Black holes exert an amazing affect on their environment, that means that once they spin, they actually drag the very material of house and time round with them. Which means nothing can sit nonetheless round a rotating black gap, together with the “plates” that these cosmic titans feed from.
These flattened clouds of gasoline and dirt surrounding supermassive black holes are referred to as accretion disks. Round some supermassive black holes, the churning of those disks is among the most effective methods of changing vitality within the identified universe — altering gravitational and kinetic vitality to brilliant electromagnetic vitality, which we all know higher as simply “gentle.”
Astronomers know that dimmer accretion disks “wobble” like slowing, spinning tops round some black holes. However what hasn’t been clear is whether or not extremely brilliant, or “ultraluminous,” accretion disks additionally wobble, or “course of,” as they spin. That’s what researchers from the College of Tsukuba got down to uncover.
“The gravitational vitality of the accreting matter is launched, after which part of the launched vitality is transformed to thermal, magnetic and radiation vitality. In consequence, it’s thought that robust radiation and jets seem,” the authors wrote in a paper revealed in the Astrophysical Journal.
Spinning black holes have wobbly dance companions
Supermassive black holes with plenty thousands and thousands, or generally even billions, of occasions that of the solar are believed to dwell on the hearts of all giant galaxies — however not all of those black holes are surrounded by accretion disks.
