We thought it about time we get to know our 8 legged, ocean-dwelling cousins a bit of higher, so we requested marine biologist and cephalopod skilled, Marie-Therese Noedl to delve into all there may be to know concerning the good, agile and utterly superb Octopus.
In regards to the Octopus
Octopuses are soft-bodied animals well-known for his or her eight tactile arms, massive eyes and clever behaviour. Along with squid, cuttlefish and the chambered nautiluses they’re grouped into an animal class referred to as Cephalopoda. The phrase is derived from Greek and actually means head-foot, which pertains to the truth that their arms are straight hooked up to their head.
Scientists have recognized over 300 octopus species and they are often present in each ocean of the world. Most octopuses stay on the seafloor in dens beneath rocks or in crevices. With just a few exceptions, they like a solitary way of life and solely work together with different octopuses when it’s time to mate. However even then males wish to maintain their distance, as females can generally snack on their mates within the course of.
Octopuses present plenty of fascinating options: they’ve a funnel for jet propulsion, adaptive pores and skin for camouflage, an ink sack to fend off predators, three hearts and pulsating veins, massive eyes, which are similar to our human eyes, an elaborate mind, and prehensile arms with some thoughts of their very own. Contemplating that their closest family members are clams and snails, it isn’t shocking that many individuals jokingly discuss with them as aliens. Scientists are nonetheless making an attempt to totally perceive how cephalopods developed into these clever and agile creatures. Nevertheless, learning their fossils has offered us with some clues about cephalopod evolution.

Evolution
As we speak we imagine that cephalopods derived from a bunch of small, bottom-dwelling mollusks (delicate bodied animals) referred to as monoplacophorans, that regarded similar to limpets and lived about 530 million years in the past (mya). Over time their shells elevated in dimension and guarded the early cephalopods from predators. As well as, their buoyancy allowed them to swim freely by the water column and hunt for prey. For a really very long time cephalopods dominated the world’s oceans. The arrival of recent fishes and mammals round 66 mya, nonetheless, marked the top of shelled cephalopods. Their giant and gradual our bodies have been a welcome snack for the agile and quick new predators. Nautiloids have been the one shelled cephalopod to outlive this mass extinction as they adjusted to a life within the deeper seas. The evolutionary strain from fish and mammals compelled cephalopods to adapt their bodyplan to a equally agile and predatory way of life. Over time cephalopods internalised, decreased or (in case of octopuses) utterly misplaced their shell. This did make them quicker and extra versatile but in addition rendered them extra weak to predators. So as to defend themselves from turning right into a tasty snack, octopuses due to this fact developed fascinating defence mechanisms and novel options…
Jet propulsion
The precise physique of the octopus – the mantle – is a big, muscular bulge, which comprises all important
organs, together with their gills (and sure, it type of appears to be like like their nostril). When the octopus breathes in, the sturdy mantle musculature pumps water into the mantle cavity. The water then will get expelled by a construction referred to as the funnel. Though octopuses desire to crawl, this mechanism is used throughout jet propulsion, which helps the octopus to take away itself from a scene as quick as potential.

Camouflage
The octopus pores and skin can change each texture and color to be able to match their surroundings. Though octopuses are themselves most definitely colour-blind (there’s a probability that they understand color barely in another way than us), they use three several types of pores and skin cells (chromatophores, iridiophores and leucophores) to mix into any background inside a blink of an eye fixed. Some octopuses take this camouflage to the following degree and adapt their physique to appear like a very completely different (and extra harmful) animal species all collectively. The mimic octopus as an illustration can reproduce the form of as much as 15 completely different animals together with a venomous sea snake and the spikey lionfish.
Ink
A quite common approach for a cephalopod to get out of an iffy scenario is by ejecting ink. This liquid comprises melanin (which offers the color), a mucus (which offers the 3D texture) and an irritant referred to as tyrosinase (which disrupts scent and style). When threatened, the octopus will eject ink by the funnel, which distracts the predator and buys the animal time to flee the scene. Other than defence, cephalopods additionally use ink as a approach to talk with different cephalopods (as a warning) and to hunt. Apparently, the octopus is just not proof against its personal ink and can die if uncovered to it for an prolonged time period (as an illustration in a fish tank).

