Late-night habits have become a norm for many, but did you know that they may be harming more than just your liver? While most people are aware of the liver’s vulnerability to sleep deprivation, they often overlook the impact on the thyroid. In fact, your thyroid’s health could be at risk every time you stay up past midnight.
What Happens to Your Thyroid When You Stay Up Late?
The body is controlled by an internal biological clock, connecting every organ to a rhythmic cycle influenced by light. This includes the thyroid, which secretes thyroid hormones in a pattern tied to this clock. The secretion typically peaks between 2 and 4 a.m., and gradually decreases as the day progresses. Under normal sleep conditions, thyroid function stays balanced.
However, poor sleep, frequent late nights, or sleep deprivation disrupts this internal rhythm, leading to an imbalance in thyroid hormone production. When the biological clock is disturbed, it can increase DNA damage, affect cell growth, and promote the development of thyroid disorders, including nodules and dysfunction.

How Does Staying Up Late Affect Your Thyroid?
The consequences of staying up too late go beyond feeling tired the next morning. Here’s how it can seriously impact your thyroid:
1. Hyperthyroidism or Hypothyroidism
Your body’s internal clock helps regulate hormone production. Staying up late or sleeping poorly disrupts this balance, which can lead to either hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormones) or hypothyroidism (insufficient thyroid hormones). This imbalance leads to a variety of health issues, from weight gain to fatigue, anxiety to depression.
2. Increased Risk of Thyroiditis
Sleep is a crucial recovery period for the body. Chronic lack of sleep weakens the immune system, which increases the likelihood of autoimmune diseases. Thyroiditis, an inflammation of the thyroid, is one such disease that can be triggered by an impaired immune system due to insufficient rest.
3. Hormonal Imbalance from Stress
Staying up late often comes with stress—whether from work, personal issues, or general anxiety. Prolonged stress raises cortisol levels, which negatively affects thyroid function. This can lead to further hormonal imbalances, complicating thyroid health.

Thyroid Health: Why It’s More Than Just a Local Issue
Your thyroid, located in the neck, plays an essential role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. When your thyroid is healthy, it helps maintain the body’s internal balance. But when it malfunctions, the whole body feels the impact.

1. Metabolism Issues
The thyroid regulates your body’s metabolic processes. When thyroid function is impaired, it can drastically alter how your body handles sugar, fat, and protein. Hyperthyroidism leads to rapid weight loss, increased appetite, and heat intolerance, while hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, sluggishness, and cold sensitivity.
2. Growth and Development Problems
In children, thyroid hormone deficiency can severely impact growth and cognitive development, leading to developmental delays and conditions like cretinism.
3. Cardiovascular Health
Thyroid dysfunction can cause a range of heart issues, from increased heart rate and arrhythmias to potentially fatal heart failure.

