NASA stays in an ongoing check mode to find out what’s behind the ablative thermal protecting materials that chipped away unexpectedly from the Artemis 1 Orion warmth defend throughout its reentry into Earth’s ambiance again on Dec. 11, 2022.
The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis 1 mission splashed down within the Pacific Ocean after a 25.5-day mission.
In the course of the high-speed, 25,000 miles per hour return from lunar distance, the thermal safety system of Orion’s crew module should endure blistering temperatures to maintain crew members secure. Measuring 16.5 ft in diameter, Orion’s warmth defend is the most important of its sort developed for missions carrying astronauts.
Root trigger
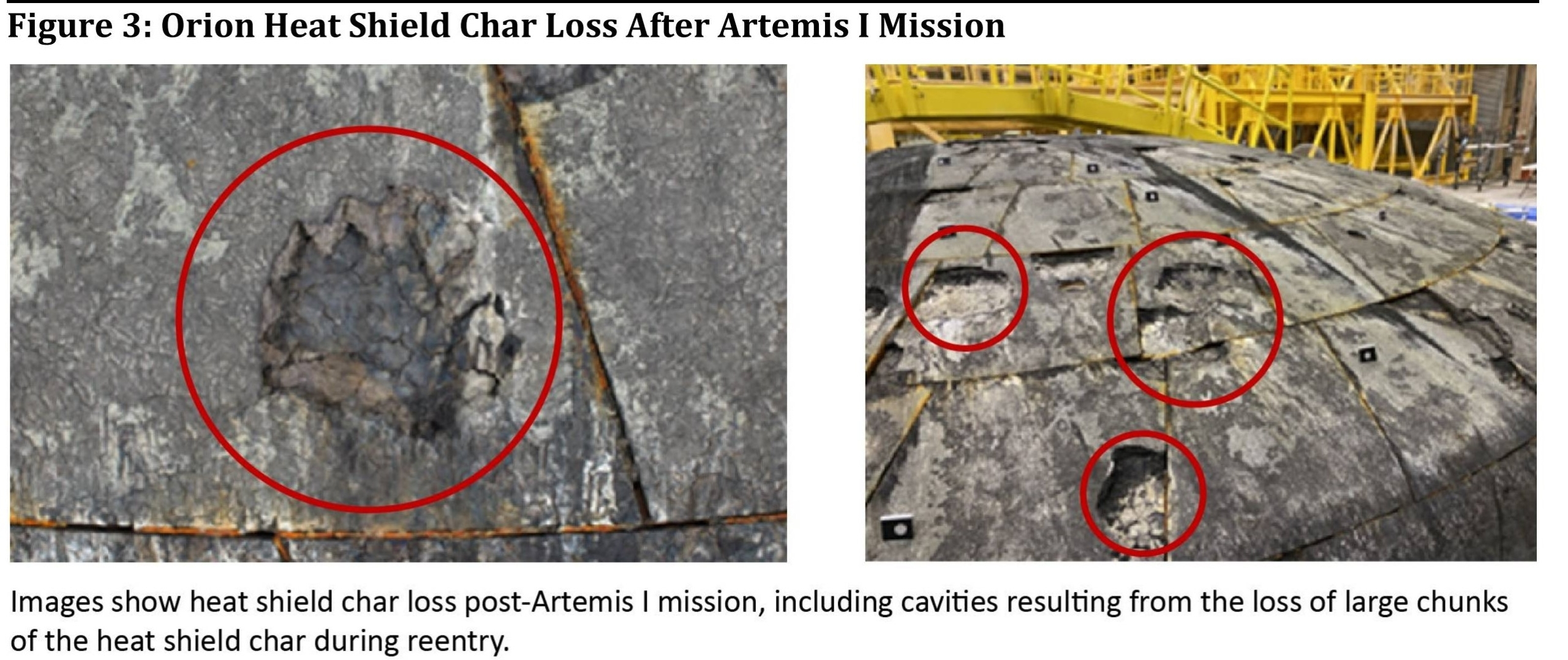
However in a post-flight evaluation of the Artemis 1 warmth defend, NASA recognized greater than 100 areas the place ablative thermal protecting materials was liberated throughout its speedy reentry.
Work to find out the basis trigger did conclude final summer time, mentioned NASA’s Lori Glaze Deputy Affiliate Administrator (Performing) Exploration Methods Improvement Mission Directorate.
Talking Oct. 29 on the Annual Assembly of the Lunar Exploration Evaluation Group being held in Houston, Texas, Glaze didn’t say what root trigger was uncovered.
Nonetheless, Glaze mentioned that further testing is ongoing earlier than any ultimate dedication is made. That testing will conclude by the top of November, then offered to NASA chief, Invoice Nelson, for a ultimate determination.
Artemis II
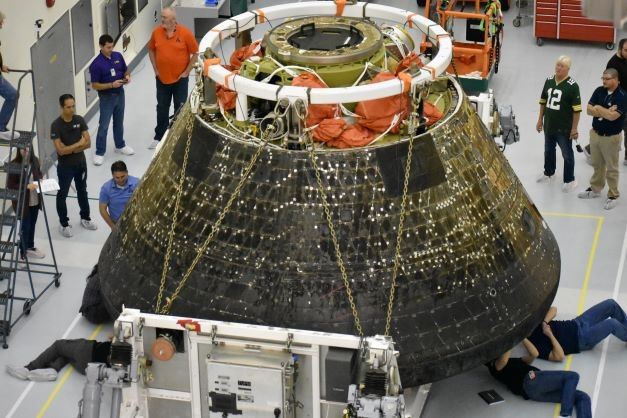
In the meantime, NASA is shifting ahead on readying the Artemis 2 {hardware} to assist hurling a four-person crew to sojourn out past the moon, then return to Earth.
The Artemis 2 crew is to depart Earth no sooner than September 2025 on a 10-day trek.
In traditional “wait a minute” type, a NASA Workplace of Inspector Common (OIG) report was issued in Could of this yr – “NASA’s Readiness for the Artemis II Crewed Mission to Lunar Orbit” – calling consideration to this subject and others earlier than sending off the primary human crew towards the moon since 1972 – the Apollo 17 mission.
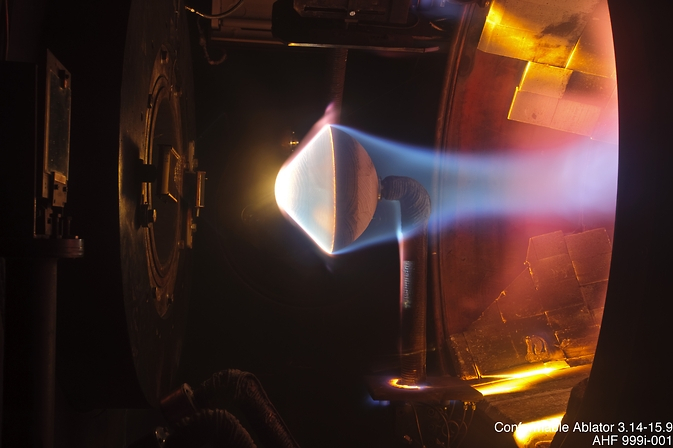
To make sure the security of the crewed Artemis 2 mission, the OIG report beneficial the Affiliate Administrator for Exploration Methods Improvement Mission Directorate to make sure the basis reason behind Orion warmth defend char liberation is effectively understood previous to launch of the Artemis 2 mission.
The OIG report known as for evaluation of Orion separation bolts utilizing up to date fashions that account for char loss, design modifications, and operational modifications to Orion previous to the Artemis 2 launch.
The report by the NASA OIG additionally notes that “human spaceflight by its very nature is inherently dangerous, and the Artemis marketing campaign isn’t any exception. We urge NASA management to proceed balancing the achievement of its mission goals and schedule with prioritizing the security of its astronauts and to take the time wanted to keep away from any undue threat.”
Avcoat modifications
The warmth defend options the identical ablative materials known as Avcoat utilized in Apollo lunar outings and return-to-Earth missions. Nonetheless, the constructing course of has modified, in line with Lockheed Martin that usual Orion’s thermal safety system.
“As a substitute of getting staff fill 300,000 honeycomb cells one after the other with ablative materials, then heat-cure the fabric and machine it to the right form, the staff now manufactures Avcoat blocks – simply fewer than 200 – which can be pre-machined to suit into their positions and bonded in place on the warmth defend’s carbon fiber pores and skin,” the aerospace agency’s web site explains. That course of is a timesaver in placing on the Avcoat – a couple of quarter of the time.

