within the conventional account
xfi,roth is the quantity of bonds we are going to place within the Roth account
3. These are the constraints which have to be revered. All positions for every asset should add as much as what now we have allotted to the asset general. All positions in every account should add as much as the out there steadiness in every account.
xeq,tax + xeq,trad + xeq,roth = 105,000
xfi,tax + xfi,trad + xfi,roth = 45,000
xeq,tax + xfi,tax = 50,000
xeq,trad + xfi,trad = 50,000
xeq,roth + xfi,roth = 50,000
4. That is the target operate, which makes use of the constants and determination variables to precise the after-tax worth of your complete portfolio, represented by the sum of six phrases (the after-tax worth of every asset in every of the three accounts).
maxx req,taxxeq,tax + req,tradxeq,trad + req,rothxeq,roth + rfi,taxxfi,tax + rfi,tradxfi,trad + rfi,rothxfi,roth
Linear optimization turns the entire above into a fancy geometric illustration, and mathematically closes in on the optimum answer. It assigns values for all determination variables in a manner that maximizes the worth of the target operate, whereas respecting the constraints. Accordingly, every determination variable is a exact instruction for the way a lot of which asset to place in every account. If a variable comes out as zero, then that specific account will comprise none of that specific asset.
An precise Betterment portfolio can doubtlessly have twelve asset lessons,15 relying on the allocation. Which means TCP should successfully deal with as much as 36 “property,” every with its personal after-tax return. Nevertheless, the total complexity behind TCP goes properly past rising property from two to 12.
Up to date constants and constraints will set off one other a part of the optimization, which determines what TCP is allowed to promote, as a way to transfer an already coordinated portfolio towards the newly optimum asset location, whereas minimizing taxes. Reshuffling property in a TDA or TEA is “free” within the sense that no capital positive aspects might be realized.10 Within the taxable account, nonetheless, TCP will try to maneuver as shut as attainable in the direction of the optimum asset location with out realizing capital positive aspects.
Anticipated returns will periodically be up to date, both as a result of the risk-free price has been adjusted, or as a result of new extra returns have been derived through Black-Litterman.
Future money flows could also be much more materials. Extra funds in a number of of the accounts might considerably alter the constraints which outline the dimensions of every account, and the goal greenback allocation to every asset class. Such occasions (together with dividend funds, topic to a de minimis threshold) will set off a recalculation, and doubtlessly a reshuffling of the property.
Money flows, particularly, could be a problem for these managing their asset location manually. Inflows to only one account (or to a number of accounts in unequal proportions) create a pressure between optimizing asset location and sustaining asset allocation, which is difficult to resolve with out mathematical precision.
To take care of the general asset allocation, every place within the portfolio have to be elevated pro-rata. Nevertheless, a number of the extra property we have to purchase “belong” in different accounts from an asset location perspective, despite the fact that new money shouldn’t be out there in these accounts. If the taxable account can solely be partially reshuffled because of built-in positive aspects, we should select both to maneuver farther away from the goal allocation, or the goal location.11
With linear optimization, our preferences will be expressed by extra constraints, weaving these issues into the general drawback. When fixing for brand new money flows, TCP penalizes allocation drift larger than it does location drift.
Towards this background, you will need to notice that anticipated returns (the important thing enter into TCP, and portfolio administration usually) are educated guesses at finest. Irrespective of how hermetic the mathematics, cheap individuals will disagree on the “appropriate” approach to derive them, and the longer term could not cooperate, particularly within the short-term. There isn’t any assure that any specific asset location will add essentially the most worth, and even any worth in any respect. However given many years, the probability of this consequence grows.
Half V: Monte Carlo—Betterment’s Testing Framework
To check the output of the linear optimization technique, we turned to a Monte Carlo testing framework,12 constructed solely in-house by Betterment’s consultants. The forward-looking simulations mannequin the conduct of the TCP technique all the way down to the person lot stage. We simulate the paths of those tons, accounting for dividend reinvestment, rebalancing, and taxation.
The simulations utilized Betterment’s rebalancing methodology, which corrects drift from the goal asset allocation in extra of three% as soon as the account steadiness meets or exceeds the required threshold, however stops wanting realizing STCG, when attainable.