Blue blood
With elevated agility got here the necessity for higher oxygen provide. Like all mollusks, octopuses have blue copper primarily based blood (haemocyanin) somewhat than pink iron primarily based blood (haemoglobin) like people. Sadly, octopus blood binds oxygen much less effectively than human blood. To beat these deficiencies and to assist their excessive oxygen calls for, octopuses have developed a very closed circulatory system. That is powered by three hearts, one common (systemic) coronary heart, which pumps the blood by the physique, and two auxiliary (branchial) hearts, which pump the blood by the gills. As well as, in areas furthest away from the systemic coronary heart (e.g. arms), pulsating veins assist to maintain the blood strain up.
Eyesight
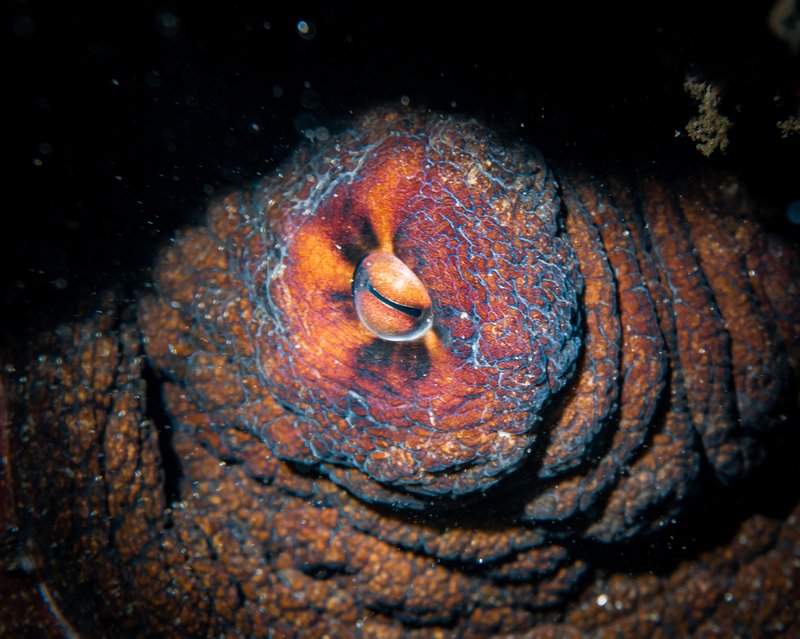
So as to compete with vertebrate predators, cephalopods developed an elaborate imaginative and prescient system, much like people. Their eyes include an iris, a pupil, and a lens. Since cephalopods lack the receptors they would wish to understand color, scientists assume that they’re color blind. Nevertheless, it’s potential that cephalopods can detect color in another way, involving a fancy mechanisms dividing wavelengths up individually after which focusing every particular person color into the retina.
Nervous system
With such excessive demand for processing data, it isn’t shocking that the cephalopod mind is comparatively giant for a mollusk. Like in all cephalopods, the octopus mind is split into a number of lobes, every of which has a distinct perform and processes data from a distinct area inside the animal (e.g. pores and skin and eyes). The central mind is located between the octopus eyes and has a doughnut-like form, as their oesophagus runs proper by its centre. And sure, meaning octopuses swallow their meals by their mind. So as to not harm the mind within the course of, their parrot like beak (the one arduous construction in an octopus physique) and a specialised tongue (radula) course of their meals into small particles.
The octopus physique comprises over 500 Million neurons, about the identical quantity as a canine’s mind. As compared, a sea slug has about 18 000 neurons and a human round 86 billion. Nevertheless, over two thirds of these neurons really reside inside their arms. Researchers have discovered, that the octopus arms can work considerably independently from the central mind by creating reflex loops to create coordinated motion. Which means octopuses can transfer their arms independently, with out ready for the mind to instruct them to take action. Nevertheless, interplay with the central mind remains to be needed to assist interpret the data acquired by the arms.

