Demise by black gap is not at all times inevitable for stars that exist in binary methods with one in all these cosmic titans.
There could also be a manner for small stars in such methods to dodge their anticipated fates: violent supernovas that finish within the creation of one other black gap. This anticipated mechanism can be believed to show the small stars into snacks for his or her black gap companions.
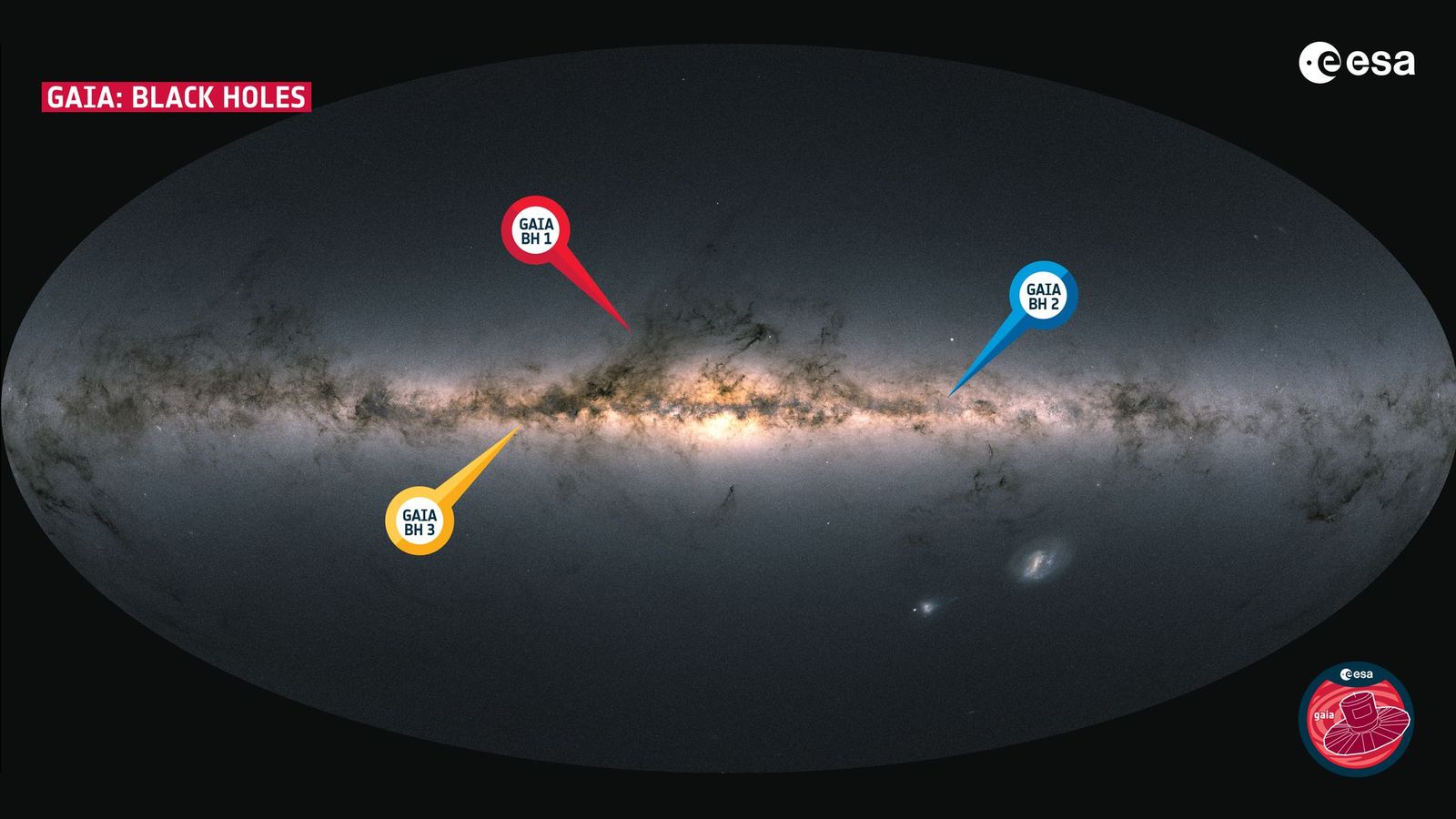
The revelation comes courtesy of two unusual black gap binary methods found by the high-precision star-tracking Gaia area telescope. The methods really comprise two of the closest black holes to Earth.
The black holes are designated BH1 and BH2 and are situated simply 1,560 and three,800 light-years from Earth within the path of the constellation Ophiuchus. The methods through which they dwell comprise stars in extensive orbits that are not being fed upon by their black gap companions and are nonetheless on the identical stage of evolution because the solar.
That is extraordinary, as companion stars aren’t purported to survive their huge accomplice star’s transformation right into a black gap. That’s as a result of the transformation to a black gap is violent and turbulent, seeing huge stars swell up and engulf companions earlier than exploding and lashing smaller companions with stellar materials and sufficient power to destroy them or kick them out of orbit. Meaning small companion stars to black holes are typically both destroyed, devoured, or ejected.