Betterment’s administration charges have been assessed in all accounts, and ongoing taxes have been paid yearly from the taxable account. All taxable gross sales first realized out there losses earlier than touching LTCG.
The simulations assume no more money flows apart from dividends. This isn’t as a result of we don’t anticipate them to occur. Somewhat, it’s as a result of making assumptions round these very private circumstances does nothing to isolate the good thing about TCP particularly. Asset location is pushed by the relative sizes of the accounts, and money flows will change these ratios, however the timing and quantity is extremely particular to the person.19 Avoiding the necessity to make particular assumptions right here helps preserve the evaluation extra common. We used equal beginning balances for a similar cause.13
For each set of assumptions, we ran every market situation whereas managing every account as a standalone (uncoordinated) Betterment portfolio because the benchmark.14 We then ran the identical market eventualities with TCP enabled. In each instances, we calculated the after-tax worth of the mixture portfolio after full liquidation on the finish of the interval.15 Then, for every market situation, we calculated the after-tax annualized inner charges of return (IRR) and subtracted the benchmark IRR from the TCP IRR. That delta represents the incremental tax alpha of TCP for that situation. The median of these deltas throughout all market eventualities is the estimated tax alpha we current under for every set of assumptions.
Half VI: Outcomes
Extra Bonds, Extra Alpha
A better allocation to bonds results in a dramatically larger profit throughout the board. This is smart—the heavier your allocation to tax-inefficient property, the extra asset location can do for you. To be extraordinarily clear: this isn’t a cause to pick out a decrease allocation to shares! Over the long-term, we anticipate a better inventory allocation to return extra (as a result of it’s riskier), each earlier than, and after tax. These are measurements of the extra return because of TCP, which say nothing in regards to the absolute return of the asset allocation itself.
Conversely, a really excessive allocation to shares exhibits a smaller (although nonetheless actual) profit. Nevertheless, youthful clients invested this aggressively ought to step by step cut back danger as they get nearer to retirement (to one thing extra like 50% shares). Trying to a 70% inventory allocation is due to this fact an imperfect however cheap approach to generalize the worth of the technique over a 30-year interval.
Extra Roth, Extra Alpha
One other sample is that the presence of a Roth makes the technique extra invaluable. This additionally is smart—a taxable account and a TEA are on reverse ends of the “favorably taxed” spectrum, and having each presents the largest alternative for TCP’s “account arbitrage.” However once more, this profit shouldn’t be interpreted as a cause to contribute to a TEA over a TDA, or to shift the steadiness between the 2 through a Roth conversion. These choices are pushed by different issues. TCP’s job is to optimize the relative balances because it finds them.
Enabling TCP On Present Taxable Accounts
TCP must be enabled earlier than the taxable account is funded, that means that the preliminary location will be optimized with out the necessity to promote doubtlessly appreciated property. A Betterment buyer with an present taxable account who permits TCP shouldn’t anticipate the total incremental profit, to the extent that property with built-in capital positive aspects must be offered to attain the optimum location.
It’s because TCP conservatively prioritizes avoiding a sure tax in the present day, over doubtlessly lowering tax sooner or later. Nevertheless, the optimization is carried out each time there’s a deposit (or dividend) to any account. With future money flows, the portfolio will transfer nearer to regardless of the optimum location is decided to be on the time of the deposit.
Half VII: Particular Issues
Low Bracket Taxpayers: Beware
Taxation of funding earnings is considerably totally different for individuals who qualify for a marginal tax bracket of 15% or under. As an instance, now we have modified the chart from Half II to use to such low bracket taxpayers.
TCP shouldn’t be designed for these buyers. Optimizing round this tax profile would reverse many assumptions behind TCP’s methodology. Municipal bonds now not have a bonus over different bond funds. The arbitrage alternative between the abnormal and preferential price is gone. In truth, there’s barely tax of any sort. It’s fairly seemingly that such buyers wouldn’t profit a lot from TCP, and should even cut back their general after-tax return.
If the low tax bracket is short-term, TCP over the long-term should still make sense. Additionally notice that some combos of account balances can, in sure circumstances, nonetheless add tax alpha for buyers in low tax brackets. One instance is when an investor solely has conventional and Roth IRA accounts, and no taxable accounts being tax coordinated. Low bracket buyers ought to very fastidiously think about whether or not TCP is appropriate for them. As a common rule, we don’t advocate it.
