アフリカ南部には、息を呑むような水の荒野が広がっています。オカバンゴデルタ。通常のデルタとは異なり、このデルタは海に流れ出していません。代わりに、それは砂漠全体に広がり、地球上最大の内陸デルタ地帯そしてアフリカで最も注目すべき生態系の一つです。
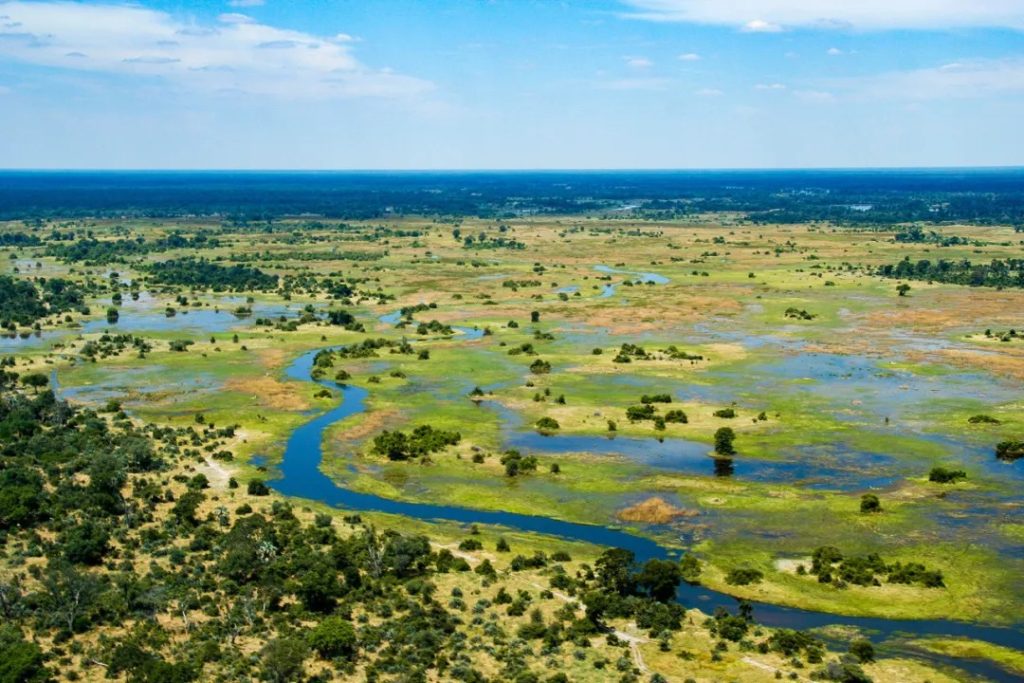

ここで、川は砂の中に消えます。カラハリ砂漠、乾燥した風景を、大まかに覆う緑豊かなオアシスに変えます。15,000平方キロメートル。

乾燥したサバンナばかりというアフリカの一般的なイメージを覆す、異常な景観。毎年、「奇跡の洪水」とも呼ばれる劇的な自然現象がこの地域に活気をもたらします。