So here is the lingering and nagging query: Is it attainable that modifications within the Avcoat could also be wanted? In that case, that call would seemingly necessitate de-coupling the warmth defend from the Artemis 2 Orion capsule.
Warmth defend hiccups
When the warmth defend subject first got here to gentle, House.com contacted the Orion program workplace at NASA Johnson House Middle for remark concerning the warmth defend hiccups.
“Throughout Artemis 1 post-flight inspection, engineers noticed variations of Avcoat materials throughout the looks of Orion’s warmth defend. Some areas of anticipated charred materials ablated away in a different way than laptop modeling and floor testing predicted, and there was barely extra liberation of the charred materials throughout re-entry than anticipated,” this system workplace acknowledged.
“We anticipate the fabric to ablate with the 5,000 levels Fahrenheit the spacecraft encounters on a re-entry by Earth’s ambiance, and to see charring of the fabric by a chemical response, however we didn’t anticipate the small items that got here off, versus being ablated,” the NASA statements provides.

Wholesome margin
“We don’t know but precisely how a lot was liberated, which is why we’re analyzing the info, however there was a wholesome margin remaining of virgin Avcoat, and temperature information contained in the cabin remained at anticipated ranges, so if crew had been on board they might not have been in peril,” explains this system workplace assertion.

“It is nonetheless too early in our testing and evaluation to reach at any potential suggestions or options that handle further char liberation,” NASA responded. “It is attainable the phenomenon could [be] a part of what the warmth defend is, and what we’d anticipate as we return from the moon, however we’ll let the info inform us.”
Lastly, the NASA Orion program workplace acknowledged: “We’ll proceed to guard for variations that would occur throughout re-entry as we wish to guarantee we now have vital margin towards the assorted sorts of uncertainties that may happen because the spacecraft re-enters the ambiance. Our groups need the arrogance that we now have the very best warmth defend attainable to fly people going ahead.”
In double-checking with the NASA Orion program workplace, House.com was suggested “we now have not made any choices but, however NASA will present an replace on our plans after the completion of the investigation, and we now have decided a ahead path.”