Potential Issues with Coordinating Accounts Meant for Totally different Time Horizons
We started with the premise that asset location is wise solely with respect to accounts which might be usually meant for a similar function. That is essential, as a result of inconsistently distributing property will end in asset allocations in every account that aren’t tailor-made in the direction of the general aim (or any aim in any respect). That is high-quality, so long as we anticipate that each one coordinated accounts might be out there for withdrawals at roughly the identical time (e.g. at retirement). Solely the mixture portfolio issues in getting there.
Nevertheless, uneven distributions are much less diversified. Short-term drawdowns (e.g., the 2008 monetary disaster) can imply {that a} single account could drop considerably greater than the general coordinated portfolio. If that account is meant for a short-term aim, it might not have an opportunity to recuperate by the point you want the cash. Likewise, if you don’t plan on depleting an account throughout your retirement, and as a substitute plan on leaving it to be inherited for future generations, arguably this account has an extended time horizon than the others and will thus be invested extra aggressively. In both case, we don’t advocate managing accounts with materially totally different time horizons as a single portfolio.
For the same cause, you must keep away from making use of asset location to an account that you just anticipate might be long-term, however one that you could be look to for emergency withdrawals. For instance, a Security Web Objective ought to by no means be managed by TCP.
Massive Upcoming Transfers/Withdrawals
If you can be making giant transfers in or out of your tax-coordinated accounts, you could wish to delay enabling our tax coordination device till after these transfers have occurred.
It’s because giant modifications within the balances of the underlying accounts can necessitate rebalancing, and thus could trigger taxes. With incoming deposits, we will intelligently rebalance your accounts by buying asset lessons which might be underweight. However when giant withdrawals or transfers out are made, regardless of Betterment’s clever administration of executing trades, some taxes will be unavoidable when rebalancing to your general goal allocation.
The one exception to this rule is that if the massive deposit might be in your taxable account as a substitute of your IRAs. In that case, you must allow tax-coordination earlier than depositing cash into the taxable account. That is so our system is aware of to tax-coordinate you instantly.
The aim of tax coordination is to scale back the drag taxes have in your investments, not trigger extra taxes. So if an upcoming withdrawal or outbound switch might trigger rebalancing, and thus taxes, it will be prudent to delay enabling tax coordination till you will have accomplished these transfers.
Mitigating Behavioral Challenges By Design
There’s a broader situation that stems from finding property with totally different volatility profiles on the account stage, however it’s behavioral. Uncoordinated portfolios with the identical allocation transfer collectively. Asset location, then again, will trigger one account to dip greater than one other, testing an investor’s abdomen for volatility. Those that allow TCP throughout their accounts must be ready for such differentiated actions. Rationally, we should always ignore this—in any case, the general allocation is identical—however that’s simpler stated than finished.
How TCP Interacts with Tax Loss Harvesting+
TCP and TLH work in tandem, looking for to attenuate tax influence. As described in additional element under, the exact interplay between the 2 methods is extremely depending on private circumstances. Whereas it’s attainable that enabling a TCP could cut back harvest alternatives, each TLH and TCP derive their profit with out disturbing the specified asset allocation.
Operational Interplay
TLH+ was designed round a “tertiary ticker” system, which ensures that no buy in an IRA or 401(okay) managed by Betterment will intervene with a harvested loss in a Betterment taxable account.
A sale in a taxable account, and a subsequent repurchase of the identical asset class in a certified account could be incidental for accounts managed as separate portfolios. Beneath TCP, nonetheless, we anticipate this to sometimes occur by design. When “relocating” property, both throughout preliminary setup, or as a part of ongoing optimization, TCP will promote an asset class in a single account, and instantly repurchase it in one other. The tertiary ticker system permits this reshuffling to occur seamlessly, whereas trying to guard any tax losses which might be realized within the course of.