この毎年のサイクルのおかげで、デルタ地帯は世界で最も豊かな野生動物の生息地の 1 つとなり、自然愛好家やサファリ探検家にとって夢の目的地となりました。
で2014年、ユネスコ世界遺産委員会オカバンゴデルタを正式に追加しましたユネスコ世界遺産リスト、地球上で最も並外れた自然の宝庫の一つとして認められています。の一つとしても広く認められています。アフリカの七大自然の驚異。
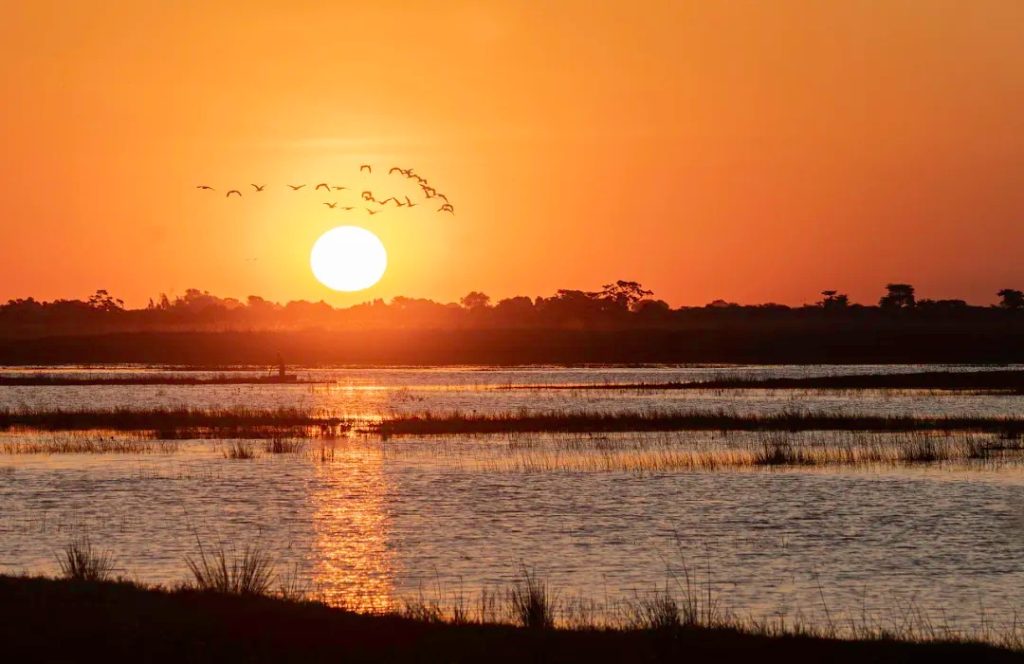

野生生物のワンダーランドを生み出す逆流川
オカバンゴ デルタの魔法は地理的な矛盾から始まります。