4. Digestive Issues
People with thyroid issues may experience digestive disruptions such as constipation (hypothyroidism) or diarrhea (hyperthyroidism). Thyroid imbalance can also cause liver dysfunction.
5. Reproductive Problems
Thyroid dysfunction impacts reproductive health. In women, it may cause menstrual irregularities or infertility. Men may suffer from erectile dysfunction or even infertility.
6. Neurological Symptoms
Changes in thyroid function can alter mood and mental health. Hyperthyroidism may cause agitation, anxiety, and hyperactivity, while hypothyroidism often leads to depression, memory problems, and fatigue.
7. Blood Disorders
Thyroid problems may also result in anemia and other blood-related conditions, making it harder for the body to function normally.
How to Recognize Thyroid Problems Early
Your thyroid will often send you warning signs. Here’s how to spot them:
1. Neck Swelling or Lumps
A lump or swelling in the neck could be a thyroid nodule, which may be benign or malignant. While most nodules are harmless, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you notice rapid growth or significant changes.
2. Hoarseness or Voice Changes
A persistent hoarse voice may be due to pressure on the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which is affected by thyroid enlargement or inflammation.
3. Difficulty Swallowing
Thyroid enlargement or nodules can press against the esophagus, making swallowing difficult. If this occurs, it’s important to consult a doctor for further diagnosis.
4. Sudden Weight Changes
Thyroid hormones play a key role in regulating metabolism. If you experience sudden, unexplained weight loss or gain, it might be a sign of thyroid issues. Hyperthyroidism speeds up metabolism, causing weight loss, while hypothyroidism slows it down, resulting in weight gain.
5. Emotional or Mental Changes
Thyroid dysfunction can affect your mood and mental state. Hyperthyroidism may lead to irritability, anxiety, and insomnia, while hypothyroidism can cause depression, lethargy, and difficulty concentrating.
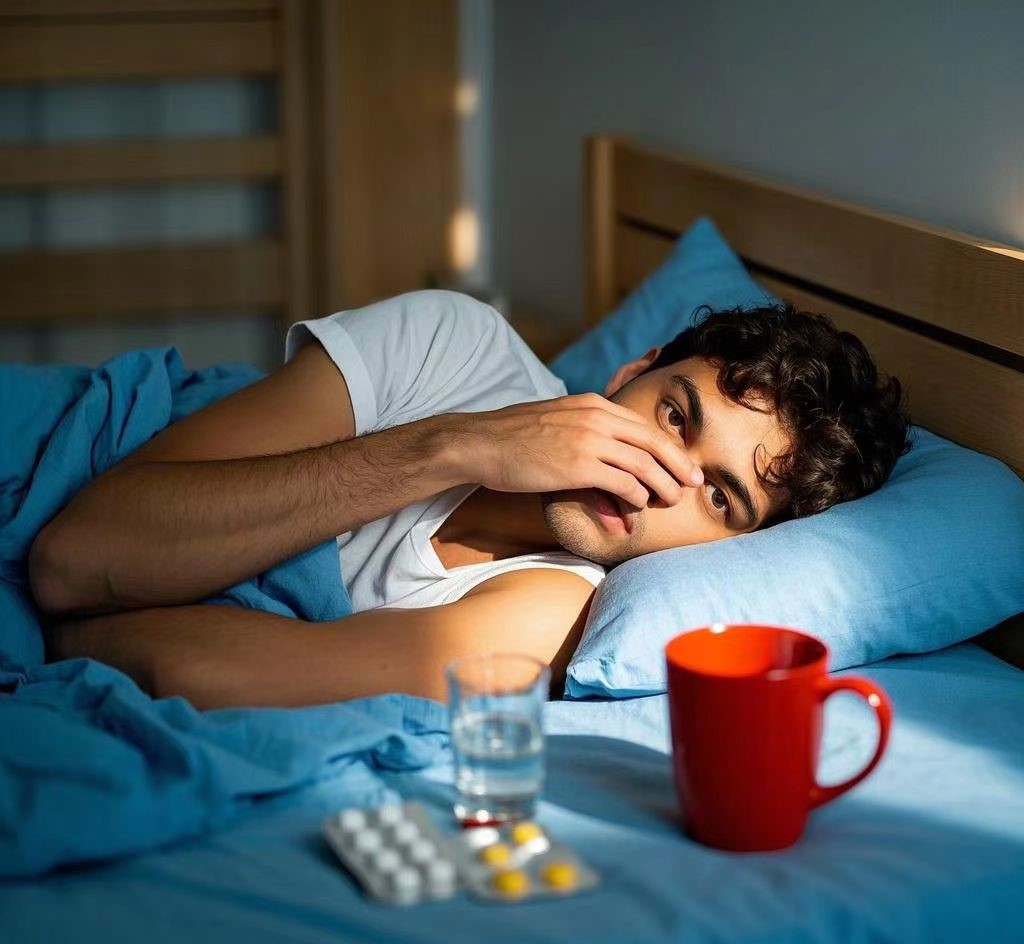

How to Protect Your Thyroid Health
Here’s how to protect your thyroid and keep it functioning at its best:
1. Prioritize Sleep
Aim for at least 7 hours of sleep per night. A regular sleep schedule helps maintain healthy thyroid function. Avoid using electronics at least 30 minutes before bedtime to prevent the blue light from disrupting your natural sleep cycle.

2. Maintain a Balanced Iodine Intake
Iodine is crucial for thyroid health, but it’s important to avoid both excess and deficiency. You can find iodine in foods like seaweed, fish, and iodized salt. However, it’s important not to overconsume iodine, as this can trigger hyperthyroidism.
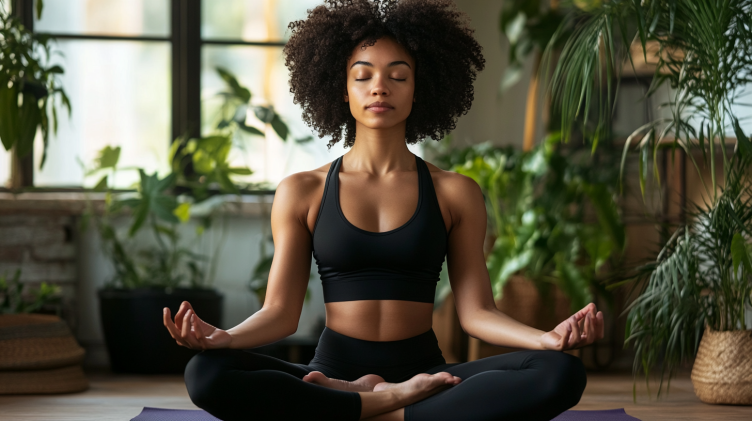
3. Reduce Stress
Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, which negatively affects thyroid health. Consider relaxing activities like yoga, listening to calming music, or engaging in light exercise to help manage stress.

4. Regular Health Checkups
Regular thyroid screenings are essential, especially for those with a family history of thyroid disorders or those who have been experiencing symptoms of dysfunction. Early detection can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Staying up late isn’t just about feeling tired the next day. It’s a silent disruptor of your thyroid health, and over time, it can lead to serious complications. By prioritizing sleep, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet, you can protect your thyroid and ensure your body stays in balance.
Remember, taking care of your thyroid today will pay off in better overall health tomorrow. Keep an eye on the signs, and take action before it’s too late.



