Conceptualizing Blended Efficiency
TCP will have an effect on the composition of the taxable account in methods which might be arduous to foretell, as a result of its choices might be pushed by modifications in relative balances among the many accounts. In the meantime, the burden of particular asset lessons within the taxable account is a cloth predictor of the potential worth of TLH (extra unstable property ought to supply extra harvesting alternatives). The exact interplay between the 2 methods is way extra depending on private circumstances, resembling in the present day’s account steadiness ratios and future money circulation patterns, than on usually relevant inputs like asset class return profiles and tax guidelines.
These dynamics are finest understood as a hierarchy. Asset allocation comes first, and determines what mixture of asset lessons we should always stick with general. Asset location comes second, and repeatedly generates tax alpha throughout all coordinated accounts, inside the constraints of the general portfolio. Tax loss harvesting comes third, and appears for alternatives to generate tax alpha from the taxable account solely, inside the constraints of the asset combine dictated by asset location for that account.
TLH is often handiest within the first a number of years after an preliminary deposit to a taxable account. Over many years, nonetheless, we anticipate it to generate worth solely from subsequent deposits and dividend reinvestments. Ultimately, even a considerable dip is unlikely to convey the market value under the acquisition value of the older tax tons. In the meantime, TCP goals to ship tax alpha over your complete steadiness of all three accounts for your complete holding interval.
***
Betterment doesn’t characterize in any method that TCP will end in any specific tax consequence or that particular advantages might be obtained for any particular person investor. The TCP service shouldn’t be meant as tax recommendation. Please seek the advice of your private tax advisor with any questions as as to whether TCP is an acceptable technique for you in gentle of your particular person tax circumstances. Please see our Tax-Coordinated Portfolio Disclosures for extra data.
Addendum
As of Might 2020, for purchasers who point out that they’re planning on utilizing a Well being Financial savings Account (HSA) for long-term financial savings, we enable the inclusion of their HSA of their Tax-Coordinated Portfolio.
If an HSA is included in a Tax-Coordinated Portfolio, we deal with it primarily the identical as an extra Roth account. It’s because funds inside an HSA develop earnings tax-free, and withdrawals will be made earnings tax-free for medical functions. With this assumption, we additionally implicitly assume that the HSA might be absolutely used to cowl long-term medical care spending.
The tax alpha numbers introduced above haven’t been up to date to mirror the inclusion of HSAs, however stay our best-effort point-in-time estimate of the worth of TCP on the launch of the characteristic. Because the inclusion of HSAs permits even additional tax-advantaged contributions, we contend that the inclusion of HSAs is almost definitely to moreover profit clients who allow TCP.
1“Enhance Your After-Tax Funding Returns.” Susan B. Garland. Kiplinger.com, April 2014.
2However see “How IRA Withdrawals In The Crossover Zone Can Set off The three.8% Medicare Surtax,” Michael Kitces, July 23, 2014.
3It’s price emphasizing that asset location optimizes round account balances because it finds them, and has nothing to say about which account to fund within the first place. Asset location considers which account is finest for holding a specified greenback quantity of a specific asset. Nevertheless, contributions to a TDA are tax-deductible, whereas getting a greenback right into a taxable account requires greater than a greenback of earnings.
4Pg. 5, The Kitces Report. January/February 2014.
5Daryanani, Gobind, and Chris Cordaro. 2005. “Asset Location: A Generic Framework for Maximizing After-Tax Wealth.” Journal of Monetary Planning (18) 1: 44–54.
6The Kitces Report, March/April 2014.
7Whereas the importance of abnormal versus preferential tax therapy of earnings has been made clear, the influence of a person’s particular tax bracket has not but been addressed. Does it matter which abnormal price, and which preferential price is relevant, when finding property? In spite of everything, calculating the after-tax return of every asset means making use of a particular price. It’s actually true that totally different charges ought to end in totally different after-tax returns. Nevertheless, we discovered that whereas the particular price used to derive the after-tax return can and does have an effect on the extent of ensuing returns for various asset lessons, it makes a negligible distinction on ensuing location choices. The one exception is when contemplating utilizing very low charges as inputs (the implication of which is mentioned below “Particular Issues”). This could really feel intuitive: As a result of the optimization is pushed primarily by the relative dimension of the after-tax returns of various asset lessons, transferring between brackets strikes all charges in the identical course, usually sustaining these relationships monotonically. The particular charges do matter so much in the case of estimating the good thing about the asset location chosen, so price assumptions are specified by the “Outcomes” part. In different phrases, if one taxpayer is in a average tax bracket, and one other in a excessive bracket, their optimum asset location might be very comparable and infrequently an identical, however the excessive bracket investor could profit extra from the identical location.
