The ever-reliable Curiosity rover is about to start a brand new quest to review large “spiderwebs” on Mars’ floor, after efficiently concluding its earlier mission, NASA has introduced. The online-like rocks span for miles and will maintain secrets and techniques in regards to the Purple Planet’s watery previous.
Over the past yr, Curiosity has been exploring Gediz Vallis — a channel carved into the steep slopes of Mount Sharp on the coronary heart of Gale Crater. Throughout this stage of its 12-year mission on Mars, the rover made some necessary discoveries, together with by accident unveiling crystals of pure sulfur and discovering “wavey” rocks left behind by an historic lake. Mission scientists additionally first seen a massive gap in one of many rover’s wheels because the wandering robotic traversed this area’s steep slopes.
However the rover’s time in Gediz Vallis is about to come back to a detailed. On Nov. 18, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) launched a last 360-degree “selfie” of the world taken by Curiosity because it ready to go off on the following leg of its epic journey, which has already lasted a decade longer than initially anticipated.
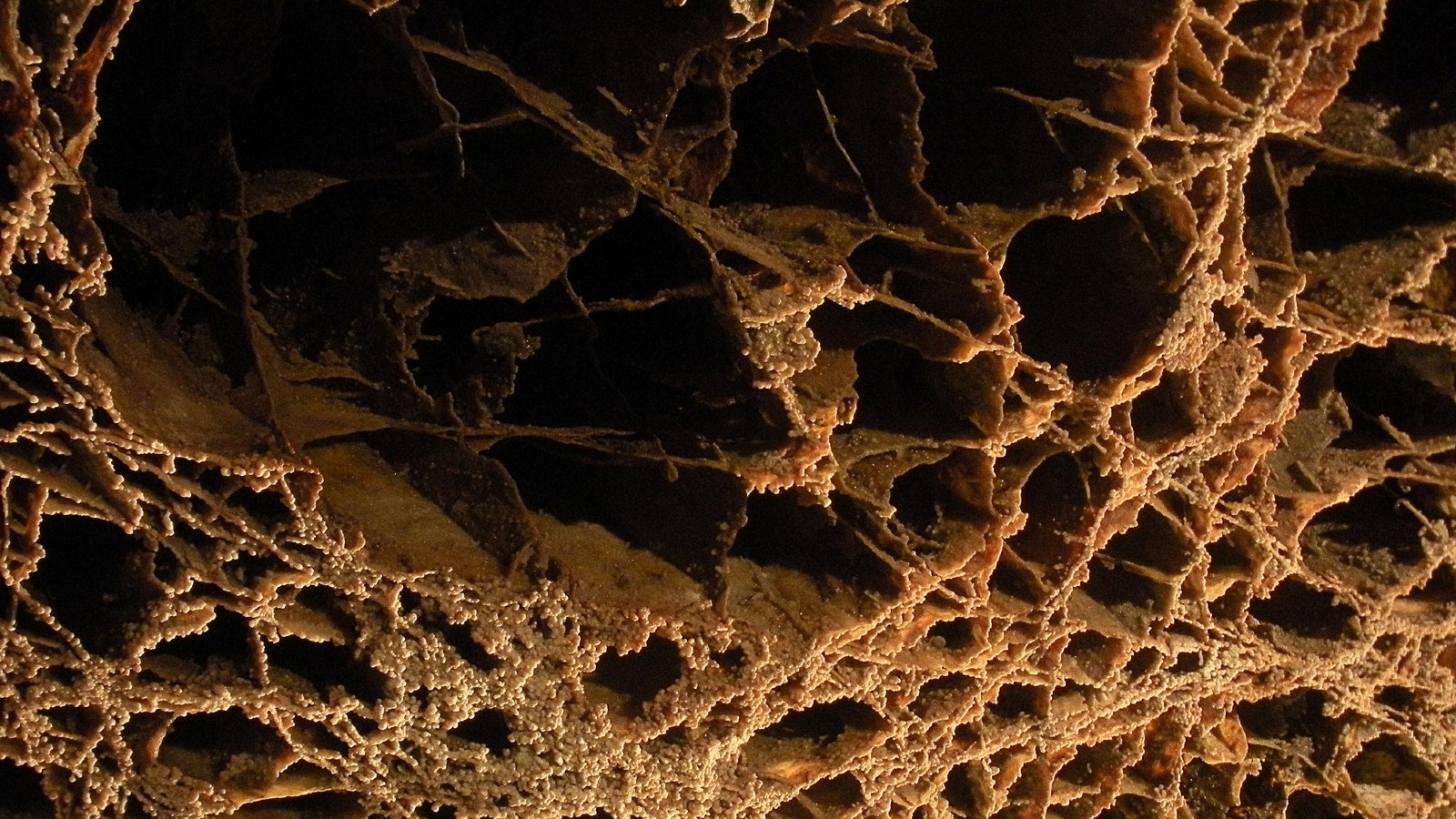
Curiosity’s subsequent goal is a big assortment of spiderweb-like floor options, often known as “the boxwork,” spanning between 6 and 12 miles (10 and 20 kilometers) throughout. This uncommon patchwork of zig-zagging rocks, or boxwork deposits, was first noticed many years in the past however has by no means been studied up shut, based on a JPL assertion.
The online-like options shouldn’t be confused with the notorious “spiders on Mars” — a geological characteristic created when carbon dioxide ice on the planet’s floor sublimates, or turns into fuel from a strong. Scientists just lately recreated these unusual options on Earth for the primary time.
Associated: 32 issues on Mars that appear like they should not be there
Boxwork deposits are additionally present in caves on Earth. They type when calcite-rich water fills gaps between rocks and hardens earlier than finally eroding away, creating “skinny blades of crystalline materials protruding from rocky partitions” just like stalactites and stalagmites, based on the Nationwide Speleological Society. The very best examples of this on our planet are present in Wind Cave Nationwide Park in South Dakota, based on the U.S. Geological Service. Nevertheless, terrestrial boxwork options are by no means various toes vast.
Martian boxwork, which has been recognized at a number of areas throughout the Purple Planet, is believed to type by way of the same course of as terrestrial boxwork. Nevertheless, as an alternative of water dripping by way of caves, the sprawling mineral veins have been left behind by the final remnants of historic, mineral-rich lakes and oceans.
Researchers hope that Curiosity will be taught extra about precisely how this occurred and what it could inform us about Mars’ watery previous. Mission scientists are notably within the minerals that make up these web-like buildings as a result of they may make clear whether or not extraterrestrial life as soon as existed on the Purple Planet.
“These ridges will embody minerals that crystallized underground, the place it will have been hotter, with salty liquid water flowing by way of,” Kirsten Siebach, a Curiosity mission scientist at Rice College in Houston who has been learning the world, stated within the assertion. “Early Earth microbes may have survived in the same atmosphere. That makes this an thrilling place to discover.”
Curiosity will arrive on the boxwork sooner or later in early 2025.





