Sixty years in the past, early within the morning of October 1, 1964, a smooth blue and white prepare slid effortlessly throughout the city sprawl of Tokyo, its elevated tracks carrying it south towards town of Osaka and a spot within the historical past books.
This was the daybreak of Japan’s “bullet prepare” period, broadly considered the defining image of the nation’s astonishing restoration from the trauma of World Warfare II. In tandem with the 1964 Tokyo Olympic Video games, this technological marvel of the Sixties marked the nation’s return to the highest desk of the worldwide neighborhood.
Within the six many years since that first prepare, the phrase Shinkansen – that means “new trunk line” – has develop into an internationally acknowledged byword for pace, journey effectivity and modernity.
Japan stays a world chief in rail know-how. Mighty conglomerates similar to Hitachi and Toshiba export billions of {dollars} price of trains and gear everywhere in the world yearly.
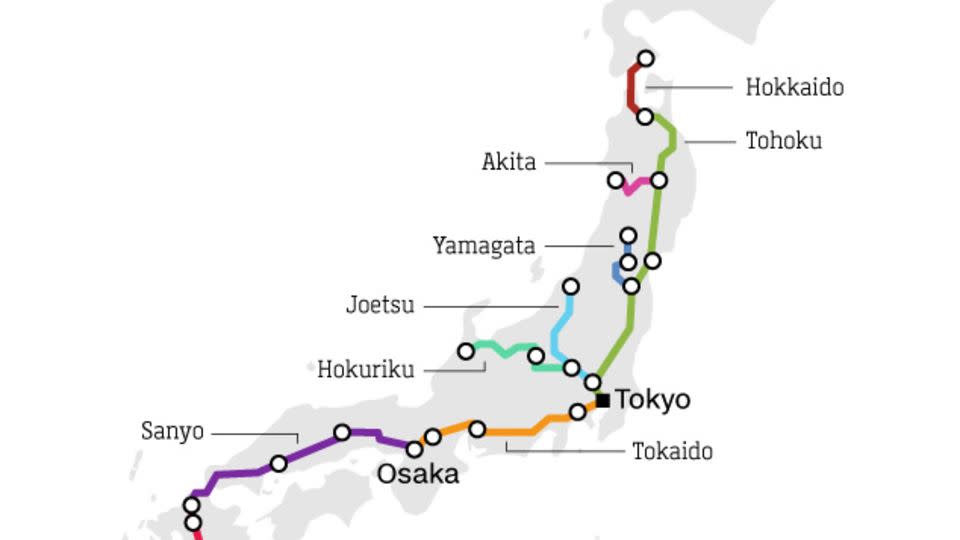
The Shinkansen community has expanded steadily because the 320-mile Tokaido line, linking Tokyo and Shin-Osaka was accomplished in 1964. Trains run at as much as 200 mph (about 322 kph) on routes radiating out from the capital – heading north, south and west to cities similar to Kobe, Kyoto, Hiroshima and Nagano.
In addition to an emblem of restoration, Shinkansen have been used as a device for Japan’s persevering with financial improvement and an agent of change in a rustic certain by conference and custom.
Pushing the boundaries
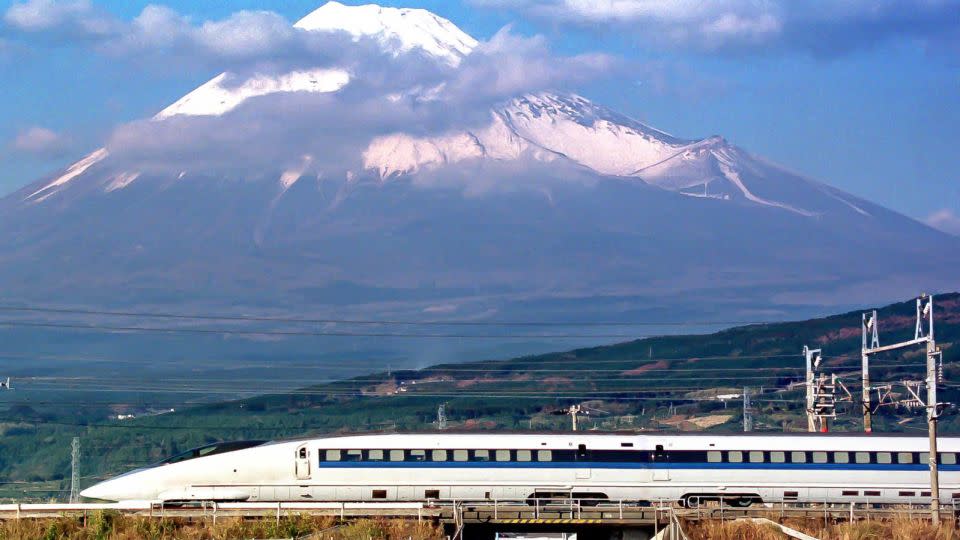

Its improvement owes an awesome deal to Japan’s early railway historical past. Slightly than the 4ft 8.5in “commonplace” gauge utilized in North America and far of Europe, a narrower gauge of 3ft 6in was chosen.