Muscular arms
The octopus arm crown consists of 8 muscular arms surrounding their mouth. Every arm is made up by a 3D community of dense muscle fibre and a central nerve chord, which permit the arm to maneuver into just about any path and even create what known as “pseudo joints”. Octopuses use their arms to discover, mate, hunt for prey and crawl or stroll. Every arm has a single or double row of round suckers (relying on the species), which the octopus makes use of to look at their surroundings. Whereas the outer sucker floor creates a seal, muscle contraction within the sucker base reduces the strain in an inside chamber and creates suction. This enables the octopus to carry an object tightly in place. Octopus suckers have impressed functions in each medication and robotics. Along with serving to the octopus perceive what their environment seems like, scientists have discovered specialised cells in these suckers, which assist the octopus to scent and style their surroundings. This implies an octopus acquires much more data from touching an object than easy texture. And if this wasn’t sufficient, octopuses are able to regenerating their arms. Some octopuses even shed just a few of their arms on objective when hunted by a predator. These sacrificed arms are supposed to distract the predator whereas the remainder of the octopus escapes.
Different fashionable cephalopods (cuttlefish and squid) have one pair of tentacles along with their 8 arms. These tentacles are used for prey seize solely and appear to have been misplaced within the octopus lineage. The evolution of those arm crowns is especially fascinating to scientists, as they’re what known as a “morphological novelty”. This implies, that no different shut relative inside the mollusks have related constructions. Finding out these new options helps us perceive the mechanisms by which new diversifications seem in evolutionary time. Apparently, to date it appears to be like like cephalopod arms are outlined by very related genes and gene pathways to human limbs throughout early embryonic growth. This doesn’t imply that our limbs are much like those of cephalopods. As a substitute, scientists imagine {that a} shared genetic program exists that defines the place a limb seems in a physique, which path it grows to and the place its back and front, and left and proper might be, respectively.
Octopus behaviour

Over 2000 years in the past, the Greek thinker Aristotle referred to as the octopus “a silly creature for it can method a person’s hand if it’s lowered within the water”. As we speak we all know that this behaviour proves fairly the alternative. Octopuses are playful, curious and clever creatures with distinct personalities. They’ll open jars and toddler proof circumstances, escape their enclosures, they are often skilled and make associations, sort out easy mazes, be taught by observing different octopuses, use instruments and even play with toys. This was shocking to scientists as a result of intelligence was regarded as a trait of social animals solely. Nevertheless, as talked about earlier than, most octopuses really desire their very own firm. Scientists imagine that octopus intelligence developed as a part of their defence mechanism to guard their delicate and weak our bodies in artistic and intelligent methods. One other fascinating octopus behaviour is the truth that they undergo completely different sleep cycles, like people.
Scientists noticed that their quiet sleep, throughout which the octopus pores and skin stays largely white, is interrupted by a really quick lively sleep part (as much as 1 min) just like the human REM part. Throughout this time the octopus pores and skin adjustments color and texture, their eyes carry out flicker actions, their suckers contract and muscle mass twitch on the physique. In people the REM part is after we expertise our most vivid desires – what would octopuses dream about (in the event that they do)?
Octopus replica
Like all cephalopods octopuses use their arms for mating. In a course of that may take a number of hours, the male octopus transfers sperm packets into the females’ mantle cavity. The feminine can mate with a number of males and shops their sperm till she is able to spawn. Most octopuses solely lay eggs as soon as of their life. They connect their eggs in lengthy strings to the ceiling or partitions of their dens and take care of them till they hatch. The feminine takes this job so significantly, that it stops feeding and by no means leaves their website. She continuously cleans and ventilates them till the infants are able to hatch. The beginning of their younger sadly marks the top of their life – chemical alerts of their mind induce a sequence of reactions that causes them to die. The younger hatchlings are then left to fend for themselves. Relying on the species, octopuses both hatch as miniature variations of their adults and begin life on the seafloor or undergo a stage, the place they drift within the open sea. There they feed on planktonic larvae till they’re sufficiently big to settle all the way down to the underside of the seafloor.

