Image your self sinking, slowly, beneath the waves.
As you fall, the Solar turns into smaller, and dimmer, and dimmer nonetheless. The chilly waters crush in round you because the stress will increase. Now you are in full darkness, so deep that the daylight cannot attain you. Then, astonishingly, you see a flicker of sunshine, from a creature in contrast to any people have seen earlier than.
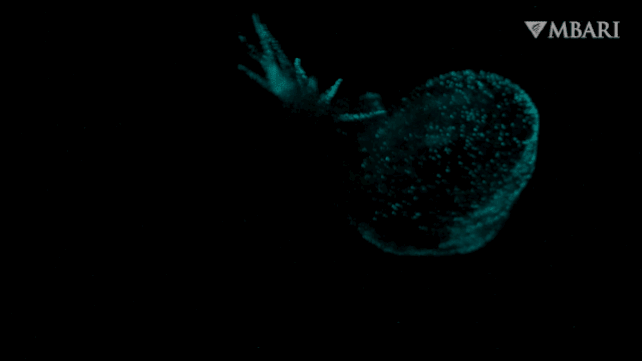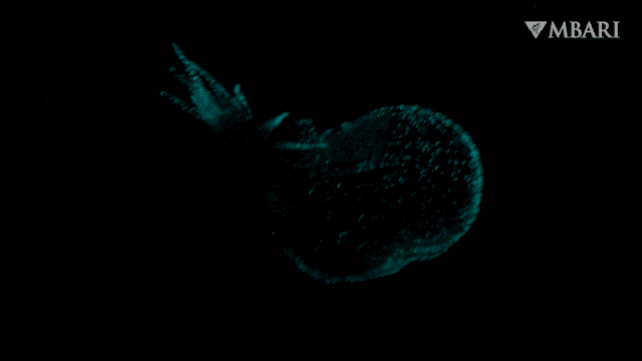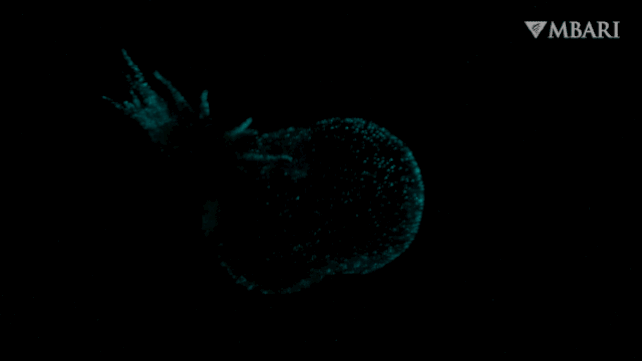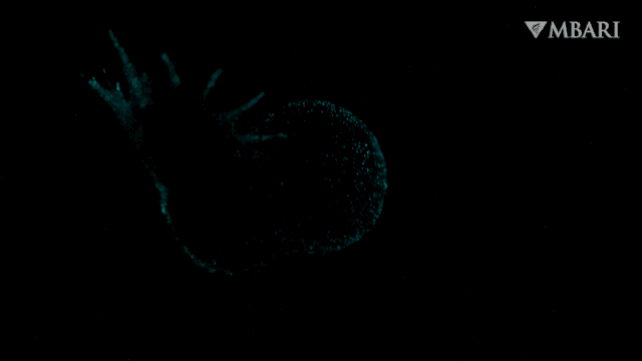
It is a nudibranch, just lately found swimming freely within the water column lit by a bioluminescent glow, adorned with a billowing hood, by researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Analysis Institute (MBARI) within the US.
That is Bathydevius caudactylus, the primary recognized nudibranch of its type: dwelling not in shallow waters, or on the seafloor, however greater than 2,200 meters (round 7,220 ft) under the floor of the Pacific Ocean within the bathypelagic zone, out in open water.
“Most nudibranchs stay on the underside in shallow water, so it was very shocking to discover a nudibranch so deep within the water column and much from the underside,” MBARI marine scientist Bruce Robison informed ScienceAlert.
“We knew of some species that stay on the deep seafloor however none had ever been reported in deep midwaters.”
Sea slugs of the nudibranch order are among the many most charismatic of the molluscs. They’re typically brightly coloured, with ornate appendages and patterns. They’re typically discovered on reefs, the place some species munch coral; others eat algae, sponges, anemones, jellyfish, and even different nudibranchs.
