I lastly have my kitchen again, and now can commit extra time to writing and consulting. I’m nonetheless pushing one other challenge, so my output right here will in all probability be restricted. I’ve taken one other take a look at my financial institution primer challenge, and realised that I’ve an excessive amount of content material — I might want to trim again the theoretical wrangling texts that I beforehand wrote. With at the moment’s article, I feel I’ve coated a lot of the content material I need to be within the e-book, though I’d stick in some cursory evaluation of some completely different banks’ stability sheets. For instance, I’d examine some teeny-tiny American financial institution versus bigger European or Canadian banks as a manner of indicating the dispersal of what “banks” are. This text has solely been calmly edited.
If the economic system was in a steady equilibrium dominated by brokers forecasting their money flows out to infinity, defaults can be a random course of – defaults would happen, however with no sample to them. Default threat can be an insurable threat (i.e., may very well be managed by actuarial calculations like life insurance coverage). Nevertheless, the existence and recognition of the time period “enterprise cycle” signifies that the flows of commerce are cycle – and defaults comply with the enterprise cycle. Throughout an enlargement, banks do face a persistent comparatively low degree of defaults and delinquent loans, which does accord with being a random, insurable threat. The issue is recessions – which see a spike in defaults. Though it’s potential for there to be a recession with no default spike (as mentioned beneath), the “fascinating” recessions are those with default spikes. The “actually fascinating” recessions are those the place the banking system itself joins in on the default development.
American Mortgage Delinquency Pattern
The above determine reveals the trendy historic expertise for mortgage difficulties for American industrial banks throughout their complete mortgage books. The odds of loans which are delinquent (debtors not assembly all obligated funds) in addition to the share of mortgage losses which are charged off are proven.
The time sequence are easy over time (“auto-correlated”), which displays the truth that they’re administered classes, and don’t mirror the actual occasions that result in default (that might be “lumpier”). If a mortgage is delinquent, it’ll stay delinquent till both the borrower recovers, or the financial institution finds a strategy to resolve the state of affairs (restructuring or forcing a default). In the meantime, charge-offs to a sure extent displays banks’ capability to resolve dangerous loans. (Though regulators are much less completely happy to permit banks to “lengthen and fake” – lengthen mortgage maturities to permit debtors to fulfill contractual obligations – than was the case traditionally. Banks which have a big e-book of “lengthen and fake” loans should not going to be trusted counterparties, and one finally ends up with a crippled banking system populated by “zombie banks.”)
The significance (or not!) of recessions to banking is evident within the determine. The 2 eras of elevated delinquencies/charge-offs occurred with the recessions related to monetary crises – the Financial savings and Mortgage debacle of the early Nineties, and the Monetary Disaster of 2008. (The Financial savings and Mortgage disaster was a drawn-out affair, with excessive delinquency charges earlier than the recession triggered by the oil value spike brought on by the invasion of Kuwait. Using excessive rates of interest by the Volcker Fed additionally created persistent credit score points in the actual economic system.)
The opposite two recessions within the time depicted don’t present credit score strains.
The recession in 2001 was concentrated within the know-how sector, the remainder of the economic system was much less affected. This recession was additionally unfold throughout different developed economies through the correlated behaviour of know-how corporations and buyers. There was a credit score loss element to the recession – know-how and telecommunications bonds did expertise giant defaults (or credit score scares, similar to by the incumbent telecom corporations in Europe that overbuilt their wi-fi infrastructure). Nevertheless, the company bond market operated because it was alleged to – the massive, concentrated credit score threat posed by giant know-how corporations was held by threat asset buyers who’ve stability sheets that may take in losses higher than leveraged entities like banks.
The recession of 2020 (which is barely seen on the determine) confirmed the other sample than standard – delinquencies fell afterwards. That is actually not what I anticipated to occur in actual time – I used to be pessimistic concerning the economic system as felt that the disruptions to exercise would result in credit score occasions. Nevertheless, the assist supplied by the federal government allowed the non-public sector to enhance its monetary place. This underlines that the recession 2020 was uncommon – it was a contraction created by authorities coverage shutting down non-public sector exercise, and never a freezing of personal sector exercise that usually displays credit score considerations.
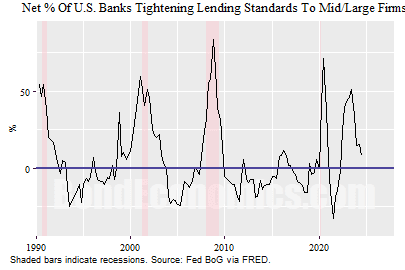
Credit score Tightening
Banks react poorly to the prospect of credit score losses, and so their willingness to make loans can be correlated with the enterprise cycle. The determine above reveals a sequence from the Senior Mortgage Officer Survey in the USA. It reveals the web share of banks that report that they’re tightening credit score requirements for giant and center market corporations. As will be seen, the web share has hit 50% in every recession since 1990 (with a spike in mid-2023 not related to a recession).
Though somebody with a cynical angle in the direction of bankers would possibly anticipate such tightening to lag the enterprise cycle, the fact is that credit score availability goes to be coincident with exercise. Lenders stepping away from extending funds to entities burning capital on ill-advised initiatives is what causes the merry-go-round of commercial capitalism to grind to halt. (That stated, regulators are superb at closing the barn door after the horse has already run far sufficient away that it’s incurring roaming costs on its cellphone.)
Credit score Spreads
If lenders should not notably completely happy to be extending new loans, pricing on loans goes to be affected. That’s, credit score spreads will widen. This suits in with the story of Part 4.1, the place the truthful worth of a credit score unfold is the same as the anticipated annualised credit score loss price. If there’s generalised stress within the credit score markets, the implied default loss price might be properly above best default loss predictions, which will be understood as buyers not being threat impartial – they want an additional incentive to take credit score threat. (From a much less theoretical perspective, technical elements out there can result in pricing that seems stupidly low cost from the angle of most buyers – sadly, these buyers are inclined to have impaired stability sheets that limits their capability to purchase a budget bonds.)
Concluding Remarks
Below regular circumstances, the enterprise cycle is a credit score cycle. A drop in financial exercise impairs incomes, resulting in credit score occasions. In the meantime, the worry of credit score occasions causes lenders to get chilly ft, resulting in the dreaded drop in exercise.
References and Additional Studying
-
When a asset-based lending bubble bursts (primarily actual property), banking techniques face crippling losses. One tactic to keep away from a recapitalisation of the banking system by the federal government is regulatory forbearance – permit banks to “lengthen and fake.” This can be a very fashionable clarification for the sluggish progress in Japan after its actual property bubble burst. Though I’ve sympathies for this argument, I feel the persistence of gradual nominal progress in Japan additionally displays the decline of the working age inhabitants and the revealed choice for value degree stability (versus inflation stability noticed in different developed international locations). One reference that makes an attempt to determine the impact of zombie banking is: Ahearne, Alan G., and Naoki Shinada. “Zombie corporations and financial stagnation in Japan.” Worldwide economics and financial coverage 2 (2005): 363-381.
-
The professional-cyclical nature of credit score is definitely demonstrated by shopping time sequence databases. The Fred financial database of the St. Louis Federal Reserve Financial institution is a really helpful useful resource for this. URL: https://fred.stlouisfed.org/
-
The heterodox financial literature emphasises the function of credit score within the enterprise cycle (though the mainstream grew to become far more within the matter after 2008). Hyman Minsky’s works stand out on this space. I summarised the subject in Chapter 5 of my e-book Recessions: Quantity I.
E mail subscription: Go to https://bondeconomics.substack.com/
(c) Brian Romanchuk 2024