ほとんどの川は最終的には海に達します。のオカバンゴ川ただし、まったく異なる道をたどります。で上昇中アンゴラ高地、川は流れます1,600キロカラハリ盆地に直接流れ込む前に、海に触れることはありません。
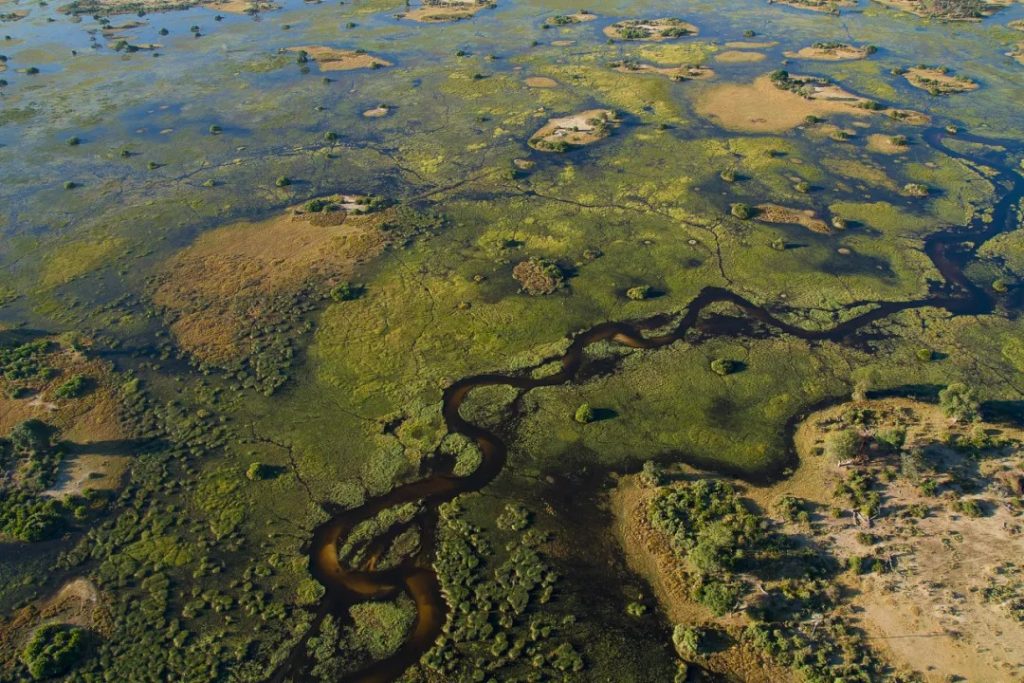

川は外側に流れ出すのではなく、砂漠を横切って広がり、巨大な湿地の迷路を形成しています。
さらに興味深いのは、水循環のタイミングです。
- 南部アフリカの大部分がアフリカに入ると、乾季、洪水はついに間のデルタに到達します。6月と8月。
- 残りの地域に雨が降ると、この地域の水は徐々に後退します。
この異常なリズムが生み出す風景は、半分陸地、半分水、一年を通して常に変化します。