8In actuality, the abnormal price is utilized to your complete worth of the TDA, each the principal (i.e., the deductible contributions) and the expansion. Nevertheless, this can occur to the principal whether or not we use asset location or not. Subsequently, we’re measuring right here solely that which we will optimize.
9TCP in the present day doesn’t account for the potential advantage of a international tax credit score (FTC). The FTC is meant to mitigate the potential for double taxation with respect to earnings that has already been taxed abroad. The scope of the profit is difficult to quantify and its applicability is determined by private circumstances. All else being equal, we’d anticipate that incorporating the FTC could considerably improve the after-tax return of sure asset lessons in a taxable account—particularly developed and rising markets shares. If maximizing your out there FTC is vital to your tax planning, you must fastidiously think about whether or not TCP is the optimum technique for you.
10Customary market bid-ask unfold prices will nonetheless apply. These are comparatively low, as Betterment considers liquidity as a consider its funding choice course of. Betterment clients don’t pay for trades.
11Moreover, within the curiosity of creating interplay with the device maximally responsive, sure computationally demanding facets of the methodology have been simplified for functions of the device solely. This might end in a deviation from the goal asset location imposed by the TCP service in an precise Betterment account.
12One other approach to take a look at efficiency is with a backtest on precise market knowledge. One benefit of this strategy is that it checks the technique on what truly occurred. Conversely, a ahead projection permits us to check 1000’s of eventualities as a substitute of 1, and the longer term is unlikely to appear like the previous. One other limitation of a backtest on this context—sufficiently granular knowledge for your complete Betterment portfolio is simply out there for the final 15 years. As a result of asset location is basically a long-term technique, we felt it was vital to check it over 30 years, which was solely attainable with Monte Carlo. Moreover, Monte Carlo truly permits us to check tweaks to the algorithm with some confidence, whereas adjusting the algorithm based mostly on how it will have carried out prior to now is successfully a kind of “knowledge snooping”.
13That stated, the technique is anticipated to alter the relative balances dramatically over the course of the interval, because of unequal allocations. We anticipate a Roth steadiness particularly to ultimately outpace the others, because the optimization will favor property with the very best anticipated return for the TEA. That is precisely what we wish to occur.
14For the uncoordinated taxable portfolio, we assume an allocation to municipal bonds (MUB) for the high-quality bonds part, however use funding grade taxable bonds (AGG) within the uncoordinated portfolio for the certified accounts. Whereas TCP makes use of this substitution, Betterment has supplied it since 2014, and we wish to isolate the extra tax alpha of TCP particularly, with out conflating the advantages.
15Full liquidation of a taxable or TDA portfolio that has been rising for 30 years will understand earnings that’s assured to push the taxpayer into a better tax bracket. We assume this doesn’t occur, as a result of in actuality, a taxpayer in retirement will make withdrawals step by step. The methods round timing and sequencing decumulation from a number of account sorts in a tax-efficient method are out of scope for this paper.
Extra References
Berkin. A. “A State of affairs Based mostly Method to After-Tax Asset Allocation.” 2013. Journal of Monetary Planning.
Jaconetti, Colleen M., CPA, CFP®. Asset Location for Taxable Buyers, 2007. https://private.vanguard.com/pdf/s556.pdf.
Poterba, James, John Shoven, and Clemens Sialm. “Asset Location for Retirement Savers.” November 2000. https://school.mccombs.utexas.edu/Clemens.Sialm/PSSChap10.pdf.
Reed, Chris. “Rethinking Asset Location – Between Tax-Deferred, Tax-Exempt and Taxable Accounts.” Accessed 2015. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2317970.
Reichenstein, William, and William Meyer. “The Asset Location Choice Revisited.” 2013. Journal of Monetary Planning 26 (11): 48–55.
Reichenstein, William. 2007. “Calculating After-Tax Asset Allocation is Key to Figuring out Threat, Returns, and Asset Location.” Journal of Monetary Planning (20) 7: 44–53.