Though this was cheaper and simpler to construct via mountainous terrain, capability was restricted and speeds have been low.
With Japan’s 4 major islands stretching round 1,800 miles (practically 3,000 kilometers) from finish to finish, journeys between the primary cities have been lengthy and sometimes tortuous.
In 1889, the journey time from Tokyo to Osaka was 16 and a half hours by prepare – higher than the 2 to a few weeks it had taken on foot only some years earlier. By 1965, it was simply three hours and 10 minutes by way of the Shinkansen.
Calls for for a “commonplace gauge” rail community began within the twentieth century, but it surely was not till the Forties that work began in earnest as a part of an formidable Asian “loop line” undertaking to attach Japan to Korea and Russia by way of tunnels below the Pacific Ocean.
Defeat in World Warfare II meant that plans for the brand new railroad have been shelved till the mid-Fifties, when the Japanese economic system was recovering strongly and higher communications between its major cities was changing into important.
Though a lot of the community serves essentially the most populous areas of Honshu, the biggest of Japan’s islands, prolonged sea tunnels permit bullet trains to run lots of of miles via to Kyushu within the far south and Hokkaido within the north.

Japan’s difficult topography and its broadly various climates, from the freezing winters of the north to the tropical humidity farther south, have made Japanese railroad engineers world leaders at discovering options to new issues as they push the boundaries of rail know-how.
Not least of those is seismic exercise. Japan is without doubt one of the most geologically unstable locations on the planet, liable to earthquakes and tsunamis and residential to round 10% of the world’s volcanoes.
Whereas this gives arguably the defining picture of the Shinkansen – a high-tech fashionable prepare flashing previous the snow-capped Mount Fuji – it additionally makes the protected operation of high-speed trains way more troublesome.
Regardless of these elements, not a single passenger has ever been killed or injured on the Shinkansen community on account of derailments over its historical past.
Japan’s high-speed rail revolution
unknown content material merchandise
–
The following technology of bullet trains, often called ALFA-X, is at present being examined at speeds of virtually 250 mph (400 kph), though the service most might be “solely” 225 mph.
The defining options of those and different latest Shinkansen trains are their terribly lengthy noses, designed to not enhance their aerodynamics, however primarily to remove sonic booms brought on by the “piston impact” of trains getting into tunnels and forcing compression waves out of the opposite finish at supersonic speeds.
This can be a explicit downside in densely populated city areas, the place noise from Shinkansen traces has lengthy been a supply of complaints.
The experimental ALFA-X prepare additionally options new security know-how designed to chop down on vibration and noise and cut back the chance of derailments in main earthquakes.
Greater than 10 billion passengers have now been carried in pace and luxury by the trains, the predictability of the operation making high-speed journey appear routine and largely taken with no consideration.
Excessive-speed rails all over the world


In 2022, greater than 295 million folks rode on Shinkansen trains round Japan.
Little marvel then that many different nations have adopted Japan’s instance and constructed new high-speed railroads during the last 4 many years.
Maybe the best-known of those is France, which has been working its Prepare à Grand Vitesse (TGV) between Paris and Lyon since 1981.