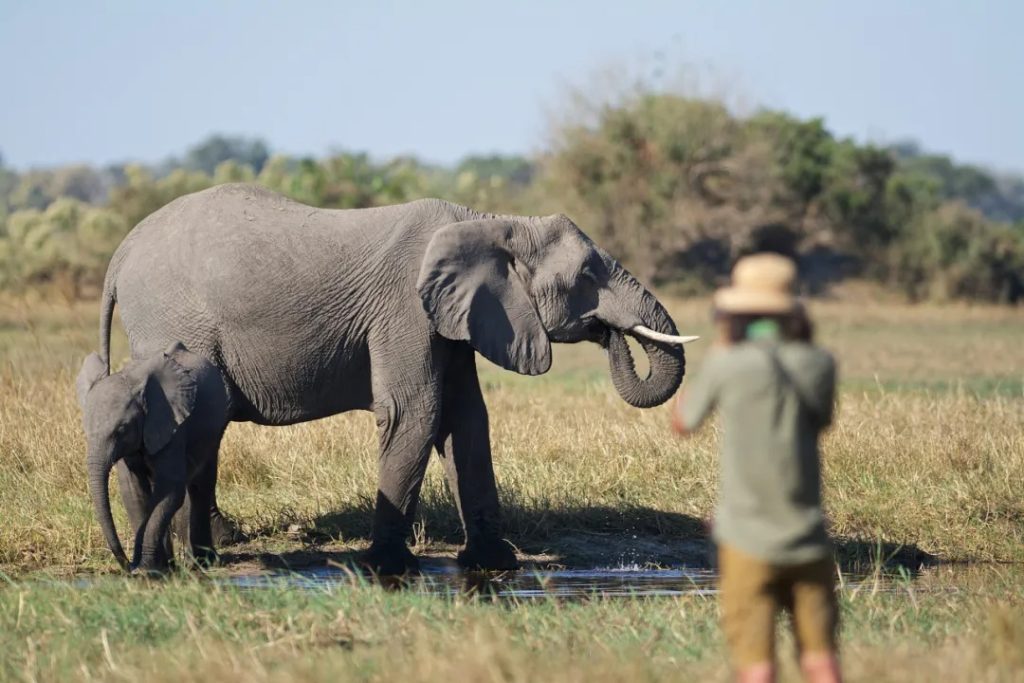

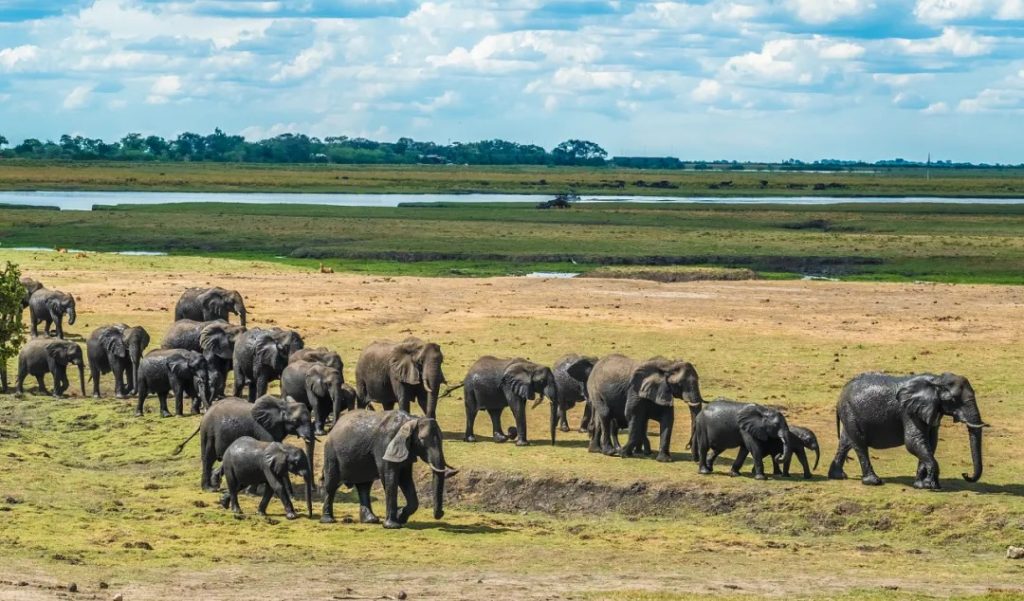
乾季には、周囲の地域から動物たちが水と食料を求めてデルタ地帯に移動します。結果は次の 1 つです。アフリカで最も野生動物の密度が高い。
20,000 平方キロメートル未満のエリア内で、エコシステムは以下をサポートします。
- より多い400種の鳥
- その周り130種の哺乳類
- 無数の爬虫類や魚類
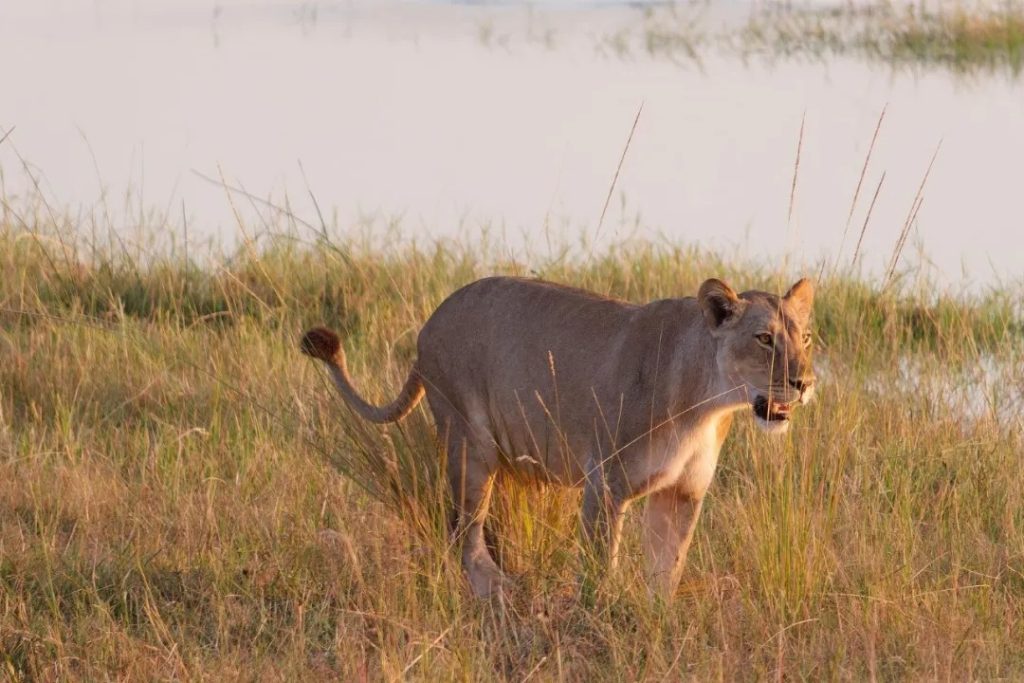

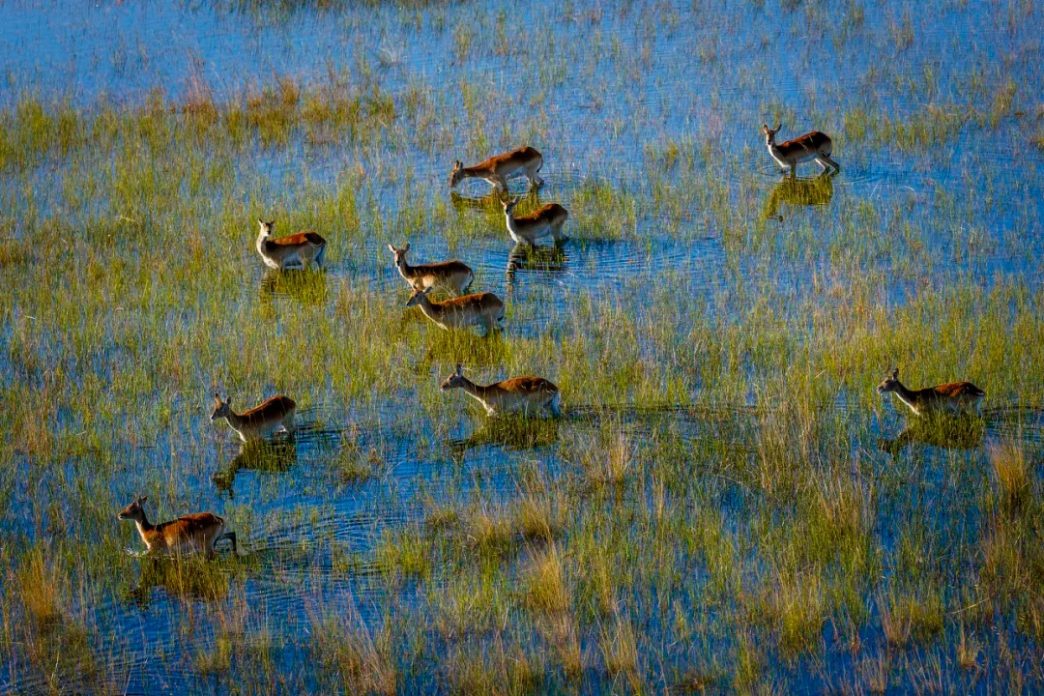