Octopus ecology
Most octopuses stay in coastal marine waters and spend a lot of their time hiding in holes, crevices and dens. Octopus dens can usually be recognized by a pile of empty crab or clam shells exterior their dens, each of that are amongst their favorite meals. Different issues these predators wish to eat are small fish, snails, shrimp and even different octopuses. They’ll use their specialised tongue to drill holes into crustaceans and snails and inject paralysing saliva into the animal. This relaxes the prey’s muscle and nearly immediately kills them. Octopuses themselves are an necessary meals supply for moray eels, dolphins, albatrosses, sperm whales, seals and even people. In actual fact, the worldwide demand of cephalopods as meals sources is rising with the decline of fish populations.
The precise variety of the world’s octopus inhabitants is just not totally identified (scientists are nonetheless discovering new species of octopuses), however they’re usually not considered beneath menace. Nevertheless, they’re identified to be delicate to pollution within the sea and have reported to build up giant quantities of hint metals and minerals by their meals. The results of rising temperatures within the sea on cephalopods is just not totally clear. A latest examine exhibits, that their our bodies are literally effectively outfitted to adapt to rising temperatures and ocean acidification for a brief period of time. Whether or not that is true in the long run and which impact these adjustments have on their younger must be decided.

Octopuses discovered alongside the UK coast
The 2 most typical octopus species discovered on the UK shoreline are the small curled octopus (Eledone cirrhosa) and the a lot bigger widespread octopus (Octopus vulgaris). The curled octopus lives from shallow coastal water all the way down to depths of 300m on a wide range of seabed varieties, together with delicate to rocky backside. The widespread octopus largely inhabits rocky areas of the Southern and Western UK shoreline. For each of those species seagrass meadows across the UK waters symbolize necessary searching grounds, the place they hunt for his or her favorite meals – the crab. These seagrass meadows are necessary marine ecosystems and the house to 1000’s of animal species. As a result of their giant biodiversity, they play an necessary function in supplying the world fisheries and thereby assist the livelihoods of many communities. Moreover, they soak up greenhouse gases (they’re answerable for sequestering 11% of carbon buried within the ocean!), produce giant quantities of oxygen, clear coastal waters (by filtering pathogens, micro organism and air pollution), and stabilise the sediment, which performs an necessary function for flood regulation. Nevertheless, they’re in regular decline worldwide. A number of tasks across the UK are engaged on restoring this necessary ecosystem to be able to deliver again the biodiversity that’s wanted for a wholesome ocean. This will even profit our favorite animal – the octopus.
What does the longer term maintain?
Cephalopods are exceptional animals that managed to push the constraints that have been set by their molluskan ancestors and reinvented themselves in lots of new methods. They lived on this planet even earlier than dinosaurs existed and hopefully will survive what’s coming sooner or later. There’s nonetheless so much left to find out about their evolution, ecology, biology and behavior immediately and that’s the reason we must work arduous to guard them.
by Marie-Therese Noedl
Marie-Therese is a Developmental Biologist who devoted a big a part of her profession to working with squid and octopuses. She studied Zoology and Marine Biology on the College of Vienna and first found her curiosity in cephalopods whereas writing her diploma thesis about octopod embryonic growth. This naturally led her to pursue a PhD learning early arm crown formation within the Hawaiian bobtail squid, throughout which she spent 5 years as a visitor scientist on the College of Hawaii in Honolulu. On her return to Europe she was recruited to work on the Italian Institute of Know-how in Genoa, the place she examined the embryonic formation of the octopus muscular arm. Later she was drawn again to the US, the place she labored on the Massachusetts Common Hospital and Harvard Medical Faculty in Boston learning tendon regeneration in fish. Household ties lately drew her again to the UK and he or she is now taking the chance to search for new instructions for her profession.
Obtain your free Constantine the Octopus Anatomy Poster!

They’re tremendous clever, have 8 arms and no bones. Constantines would possibly look a bit of completely different from their cousins within the ocean, however they’re constructed simply the identical.
Their distinctive options and distinctive skills are what make them so superior.
Obtain your individual Constantine Anatomy poster under
Constantine the Octopus Anatomy Poster
Obtain





