A Chinese language rover has discovered new proof to help the speculation that Mars was as soon as residence to an enormous ocean, together with tracing some historic shoreline the place water could as soon as have lapped, a examine mentioned Thursday.
The idea that an ocean lined as a lot as a 3rd of the Purple Planet billions of years in the past has been a matter of debate between scientists for many years, and one exterior researcher expressed some scepticism concerning the newest findings.
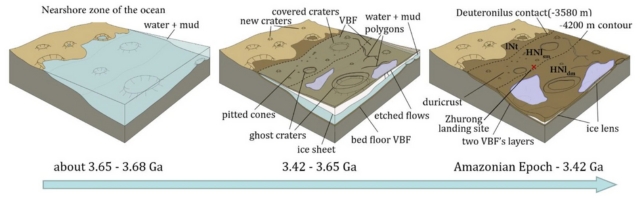
In 2021, China’s Zhurong rover landed on a plain within the Martian northern hemisphere’s Utopia area, the place earlier indications of historic water had been noticed.
It has been probing the crimson floor ever since, and a few new findings from the mission had been revealed within the new examine within the journal Scientific Reviews.
Lead examine creator Bo Wu of The Hong Kong Polytechnic College instructed AFP that quite a lot of options suggesting a previous ocean had been noticed round Zhurong’s touchdown space, together with “pitted cones, polygonal troughs and etched flows”.
Earlier analysis has urged that the crater-like pitted cones might have come from mud volcanoes, and infrequently shaped in areas the place there had been water or ice.
Info from the rover, in addition to satellite tv for pc information and evaluation again on Earth, additionally urged {that a} shoreline was as soon as close to the world, based on the examine.
The workforce of researchers estimated that the ocean was created by flooding practically 3.7 billion years in the past.
Then the ocean froze, etching out a shoreline, earlier than disappearing a bit over 3.4 billion in the past, based on their situation.
Bo emphasised that the workforce does “not declare that our findings definitively show that there was an ocean on Mars”.
That stage of certainty will possible require a mission to convey again some Martian rocks to Earth for a more in-depth look.
The coast is at all times altering
Benjamin Cardenas, a scientist who has analysed different proof of a Martian ocean, instructed AFP he was “sceptical” of the brand new examine.
He felt the researchers didn’t take sufficient under consideration how a lot the robust Martian wind had blown round sediment and worn down rocks over the previous few billion years.
“We have a tendency to consider Mars as being not very energetic, like the Moon, however it’s energetic!” mentioned Cardenas of Pennsylvania State College in america.
He pointed to previous modelling analysis which urged that “even the sluggish Martian erosion charges” would destroy indicators of a shoreline over such an extended interval.
Bo acknowledged that wind might need worn down some rocks, however mentioned the influence of meteors hitting Mars can even “excavate underground rock and sediment to the floor occasionally”.
Whereas the general concept stays contentious, Cardenas mentioned he tended “to suppose there was an ocean on Mars”.
Discovering out the reality might assist unravel a higher thriller: whether or not Earth is alone within the Photo voltaic System in being able to internet hosting life.
“Most scientists suppose life on Earth sprung up both underneath the ocean the place scorching gases and minerals from the subsurface got here to the seafloor, or very near the interface of water and air, in little tidal swimming pools,” Cardenas mentioned.
“So, proof for an ocean makes the planet seem extra hospitable.”
© Agence France-Presse