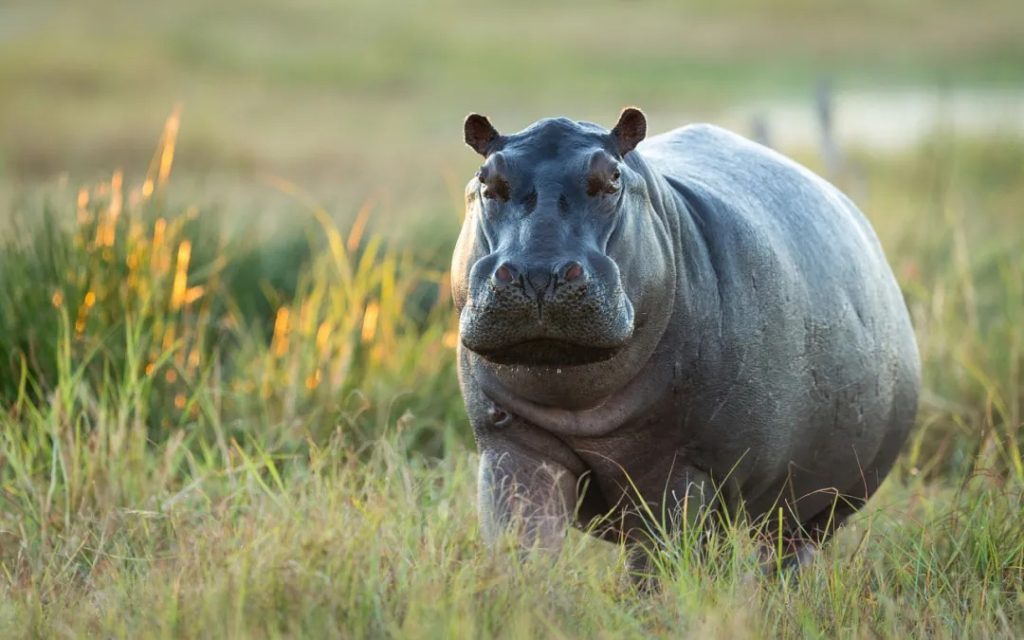
洪水が増水すると、陸地が割れて点在する島々が生じます。カバそしてナイルワニカモシカが浅い沼地を歩き回り、鳥が葦の間に巣を作りながら、曲がりくねった水路を滑空します。デルタは、多くの人が呼ぶものの壮観な舞台となる「ウォーターサファリ」。

複数の生態系が出会う風景
開けた草原が大半を占めるアフリカの多くの保護区とは異なり、オカバンゴデルタは生態系のモザイク。
ここには次のものがあります:
- 川とラグーン
- 湿地と沼地
- 草原と氾濫原
- 森林と島々
この多様性は、多種多様な野生生物にとって理想的な生息地を生み出します。