Like Japan, France has efficiently exported the know-how to different nations, together with Europe’s longest high-speed community in Spain, in addition to Belgium, South Korea, the UK and Africa’s first high-speed railroad in Morocco.
France’s TGV community has been phenomenally profitable, slashing journey instances over lengthy distances between the nation’s huge cities, creating further capability and making high-speed journey accessible and reasonably priced, even mundane for normal commuters.
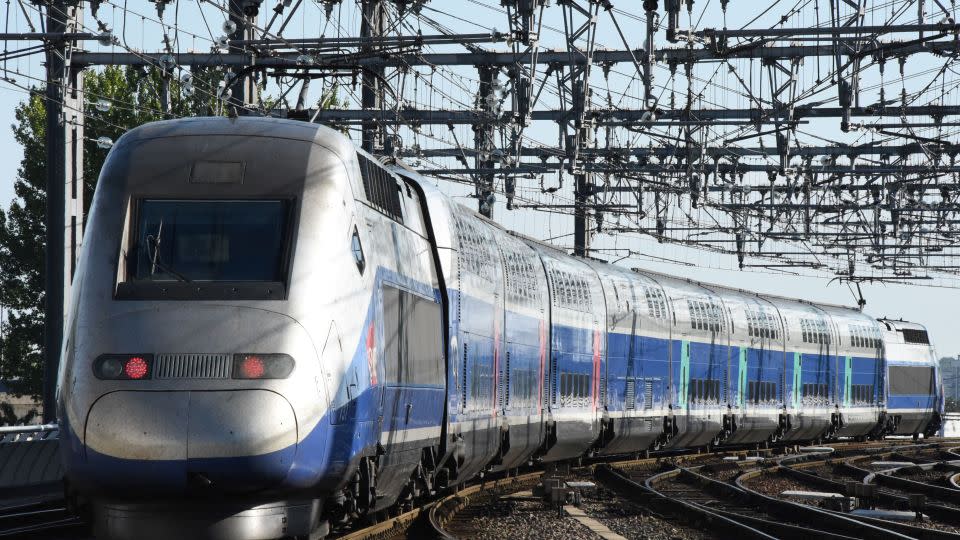


Italy, Germany, the Netherlands, Taiwan, Turkey and Saudi Arabia all now function trains on devoted traces linking their main cities, competing immediately with airways on home and worldwide routes.
Within the UK, high-speed Eurostar trains run from London to Paris, Brussels and Amsterdam, however “Excessive Velocity 2,” a second route operating north from London has been mired in controversy. What was as soon as billed as a landmark mega-project to energy an interconnected Britain into the oncoming century has now been diminished to a 140-mile hyperlink that may barely enhance on present companies.
For the second, the closest equal to the bullet prepare for British passengers are new Hitachi-built “Intercity Categorical Trains” utilizing know-how derived from their Japanese cousins, though these solely run at a most of 125 mph.
In the meantime, India and Thailand are planning intensive high-speed rail networks of their very own.
China’s railway rise
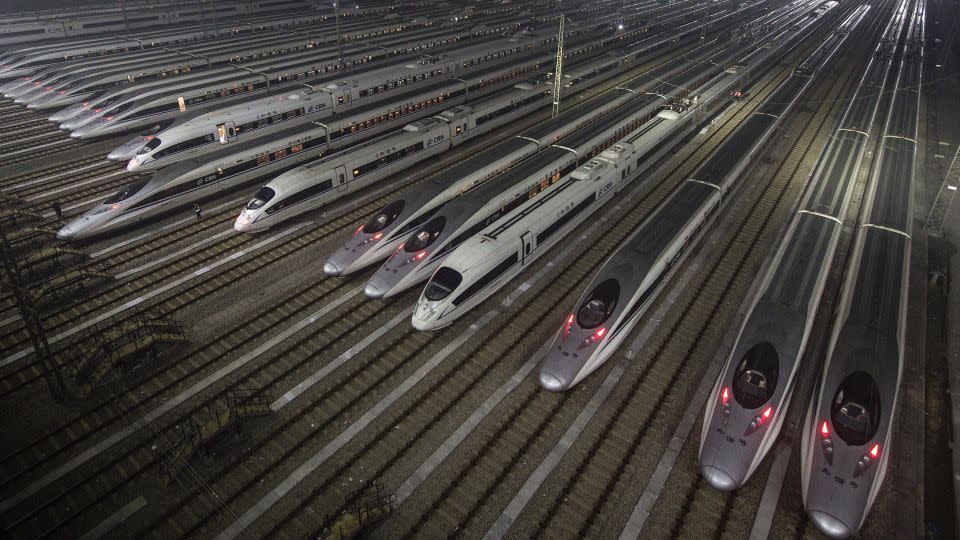


In recent times, it’s China that has eclipsed the remainder of the world, utilizing its financial would possibly to create the world’s longest high-speed railroad community.
