New analysis suggests {that a} troubling disparity within the fee of enlargement of the universe, generally known as the Hubble fixed, might come up from the actual fact Earth sits in an enormous underdense area of the cosmos.
The problem has come to be generally known as the “Hubble pressure.” It arises from the truth that there are two methods to calculate the Hubble fixed on the universe’s present age, however these strategies don’t agree.
The staff behind this analysis means that this subject arises from the truth that our galaxy, the Milky Means, sits in an underdense area or “supervoid.” That may imply that house would seem to develop quicker on this “Hubble bubble,” formally generally known as the Keenan-Barger-Cowie (KBC) supervoid (additionally barely unflatteringly known as “the native gap”) thus skewing our observations.
“Voids are areas of the universe the place the density is beneath common,” staff member and College of Saint Andrews cosmologist Indranil Banik instructed Area.com. “Supervoids are voids bigger than about 300 million light-years.”
What’s a supervoid?
The universe is increasing at an extremely fast fee, however although your commute to work might appear to get longer every day, that is solely a noticeable issue at huge cosmic scales.
That implies that the Hubble fixed measures the velocity at which distant galaxies recede away from one another.
This will likely initially appear to make a discrepancy in charges of the Hubble fixed a much less urgent subject. In spite of everything, it does not have an effect on how far you need to attain in your morning espresso.
The issue is with out understanding how briskly the universe is increasing, cosmologists cannot perceive how the cosmos advanced, and our greatest mannequin of this evolution, the Lambda Chilly Darkish Matter (Lambda CDM) or “the usual mannequin of cosmology,” is lacking one thing.
So, the Hubble pressure is undoubtedly not one thing scientists can work round or ignore.
The biggest recognized supervoid within the universe is the Eridanus supervoid, which is 1.8 billion light-years large, however the KBC supervoid isn’t any slouch within the measurement division both.
“The KBC supervoid is a area that’s about 20% much less dense than the cosmic common, centered roughly the place we’re and lengthening out to a couple of billion gentle years,” Banik mentioned. “Usually, when folks measure the Hubble fixed utilizing distances and redshifts, they do not exit too far as a result of the universe’s enlargement fee has modified over time.
“Because of this folks usually do not look past about 2 billion gentle years. However that might imply observations are throughout the KBC void.”
Why would making observations throughout the KBC supervoid make sufficient of a distinction to the Hubble fixed to present rise to the Hubble pressure?
What’s the Hubble pressure?
There are two methods to calculate the Hubble pressure; let’s name these “commentary” and “concept” (although that is actually oversimplified).
Beginning with the idea technique, scientists make observations of a “cosmic fossil” known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB). The primary gentle that traversed the cosmos, the CMB, is a subject of radiation that just about evenly and uniformly fills your entire universe.
Scientists then wind the clock ahead on the cosmos, modeling its evolution utilizing the Lambda CDM as a template. This offers them a current-day worth for the Hubble fixed.
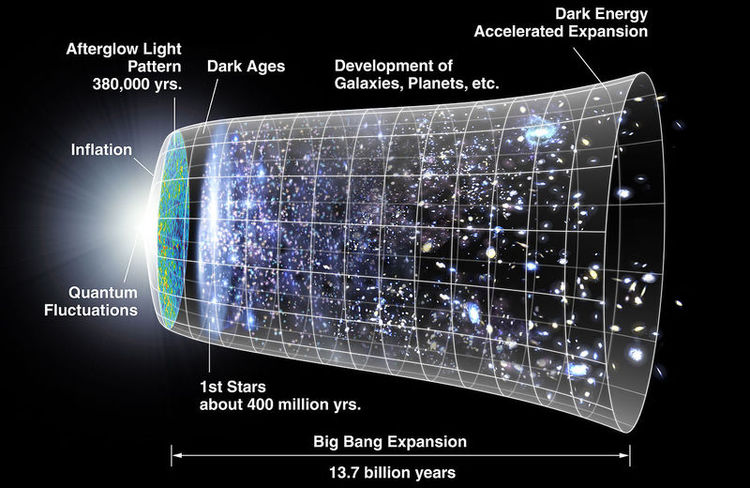
Within the “commentary” technique, scientists use astronomical information to measure distances to galaxies that host kind Ia supernovas or variable stars, two examples of objects that astronomers name “normal candles.”