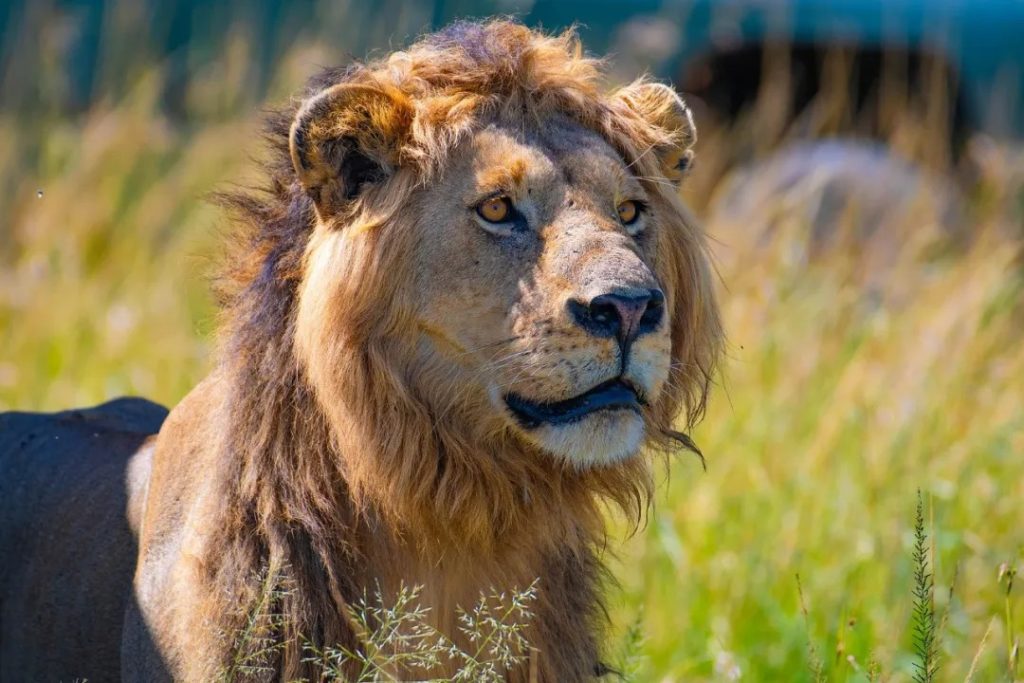
訪問者は、次のような強力な捕食者に遭遇するかもしれません。ライオンそして電光石火の速さでチーター開けた平地で。湿潤な地域では、大規模なアフリカのブッシュゾウ群れとアフリカ水牛沼地や湿地の中を移動します。
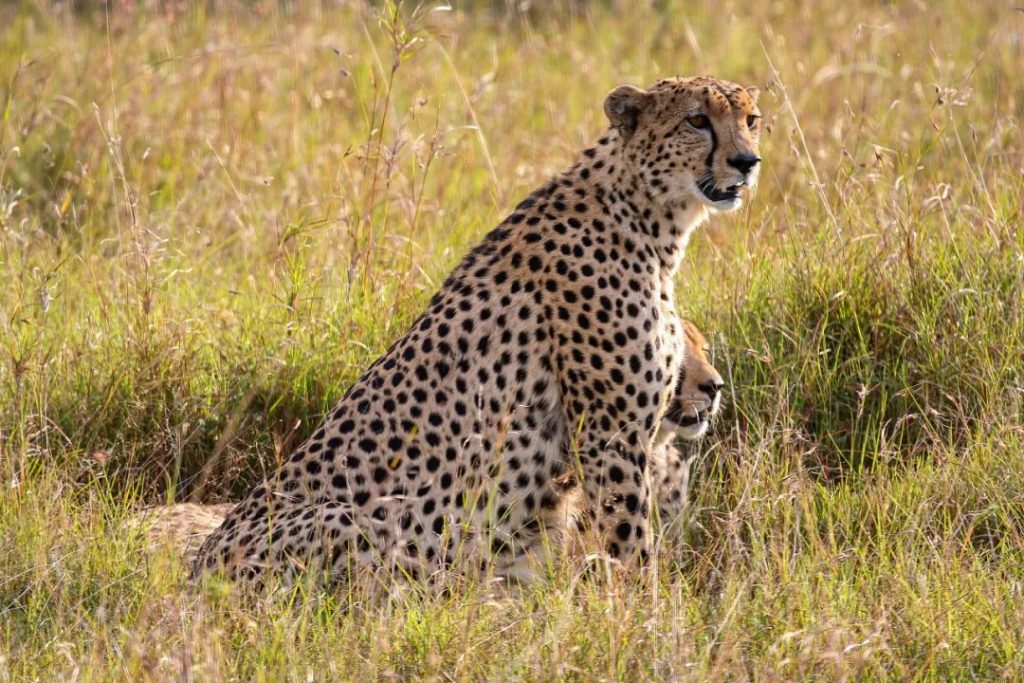

森や川岸の間には、次のようなとらえどころのないハンターが隠れています。ヒョウそしてブチハイエナ。
この驚くべき生態学的多様性こそが、まさにオカバンゴ デルタがしばしば「デルタ地帯」と言われる理由です。アフリカの「野生動物観察の天井」—究極のサファリ環境。