The place accretion disks are current, the immense gravity of the central black gap generates an enormous quantity of friction within the flattened clouds, heating gasoline and dirt and reworking the matter into plasma. This causes accretion disks to glow brightly in areas that scientists name lively galactic nuclei (AGNs).
Moreover, as a result of black holes are “messy eaters,” a few of the materials in accretion disks is channeled towards the poles of blacks gap by highly effective magnetic fields, the place they’re blasted out as high-energy twin jets of plasma. Touring at speeds approaching that of sunshine, these jets are accompanied by highly effective electromagnetic emissions.
The emissions from these supermassive black hole-powered sources are seen as “quasars” right here on Earth. Some accretion disk and plasma jet emissions in AGNs could be so brilliant that they outshine the mixed gentle of each star of their house galaxy.
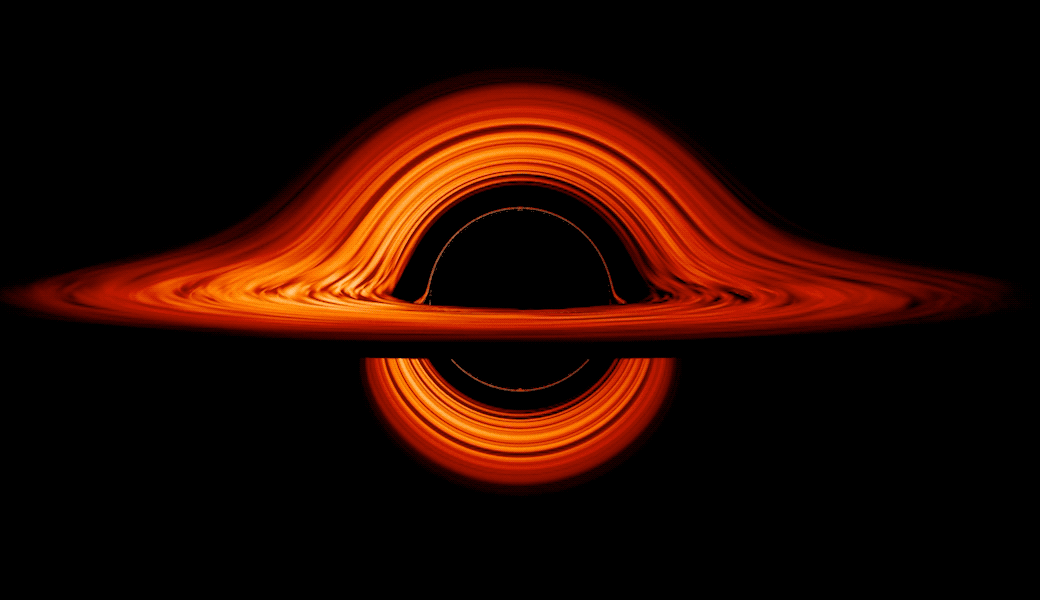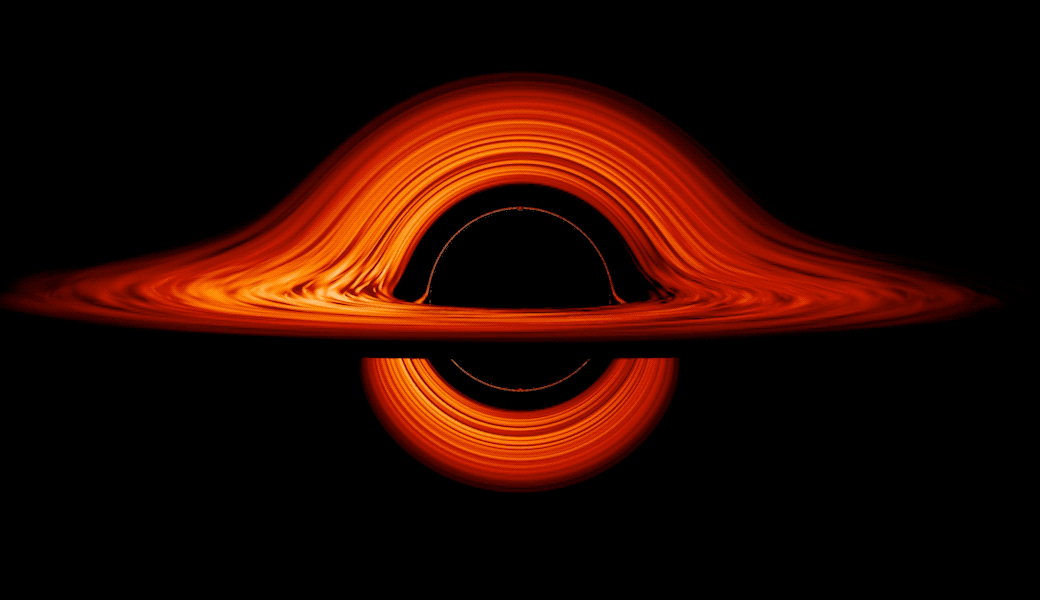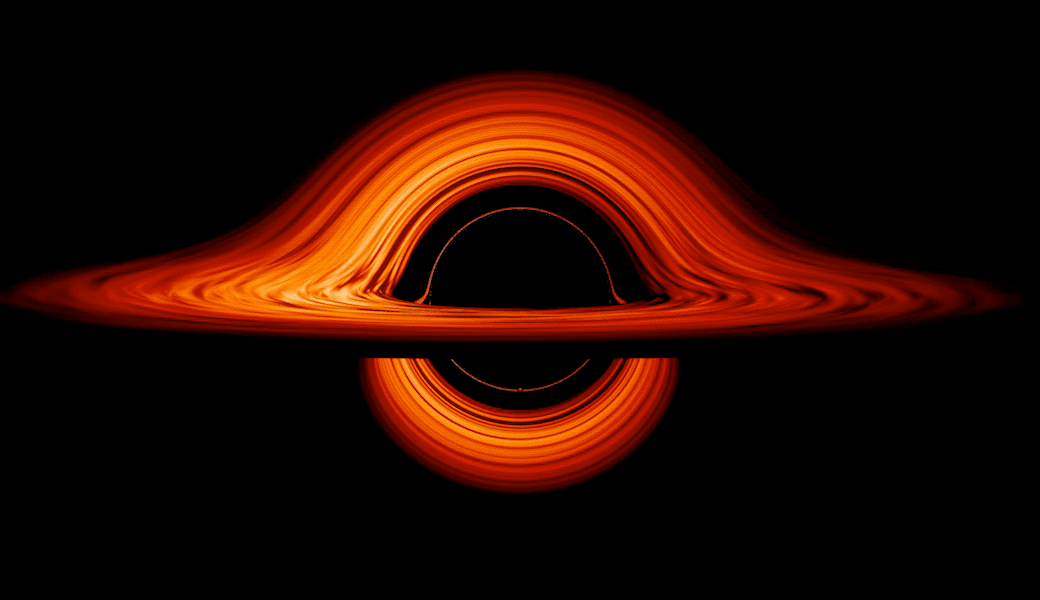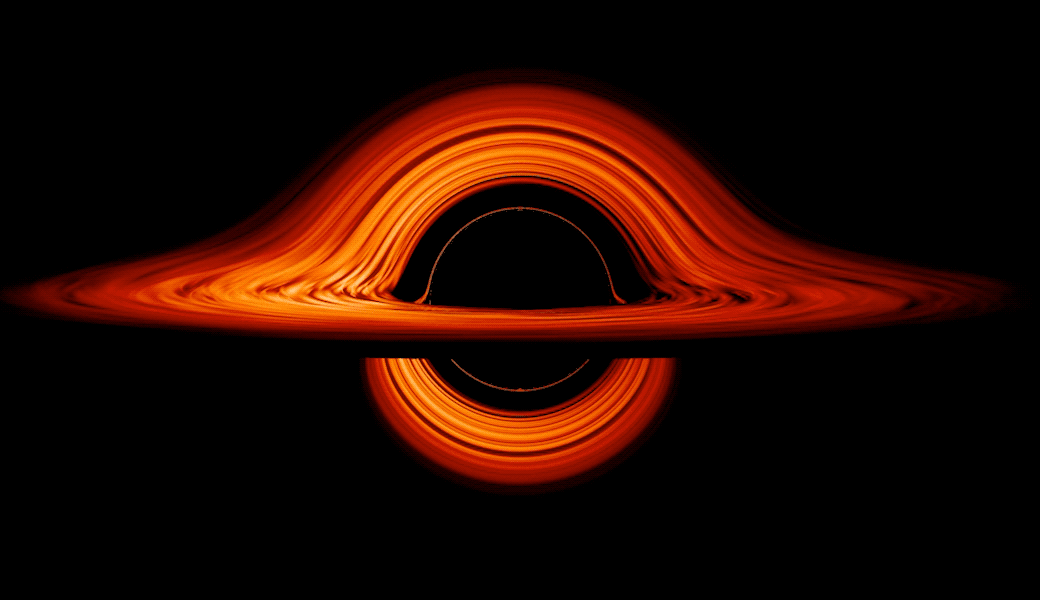
The staff behind this analysis wished to know if the brightest or most “ultraluminous” accretion disks wobble in the identical approach as their much less luminous counterparts. To find out this, the researchers carried out a large-scale simulation that factored within the dynamics of electromagnetic radiation and Albert Einstein’s 1915 idea of gravity, basic relativity.
This confirmed for the primary time that ultraluminous accretion disks certainly course of issues like dimmer accretion disks as they’re dragged round by the supermassive black holes at their hearts.
“The gasoline is especially ejected across the rotation axis of the outer a part of the disk reasonably than across the spin axis of the black gap,” the staff wrote of their paper. “The disk precession adjustments the ejection course of the gasoline with time.”
The staff additionally decided that the wobble transferred to the plasma jets blasted out from black holes sitting on the coronary heart of ultraluminous accretion disks. This might trigger these jets and the sunshine they emit to alter instructions. That might clarify the periodic adjustments in brightness seen in ultraluminous accretion disks, one thing that has been a serious puzzle for scientists.
The College of Tsukuba staff now intends to substantiate that the black holes on the hearts of those accretion disks and this analysis are certainly spinning.
They’ll do that by performing an evaluation evaluating long-term simulations with astronomical observations of those programs. This might strengthen our understanding of how the spin of black holes is essential in influencing a wide range of cosmic phenomena and ensure the impact of spinning black holes on the very material of house and time.
A examine about these outcomes was revealed in September in The Astrophysical Journal.





