Superman is not the one one with X-ray imaginative and prescient. Loads of exploding stars are additionally adept at blasting outbursts of this high-energy mild. Now, because of an opportunity discovery, scientists are conscious of a wholly new explosive stellar supply of X-ray radiation. These outbursts’ mild output did not resemble any earlier cosmic explosion. Meet the “millinovas,” a time period that can now undoubtedly make its approach into the lexicon of house fans!
In a brand new examine, astronomers found 28 of millinovas within the Giant Magellanic Cloud (LMC) and the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), two satellite tv for pc galaxies of the Milky Means. They then found that the primary of those explosions could have been noticed eight years in the past however wasn’t recognized.
Although the scientists do not fairly understand how these occasions generate X-rays, they imagine millinovas are induced when useless remnant stars referred to as white dwarfs feed off a swelled-up companion star.
“We got here throughout a gaggle of outbursting variable stars exhibiting very attribute triangle-shaped symmetrical outbursts that didn’t resemble any beforehand recognized variable stars,” group member and College of Warsaw scientist Przemek Mróz informed Area.com. “We discovered this new group of stars by probability.”
Associated: Gold mine of kilonova explosions cast by neutron stars crashing collectively
The group was looking out 20 years’ value of information from the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE) for long-duration, light-curving “gravitational microlensing occasions” that might point out the presence of black holes left over from after the Massive Bang — so-called “primordial black holes” — within the halo of darkish matter that surrounds the Milky Means.
“Over the previous months, I’ve been engaged on a venture aiming to seek for signatures of large primordial black holes within the Milky Means darkish matter halo,” Mróz mentioned. “We didn’t discover any, which demonstrated that such large black holes would possibly make up lower than a couple of % of darkish matter.”
Ordinarily, this may occasionally have upset the group. However the outcome led to the invention of those unusual stellar X-ray sources, now generally known as millinovas (or, extra appropriately, “millinovae”).
Hotter and brighter than the solar
The OGLE knowledge revealed a number of objects within the LMC and SMC that brightened by between 10 and 20 instances over the course of some months. Some even confirmed repeated explosive outbursts as regularly as as soon as each few years, whereas others solely exploded as soon as throughout the statement interval.
One particularly, designated OGLE-mNOVA-11, which erupted on the finish of final 12 months, allowed the group to carry out an in depth examine of those objects.
“In November 2023, one of many objects entered an outburst state, so we determined to hold out some further follow-up observations to review it in additional element,” Mróz mentioned. “We obtained a set of optical spectra with the Southern African Giant Telescope (SALT) telescope. We discovered emission traces from helium, carbon, and nitrogen ionized atoms, indicating extraordinarily excessive temperatures.”
Mróz added that the researchers additionally noticed this object with NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, which detected gentle X-rays coming from the supply. The group theorized that these X-rays had been produced by a fuel heated to the temperature of over 1 million levels Fahrenheit (600,000 levels Celsius).
That’s about 3 times hotter than the most popular recognized star within the universe, WR 102, and 100 instances hotter than the floor temperature of the solar. If OGLE-mNOVA-1 had occurred in our photo voltaic system, it could have been 100 instances brighter than the solar from our perspective.
What these 28 occasions resembled was an odd and, till now, seemingly distinctive cosmic explosion referred to as ASASSN-16oh, which was detected in 2016 by the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae and which the group now thinks was a millinova.
“We imagine OGLE-mNOVA-11, ASASSN-16oh, and the opposite 27 objects type a brand new class of transient X-ray sources,” Mróz mentioned. “We’ve named them millinovae, as their peak brightness is roughly a thousand instances decrease than that of classical novae.”
So what precisely are millinovas, how are they created, and what units them aside?
A distinct kind of exploding useless star
Regardless of the shortage of similarity between classical novas and dwarf novas, white dwarfs do appear to be behind the millinova thriller.
These stellar remnants are created when stars with lots just like that of the solar exhaust their gas for nuclear fusion, the method that converts hydrogen to helium of their cores. As nuclear fusion proceeds within the star’s outer layers, it swells up as a so-called “subgiant” or “crimson large star.”