This destiny is usually sealed by interactions like mass transfers between the small companion stars and the large stars that delivery black holes, or “progenitor stars,” earlier than their deaths.
“We investigated a strategy to keep away from an interplay of the black gap progenitor with its companion,” analysis lead writer Matthias Kruckow informed House.com.
These outcomes will blow you away
With plenty round 10 occasions that of the solar, the celebs that died to delivery black holes BH1 and BH2 ought to have been so giant that they interacted with their smaller companion stars throughout their deaths.
Nevertheless, if this had been the case, then the companion stars of BH1 and BH2 ought to have been compelled out of their primary sequence lifetime; the stage accounts for 90% of a star’s life, throughout which it’s an abnormal star just like the solar that burns hydrogen to forge helium in its core. Nevertheless, plainly the celebs accompanying BH1 and BH2 should be in the principle sequence part, although this nonetheless is not clear.
Moreover, the switch of mass between the companion stars and the celebs that died to create these black holes ought to have tightened the orbits of those methods.
In these situations, methods develop with black holes in binaries with companion stars. Nevertheless, in these instances, the companion stars in these tight orbits can be so near the black gap that this cosmic titan would start stripping away stellar materials. This materials would type a disk of fabric across the black gap that step by step feeds it.
The immense gravity of the black gap causes large tidal forces to come up within the accretion disks, inflicting fiction and heating that results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation, together with X-rays.
Thus, black gap/star binaries are often recognized by their robust X-ray emissions. Nevertheless, the BH1 and BH2 methods lack these X-ray signatures.
If the celebs had been shut sufficient to their black gap companions, they may have even been squashed and squeezed right into a strand of stellar pasta by the immense gravity and tidal forces generated inside them.
This loss of life by “spaghettification” and the devouring of stellar materials is called a Tidal Disruption Occasion or a “TDE.” They’re related to shiny emissions of radiation. And, once more, it’s one thing the celebs round BH1 and BH2 have prevented.
However how?
The reply is blowing within the wind
Following the evolution of stars with plenty in extra of 80 occasions that of the solar, Krucow and crew come across an answer and a possible survival mechanism for small stars round black holes.
Kruckow defined that the important thing to survival is the robust winds that blow from extraordinarily huge stars with excessive concentrations of parts heavier than hydrogen and helium, which astronomers name “metals.”
These winds not solely assist forestall the mass switch from occurring between the celebs earlier than the black gap kinds, but in addition trigger the large progenitor star to lose mass and shrink. The robust winds from the large star additionally push the companion star right into a wider orbit.
These parts assist defend the companion star from being engulfed as their huge companions go supernova. The identical elements additionally create a wider orbit that forestalls the star from experiencing a ugly loss of life through TDE or from being consumed by its black gap companion.
The truth that each BH1 and BH2 have comparable plenty indicated to the crew that each methods adopted this identical channel of evolution.
“It was enlightening that the winds at totally different phases of the stellar evolution are answerable for totally different traits of those sorts of binary methods,” Kruckow mentioned.
Gaia has additionally uncovered a 3rd black gap binary system, which Kruckow revealed appears to be a unique sort of system.
“Gaia BH3 may be very totally different in lots of points, not solely its totally different mass, however the companion has a unique metallicity, which is far decrease than for Gaia BH1 and BH2,” Kruckow mentioned. “Moreover, Gaia BH3 is related to a stream of stars, which is believed to be the remnant of a star cluster.”
Whereas these winds and the extensive binaries the winds assist to create are useful for the survival of small stars round black holes, they’re considerably of a hindrance to astronomers searching such methods.
Kruckow defined that this wider orbit initially made it tough to substantiate BH1 and BH2 as binaries as a result of astronomers may solely observe the sun-like star parts whereas their black gap companions remained invisible.
“Moreover, the lengthy durations required to reobserve the star over a very long time to cowl the total orbit. That is wanted to distinguish binaries from random flybys,” Kruckow added.
The researcher defined that Gaia is designed to make pictures with very excessive decision, which suggests a comparability of pictures permits astronomers to see the tiny motion these distant stars have.
“In the meanwhile, that is the one strategy to detect these extensive black gap/ star binary methods,” Kruckow mentioned.

“Sadly, it is vitally unsure how widespread methods like these of BH1 and BH2 could also be, however we count on to have a whole bunch to 1000’s of them in our galaxy,” Kruckow mentioned. “The uncertainty comes from a lack of understanding of extraordinarily huge stars that type black holes. Particularly when these stars are in binaries.”
Regardless of this uncertainty, the crew expects that Gaia ought to be capable of uncover a number of % of those binaries within the Milky Means.
“Thus, we are able to hope for tens to 100 to be found with the upcoming knowledge releases from Gaia,” Kruckow concluded.
The crew’s analysis is out there as a preprint on the repository web site arXiv.




