Utilizing the James Webb House Telescope, astronomers have found the primary “Einstein zig-zag,” a picture of 1 quasar repeated six instances in a single picture. The association was created because of an impact first proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915 known as “gravitational lensing,” and it may assist scientists avert a disaster in cosmology.
This technique, designated J1721+8842, is comprised of a quasar — which is a particularly luminous galactic core — lensed by two extensively separated, however completely aligned, galaxies. Not solely is that this sighting extremely uncommon, marking a captivating instance of a curious spacetime-bending phenomenon launched in Albert Einstein’s magnum opus principle of gravity, normal relativity, however the J1721+8842 zig-zag additionally has an influence that normal gravitational lenses do not.
The primary Einstein zig-zag seen by humanity may assist scientists deal with two of cosmology’s biggest mysteries. The primary thriller issues is the character of darkish vitality, or the power driving the accelerating enlargement of the universe that accounts for round 70% of the cosmic vitality and matter funds, and the second has to do with a disparity scientists discover when measuring the worth of the pace of the universe’s enlargement: the Hubble fixed.
“I’m thrilled, not solely as a result of it is a fascinating pure phenomenon but in addition as a result of this technique is extremely promising for measuring cosmological parameters,” Martin Millon, discovery staff member and a Stanford College cosmologist, informed House.com. “This lens system affords the potential to put stringent constraints on each the Hubble fixed and the darkish vitality equation of state, one thing that’s usually not attainable”
What’s a gravitational lens anyway?
Common relativity states that objects with mass trigger a curvature within the very cloth of area and time, united as a single entity known as “spacetime.” The better the mass of an object, the better the “dent” it causes in spacetime. As gravity arises from this curvature, the extra mass an object has, the bigger its gravitational affect.
Gravitational lensing happens when gentle from a background supply travels previous a large lensing physique on its method to Earth, and due to this fact follows the ensuing curvature in area, inflicting its personal path to curve. The sunshine from this background supply thus takes completely different paths round a gravitational lens, approaching the lensing mass at various distances being curved in several quantities. This implies this gentle from the identical background supply can arrive at completely different instances to the identical telescope.
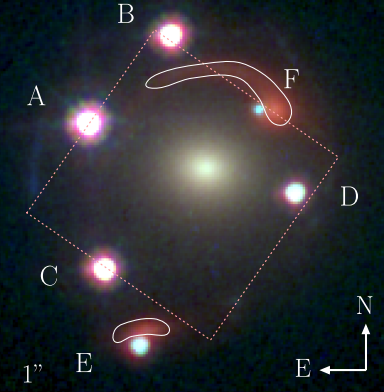
Consequently, a single background light-emitting physique can seem at a number of locations in a single picture. These objects can type preparations like Einstein rings, Einstein crosses, and, on this at the moment distinctive case, an Einstein zig-zag.
The JWST wasn’t truly the primary telescope to identify J1721+8842. The lensed quasar, which is extra particularly composed of brightly glowing fuel and dirt round a feeding supermassive black gap, was noticed by Cameron Lemon in 2017 utilizing the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Speedy Response System (Pan-STARRS) positioned at Haleakala Observatory in Hawaii.
At first, the quasar gave the impression to be lensed simply 4 instances. Nonetheless, the sensitivity of the JWST has revealed that two galaxies are literally lensing this distant quasar six instances, with the extra distant galaxy on this association additionally being lensed by the nearer galaxy.
“Sometimes, gravitational lenses created by a single galaxy type both two or 4 photos of the background supply, relying on the alignment. On this case, there’s an distinctive alignment between two galaxies and a background quasar, forming a uncommon six-image configuration,” “We known as it an ‘Einstein zigzag’ as a result of the optical path of two of the a number of photos passes by the primary galaxy on one facet earlier than being deflected by the second galaxy on the opposite facet. This optical path creates a zigzag sample between the 2 galaxies.”

Analysis lead writer and EPFL Laboratory of Astrophysics scientist Frédéric Dux informed House.com that that is the primary time that scientists have discovered such an ideal alignment between three completely different our bodies that create a gravitational lens.
