최적의 건강을 추구하기 위해 특정 음식은 영양 챔피언으로 두드러집니다. 이것들슈퍼 푸드농축 용량의 비타민, 미네랄, 산화 방지제 및 섬유질을 전달하여 만성 질환에 대한 보호를 제공하면서 신체에 활력을 불어 넣습니다. 암과 싸우는 화합물에서 심장 건강에 좋은 지방에 이르기까지 전 세계 영양 전문가들이 이러한 음식을 정기적으로 통합하는 이유입니다.
음식이 “슈퍼”를 만드는 이유는 무엇입니까?
- 영양 밀도: 칼로리 당 더 많은 비타민/미네랄
- 질병 싸움 화합물: 독특한 항산화 제 및 식물 화학 물질
- 과학적 지원: 연구에서 입증 된 건강상의 이점
- 다재: 매일 식사에 쉽게 통합 할 수 있습니다
1. 자연의 완벽한 간식 : 사과
건강상의 이점
“an사과하루는 의사를 멀리 유지합니다. “과학적 장점이 있습니다.
- 케르세틴: 강력한 항 염증 항산화 제
- 펙틴 섬유: 장 건강과 소화를 지원합니다
- 폴리 페놀: 뇌졸중 및 당뇨병의 위험 감소와 관련이 있습니다
팁
최대한의 이점을 위해 피부와 함께 섭취하십시오 – 그것은 대부분의 섬유와 산화 방지제를 포함합니다!

2. 암 전투기 : 브로콜리
왜 슈퍼입니다
이 십자화과 야채는 다음과 같습니다.
- Sulforaphane: 암 줄기 세포를 파괴하는 것으로 나타난 화합물
- 인돌 -3- 카르 비놀: 호르몬의 균형을 유지하는 데 도움이됩니다
- 비타민 k: 뼈 건강 및 혈액 응고에 필수적입니다
요리 팁
가벼운 증기는 끓는 것보다 더 많은 영양소를 보존합니다. 밝은 녹색, 약간 바삭 바삭한 질감을 목표로합니다.

3. 심장 건강에 좋은 토마토
리코펜 장점
토마토그들의 붉은 색에 빚을지고 있습니다리코펜, 항산화 제.
- LDL 콜레스테롤 산화를 감소시킵니다
- 전립선 암 위험을 20% 낮출 수 있습니다.
- 요리 할 때 생체 이용할 수 있습니다
먹는 가장 좋은 방법
영양소 흡수를 향상시키기 위해 올리브 오일과 같은 건강한 지방과 짝을 이루십시오.

4. 발효 콩 경이
장 건강 부스터
전통적인발효 된 콩Tempeh 및 Miso와 같은 음식 :
- 프로바이오틱스: 개선 된 소화 및 면역
- 이소 플라본: 에스트로겐 균형 효과가있는 화합물
- 완전한 단백질: 모든 필수 아미노산이 존재합니다
이것을 시도하십시오
우마미 맛 향상을 위해 수프 나 매리 네이드에 된장 페이스트를 사용하십시오.

5. 뼈 건설 유제품
칼슘 발전소
품질유제품제공하다:
- 생체 이용 가능한 칼슘: 강한 뼈와 치아를 위해
- 비타민 K2: 동맥 대신 칼슘을 뼈로 지시합니다
- 공액 리놀레산 (CLA): 유익한 지방산
현명한 선택
더 높은 영양분 함량을 위해 가능한 경우 유기농 잔디로 먹이를주는 품종을 선택하십시오.

6. 오메가 -3 풍부한 물고기
뇌와 심장의 이점
지방이 많은 물고기처럼연어포함하다:
- EPA/DHA: 염증을 줄이는 필수 오메가 -3
- Astaxanthin: 피부 건강을위한 강력한 항산화 제
- 비타민 d: 면역 기능에 중요합니다
지속 가능성 팁
야생 또는 책임감있는 양식 옵션을 선택하십시오.


7. 완전한 단백질 : 계란
껍질의 영양
목초지가 열렸습니다계란권하다:
- 콜린: 뇌 발달에 중요합니다
- 루테인/제아잔틴: 눈 건강을 보호합니다
- 9 가지 필수 아미노산
신화를 파악합니다
계란의식이 콜레스테롤은 대부분의 사람들의 혈액 콜레스테롤에 최소한의 영향을 미칩니다.