They will then calculate how briskly these galaxies are receding by analyzing the change within the wavelengths of sunshine from these our bodies, or the “redshift.” The larger the redshift, the quicker a galaxy strikes away from us, and the Hubble fixed might be calculated from this.
“With the late universe, the primary factor to recollect is that as you look additional away, you look additional again in time,” Banik mentioned. “Photons which have been touring for longer get stretched extra on account of cosmic enlargement.”
The issue is that this commentary technique provides a Hubble Fixed worth that’s larger than the worth obtained by extrapolating ahead with the Lambda CDM.

The “concept technique” provides a price for the Hubble fixed of about 152,000 miles per hour per megaparsec (68 kilometers per second per megaparsec, or Mpc), whereas the “commentary technique” recurrently provides a better worth of between 157,000 mph per Mpc to 170,000 mph per Mpc (70 to 76 km/s/Mpc) relying on what observations are used.
An Mpc is equal to three.26 light-years or 5.8 trillion miles (9.4 trillion kilometers), so the Hubble pressure is clearly an enormous discrepancy.
“Late Universe observations inform us that the enlargement fee is 10% quicker than if we use Lambda CDM to extrapolate ahead to immediately from what the universe was like on the epoch of the CMB,” Banik mentioned. “It isn’t a discovery folks wished to make, that our greatest concept of cosmology is fallacious.
“That could be a downside, however nature doesn’t care about our theories!”

Banik and colleagues suppose that the Hubble pressure arises from the truth that the universe seems to be increasing quicker throughout the KBC supervoid.
“You may consider a supervoid as a homogeneous universe plus some concentrated unfavourable mass,” Banik mentioned. “This has a repulsive gravitational impact, which might elevate the redshifts of galaxies past that on account of cosmic enlargement alone.”
This makes a distinction as a result of the idea technique averages the Hubble fixed over your entire universe, whereas the commentary technique solely calculates it throughout the KBC supervoid. Thus, inside this “Hubble Bubble,” we have now a skewed and biased perspective.
“This is able to make the universe domestically appear like it’s increasing quicker than it really is, which in flip may clear up the Hubble pressure.”
Apparently, the staff wasn’t even excited about the Hubble pressure after they started investigating the KBC supervoid. What they really wished to know was if supervoids like this come up within the Lambda CDM.
“That’s after we realized that in the event you’re throughout the void, you’d suppose the universe is increasing quicker than it really is,” Banik defined. “So, that is additionally after we realized this would possibly clear up the Hubble pressure.”
As for locating if supervoids like “the native gap” are doable within the Lambda CDM, Banik mentioned the staff discovered that such a big and deep void can’t come up in the usual mannequin of cosmology, a minimum of because it presently stands.
Banik predicted that the decision to the Hubble pressure might be delivered as quickly as 2030. Nevertheless, for this to occur, he mentioned scientists should settle for that the universe has extra construction than anticipated in the usual cosmological mannequin.
“Realizing which side of ordinary cosmology must be revised to resolve the Hubble pressure might be a giant aid. Truly, fixing it can want a deeper concept,” Banik concluded. “My opinion is that the Hubble pressure might be solved inside ten years.
“Nevertheless, if I’m fallacious about what’s inflicting the Hubble pressure, then fixing it’s completely not on the horizon as there isn’t a good runner-up concept in keeping with different essential constraints such because the ages of the oldest stars.”
The staff’s analysis is revealed within the journal Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.