“Sometimes, a gravitational lens would contain solely two objects, say a galaxy performing as a lens, and one other galaxy behind, performing as a supply, whose gentle is bent by the foreground one,” Dux stated. “In fact, there are a lot of cases of lensing occurring on account of a number of galaxies without delay, resembling in galaxy cluster lenses. In these circumstances, the consequences of the completely different deflectors are mixed in a weak means. You would not discover a single galaxy performing as an ideal lens by itself. The alignment simply is not ok.”
That is not the case with J1721+8842, although.
The closest galaxy on this lens is so distant its gentle has been touring to Earth for two.3 billion years, whereas gentle from the extra distant galaxy has been touring to us for 10 billion years. But, regardless of the huge distance between these two galaxies, Dux stated they supply an alignment so good that they each act to detect gentle from a quasar supply positioned round 11 billion light-years away, whereas the foreground galaxy additionally acts to lens gentle from the intermediate galaxy.
“That is uncommon. We count on that one in 50,000 lensed quasars would have such a configuration … and we solely know of about 300 lensed quasars in complete, so we had been very fortunate to seek out this one!” Dux stated. “We’d not discover one other one for a very long time, if ever.”
Einstein zig-zag may handle a cosmological disaster
Dux defined that the staff is already engaged on up to date fashions of J1721+8842 to measure the Hubble fixed.
“Most lensed quasars can be utilized for this function, however the truth that this one has two completely different lenses makes the lensing mannequin lots higher constrained, and the uncertainty within the Hubble fixed worth can be smaller,” Dux stated. “That is very fascinating in a time when cosmology is in a possible disaster on account of what we name the Hubble pressure.”
The Hubble pressure arises from the truth that measuring the Hubble fixed within the very early universe and extrapolating the evolution of this worth ahead by 13.8 billion years of cosmic historical past (utilizing the perfect cosmological mannequin) ought to result in the identical worth that astronomers measure once they observe the native universe and thus measure the Hubble fixed at its present age. Nonetheless, there’s a sturdy disparity between the 2 outcomes.
“There might be measurement errors in both, so earlier than declaring a particular disaster, we have to preserve looking for potential errors and refining our measurements,” Dux stated.
By lowering the uncertainties in these measurements, this Einstein zig-zag lens may carry the arrived-at worth and the noticed worth of the Hubble fixed nearer collectively.
“Moreover, this lens will also be used concurrently to constrain the equation of the state of darkish vitality of the universe,” Dux stated. “That is very fascinating as this amount, and the Hubble fixed, are sometimes degenerate, which means we are able to ‘transfer each knobs’ in several instructions and nonetheless match the observational knowledge effectively. With this technique, we’d have the ability to break this degeneracy.”
That might enable for each values to be decided concurrently utilizing J1721+8842, one thing usually not attainable. The researcher added that that is one thing presently in progress, however a lot theoretical work and technical infrastructure growth are wanted earlier than the staff can measure the 2 values they wish to study in a “protected” means, avoiding potential biases and errors.
“J1721+8842 has different functions, resembling learning the extra distant lensing galaxy,” Dux stated. “As a result of it acts each as a lens and as a lightweight supply, showing because the distorted purple arc, we are able to exactly infer its mass. We even have a stupendous spectrum from the JWST statement to check this galaxy’s star formation historical past and the clumpiness of its matter. That is the primary actual probability to reply such questions for a galaxy this distant.”
Though the JWST was integral in discovering the true nature of J1721+8842 as an Einstein zig-zag, it is probably not the perfect instrument for looking for extra of those elusive preparations.
“The JWST supplies crazily deep observations for small patches of the sky. For the invention of extra Einstein zig-zags, we have to survey your entire sky,” Dux stated. “Gaia and sky surveys, resembling Pan-STARRS, Euclid, or the long run Vera Rubin Observatory Legacy Survey of House and Time (LSST), are the fitting instruments for this search.
“We are going to preserve in search of lensed quasars! We anticipate finding many extra with the Vera Rubin LSST and the Euclid mission. Whether or not we stumble throughout one other zigzag can be a matter of luck.”
The staff’s analysis is offered in pre-print on the paper repository arXiv.