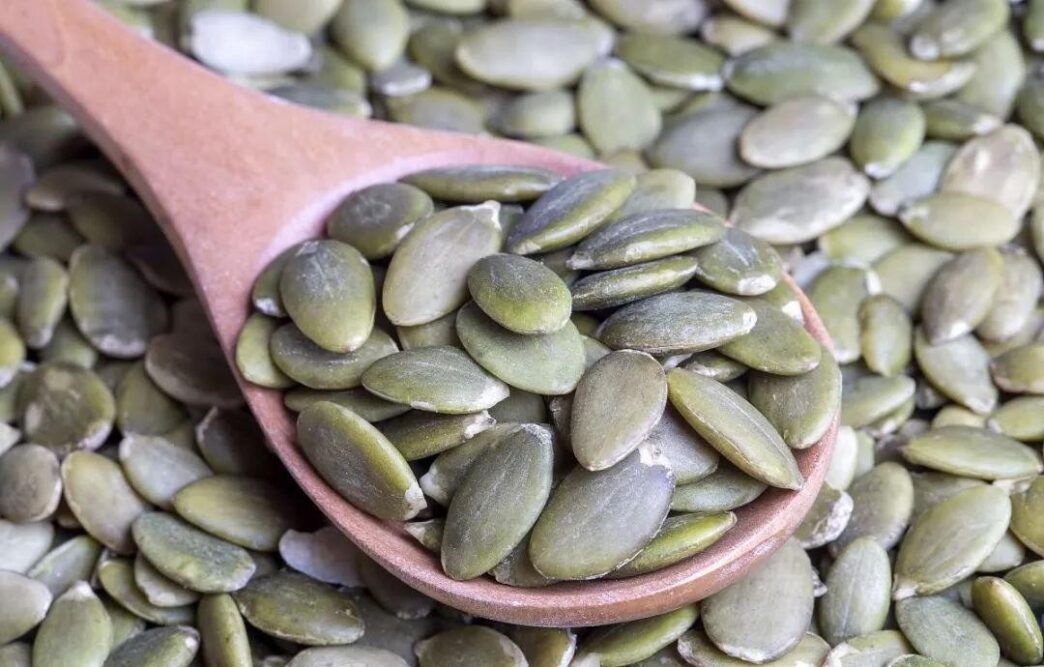
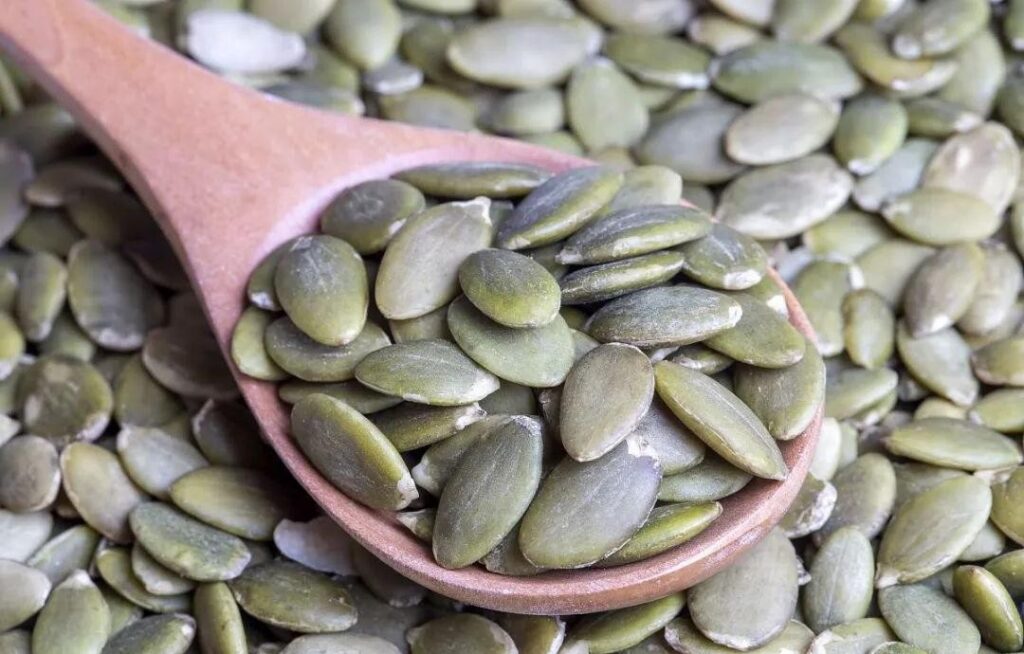
8. 강력한 씨앗
작지만 강력합니다
씨앗아마 및 치아가 제공하는 것처럼 :
- 식물 기반 오메가 -3(ALA)
- lignans: 산화 방지제 특성을 가진 식물성 에스트로겐
- 가용성 섬유: 혈당을 조절하는 데 도움이됩니다
쉬운 추가
요거트, 샐러드를 뿌리거나 스무디에 섞으십시오.