In accordance with the nation’s nationwide railway operator, the entire size stands near 28,000 miles as of the tip of 2023.
Greater than only a mode of transportation, these traces present quick hyperlinks throughout this huge nation, stimulating financial improvement and cementing political and social harmonization.
Utilizing know-how initially harvested from Japan and Western Europe, and subsequently developed by its more and more subtle railroad trade, China has shortly made itself a number one participant in high-speed rail.
This seems set to proceed because it develops magnetically levitating (Maglev) trains able to operating at nearly 400 mph.
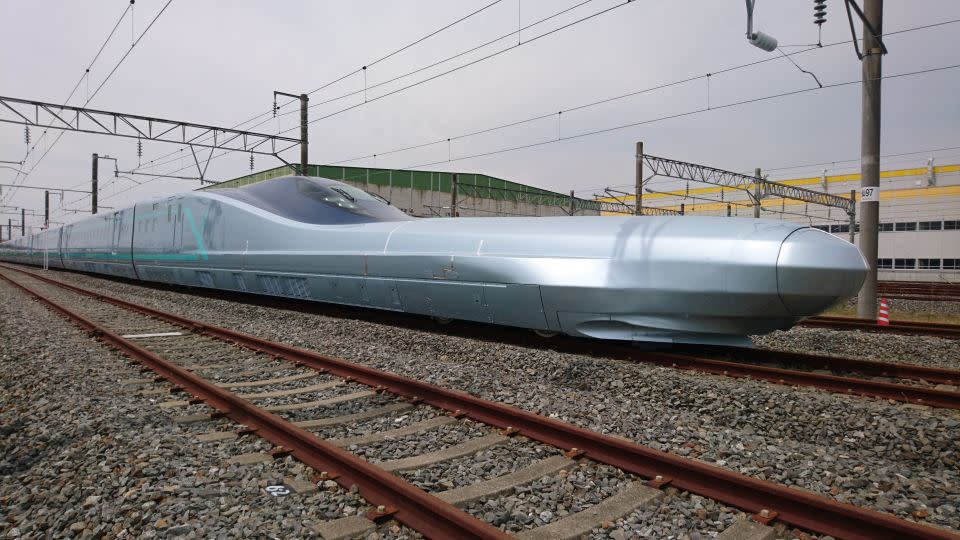


Japan has had its personal experimental Maglev line because the Seventies and is establishing a 178-mile line between Tokyo and Nagoya.
As a consequence of open in 2034, it’s going to ultimately prolong to Osaka, slicing the journey time to the latter to only 67 minutes.
“The Shinkansen is clearly way more than a method of transportation,” says British educational Christopher P. Hood, writer of “Shinkansen: From Bullet Prepare to Image of Trendy Japan.”
“It was essentially the most potent image of Japan’s postwar reconstruction and rising industrial would possibly and because it continues to evolve is prone to be so for a few years to come back.”
Though the enduring blue and white 0-Collection trains of 1964 are lengthy since retired, they nonetheless kind many individuals’s picture of what a bullet prepare seems like.
Their exceptional descendants are an indispensable a part of the transport infrastructure in Japan and plenty of different nations all over the world and, as environmental considerations make folks suppose twice about flying, they may very well be about to expertise an extra resurgence, prompting a brand new golden age for the railroad.
For extra CNN information and newsletters create an account at CNN.com