They’re various, and versatile, however that versatility was considered restricted to a sure vary. This is among the the explanation why MBARI researchers nicknamed the animal “thriller mollusc” after they got here throughout it whereas piloting the remotely operated analysis car Tiburon at a depth of two,614 meters.
“After we first filmed it glowing with the ROV, everybody within the management room set free a loud ‘Oooooh!’ on the identical time,” Haddock says. “We had been all enchanted by the sight.”
The creature they noticed had a foot like a sea slug, but in addition a big, gaping hood, and a tail that was fringed, showing like fingers undulating within the present. Via the ethereal, translucent pores and skin on its physique, roseate inner organs may be seen. And, when the ROV approached, and the creature felt threatened, it lit up with a bioluminescent glow.
This habits appears defensive: on one event, the researchers noticed one of many tendrils on the slug’s tail glow steadily whereas rotating, ultimately detaching and floating free, much like the best way a lizard may drop its tail in a bid to distract a predator.
In whole, the researchers encountered 157 people of the species throughout dives between 2000 and 2021, 32 of which they studied intimately, and 18 of which they collected for additional examine in a laboratory setting. This examine included a genome evaluation, which allowed them to position the unusual creature as a nudibranch – however one so totally different from all different nudibranchs that it required the creation of a brand new household, Bathydeviidae.
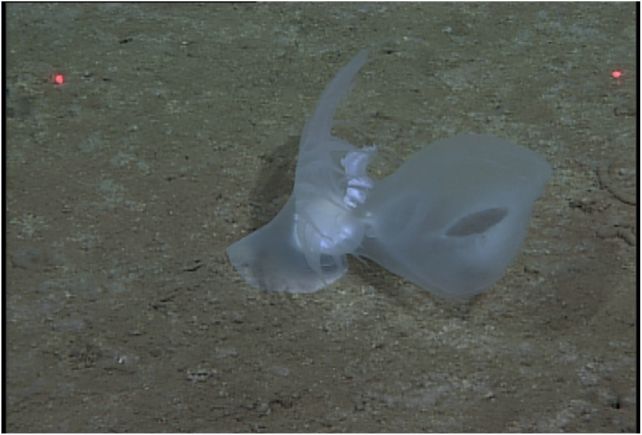

“Essentially the most thrilling facet of this discovery,” Robison informed ScienceAlert, “is that we had been in a position to take advantage of complete preliminary description of a brand new deep-sea species ever offered (anatomy, respiration, bioluminescence, replica, feeding, genetics, habits).”
Observing Bathydevius in its pure habitat, the researchers watched the animal use its voluminous hood to seize prey, indicating a eating regimen wealthy in crustaceans. Missing the raspy tongue-like appendage seen in most different nudibranchs, Bathydevius as a substitute swallows its meals by way of a mouth behind the hood.
Two different species of nudibranch use hoods equally, however they’re very distant from Bathydevius within the nudibranch household, suggesting that the trait advanced independently within the newly found species.
frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
The nudibranch, like others of its free-floating type, is hermaphroditic. On one event, the researchers had been fortunate sufficient to look at components of Bathydevius‘ reproductive technique: at a depth of two,755 meters, two people had anchored themselves to the seafloor to undertake the method of laying their frilly ribbons of eggs. Different people had been seen clinging to the seafloor in the same method, at depths as much as 4,009 meters.
In one other occasion, one of many captured people was able to launch its eggs; it did so within the tank, releasing a ribbon that drifted after which connected to the ground of the tank. After three days, the mucus matrix of the ribbon dissipated, and the eggs developed into larvae.
It is probably the most full examine of a brand new deep-sea species carried out to this point – and one that means we could have been too conservative in our assumptions about what the pure world is able to.
“Bathydevius is radically totally different from all different nudibranchs as a result of it’s nicely tailored to stay in a really totally different habitat; evolution has overcome the challenges of survival the place it lives, and it is vitally well-suited to succeed there,” Robison stated.
“This tells us that nudibranch evolution is way extra versatile than we had believed it to be.”
The analysis has been printed in Deep-Sea Analysis Half I.