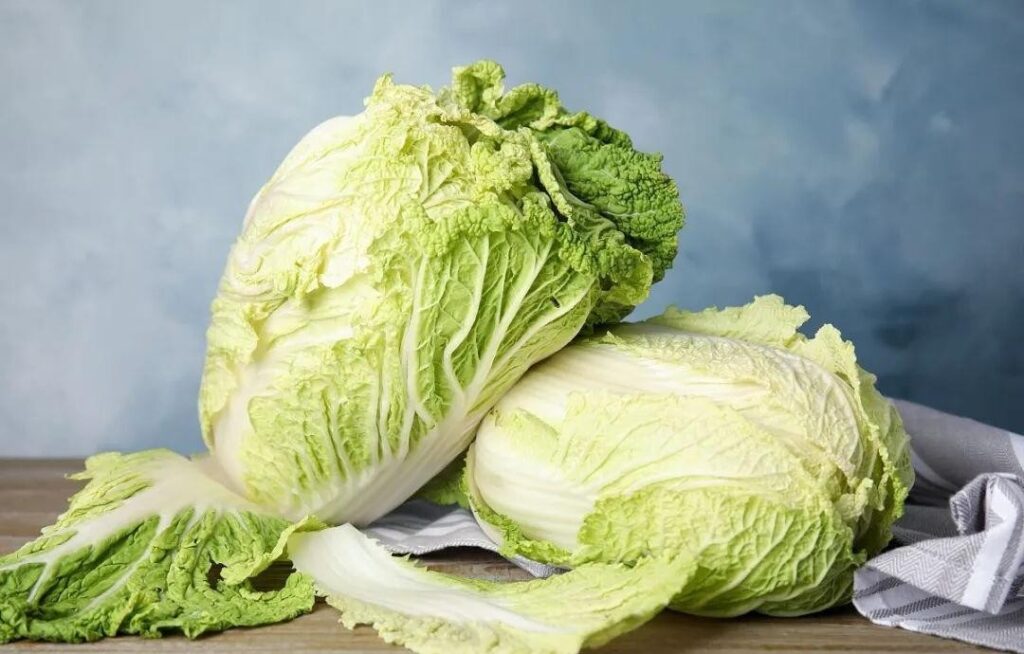
9. 수화 양배추
예산 슈퍼 푸드
이 겸손한 야채는 다음과 같습니다.
- 글루코 시놀 레이트: 암 예방 화합물
- 비타민 k: 혈액과 뼈 건강
- Sulforaphane: 특히 날로 먹었을 때
발효 보너스
프로 바이오 틱 혜택을 위해 소금에 절인 양배추를 사용해보십시오!

10. 산화 방지제가 풍부한 열매
뇌 부스터
열매블루 베리와 마찬가지로 :
- 안토시아닌:인지 기능을 향상시킵니다
- 엘라그 산: 항암 특성이 있습니다
- 혈당 충격이 낮습니다: 혈당을 스파이크하지 않습니다
스토리지 팁
영양소를 보존하고 일년 내내 즐기기 위해 신선한 딸기를 얼리십시오.

슈퍼 푸드 루틴 생성
실용적인 통합 팁
식이 요법을 쉽게 변환하십시오슈퍼 푸드-리치 습관 :
- 무지개 접근: 다른 색상을 통합합니다슈퍼 푸드다양한 영양소의 경우 매일
- 스마트 대체: 가공 된 간식을 견과류/씨앗으로 교체하십시오
- 배치 준비: 빠른 채소를 사전 세척하고 자릅니다슈퍼 푸드입장
- 스무디 부스트: 씨앗, 딸기 및 녹색을 섞어 a슈퍼 푸드펀치
결론
단일 음식은 없지만이 강국을 포함하여 정기적으로 완전한 영양을 제공합니다.슈퍼 푸드강력한식이 기초를 구축합니다. 기억하십시오 : 가장 건강한 식단은 결합 된 식단입니다다양성, 품질 및 즐거움-만들기슈퍼 푸드라이프 스타일의 지속 가능한 부분.
이번 주에 어떤 슈퍼 푸드를 사용해 보시겠습니까?의견에 알려주십시오!