Not like extra large stars, whose immense gravity ends in the creation of neutron stars or black holes after loss of life, stars just like the solar finish their lives as smoldering white dwarfs — superdense objects to make sure, however not on the identical degree.
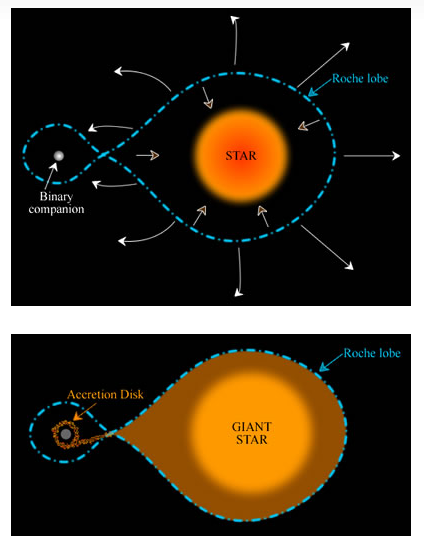
Whereas this can be a peaceable loss of life for solo stars just like the solar, many stars have binary companions that may grant them a minimum of a short lived resurrection. That is as a result of some binaries are shut sufficient for the white dwarf to start pulling materials from their companions, inflicting them to spring again to life.
In different situations, the star and the white dwarf aren’t shut sufficient to provoke this mass switch till the companion star swells up as a crimson large and fills its half of an imaginary figure-8 form, or its “Roche lobe.”
Associated: White dwarfs: Info in regards to the dense stellar remnants

White dwarfs acquiring stellar materials on this approach are already recognized to be liable for totally different nova occasions. Probably the most well-known of those are Kind Ia supernovas, by which the white dwarf is obliterated in a runaway thermonuclear explosion after stolen stellar materials piles up on its floor (although there are uncommon occasions referred to as Kind Iax supernovas, by which the white dwarf lives on as a wrecked zombie star).
Nevertheless, the group discovered that the optical mild and X-ray properties of OGLE-mNOVA-11 didn’t actually match these of “classical” novas or Kind Ia supernovas created by the thermonuclear explosion of a white dwarf when stellar materials is dumped on its floor from a companion star. Additionally they differed from the traits of “dwarf novas,” which happen in comparable circumstances however are fainter and fewer harmful and may thus repeat.
“We predict that millinovae are binary star methods composed of a white dwarf and a subgiant star, a star that has exhausted the hydrogen in its core and expanded,” Mróz mentioned. “The 2 stars orbit one another with a interval of just some days. Their proximity permits materials to circulate from the subgiant to the white dwarf.”
The College of Warsaw researcher added that, whereas it’s at present unclear how the X-ray emissions of millinovas are generated, he and the group have two preliminary concepts to work with.
“In response to one speculation, the X-rays is perhaps produced in a belt across the white dwarf’s equator, the place the fuel from the subgiant hits the white dwarf floor,” Mróz defined. “Alternatively, the X-rays could also be coming from a weak thermonuclear runaway on the white dwarf floor that’s triggered by the matter falling onto the white dwarf.
“The explosion is weak sufficient that little or regardless of is ejected from the white dwarf.”
If that is the case, the white dwarf needs to be rising in mass, which may imply that it will definitely erupts in a extra highly effective Kind Ia supernova. Thus, millinovas may very well be Kind Ia “progenitors” — an thrilling growth if true.
Kind Ia supernovas are extremely helpful to astronomers as a result of their uniform mild output permits them for use as “customary candles” for figuring out cosmic distances. Getting a tip-off as to when and the place a Kind Ia supernova is about to blow through a millinova would assist perceive these occasions higher.
Mróz defined what’s subsequent for the investigation of millinovas.
“We are going to monitor the brightness of all 29 objects in real-time and watch for the subsequent outburst to start out,” he concluded. “We additionally plan to hold out extra follow-up observations higher to know the bodily processes liable for these outbursts.”
The group’s analysis was printed on Dec. 12 within the Astrophysical Journal Letters.