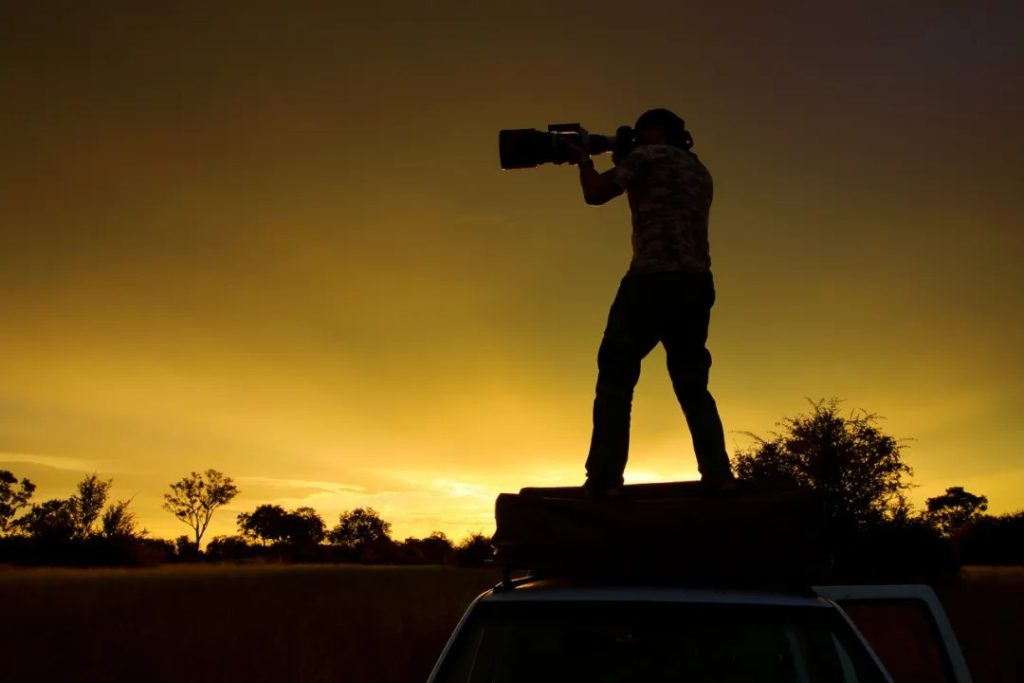
究極の 3 次元サファリ体験
世界クラスのサファリの目的地は、野生動物だけで定義されるのではなく、人々がそれをどのように体験するか。オカバンゴ デルタは、冒険を提供することで優れています。陸、水、そして空。

ランドサファリ: 野生動物を間近で追跡
陸上では、サファリは通常、特別に装備された室内で行われます。四輪駆動車またはガイド付きウォーキングツアーに参加してください。
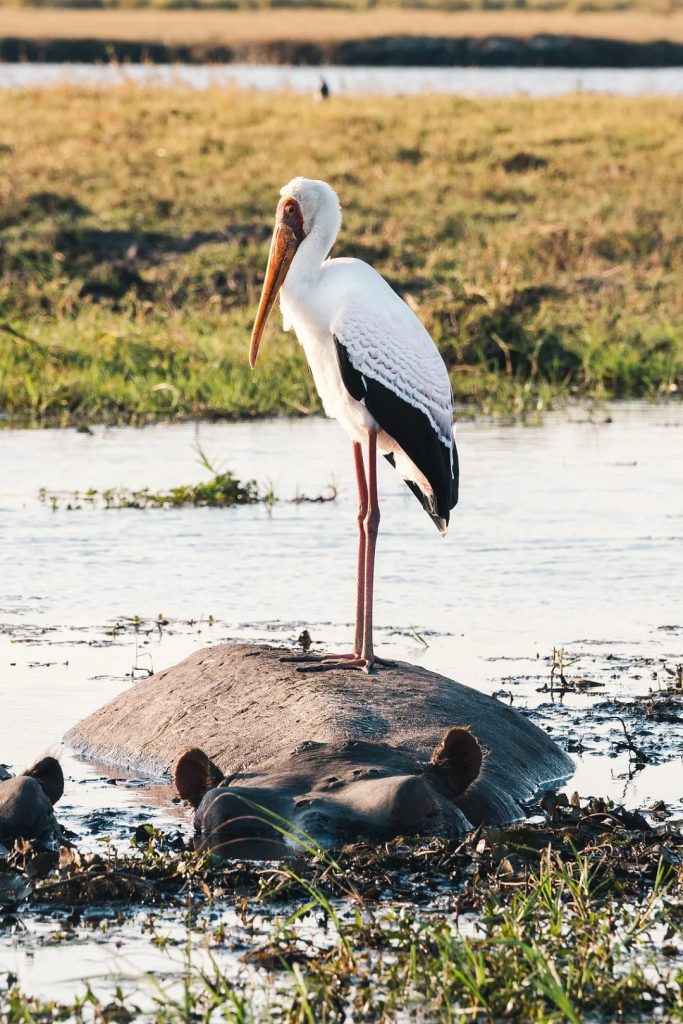

草原と湿地が入り混じっているため、多くの地域ではぬかるんだ地形用に設計された車両が必要です。これらの「湿地サファリ車」は幅広のタイヤを備えており、ガイドがほとんどの旅行者が決してアクセスできない遠隔地に到達できるようになります。
これにより、自然の生息地で動物を至近距離で追跡する素晴らしい機会が得られます。
ウォーター サファリ: デルタの代表的な体験
オカバンゴ デルタが他のアフリカの公園と本当に違うのは、水上サファリ。
旅行者は伝統的な方法で湿地を探索することがよくあります。モコロ—伝統的に船の幹から彫られた丸木舟バオバブ木。熟練した地元ガイド、として知られています。「極論者」長いポールを使ってカヌーを狭い水路にゆっくり押し込みます。
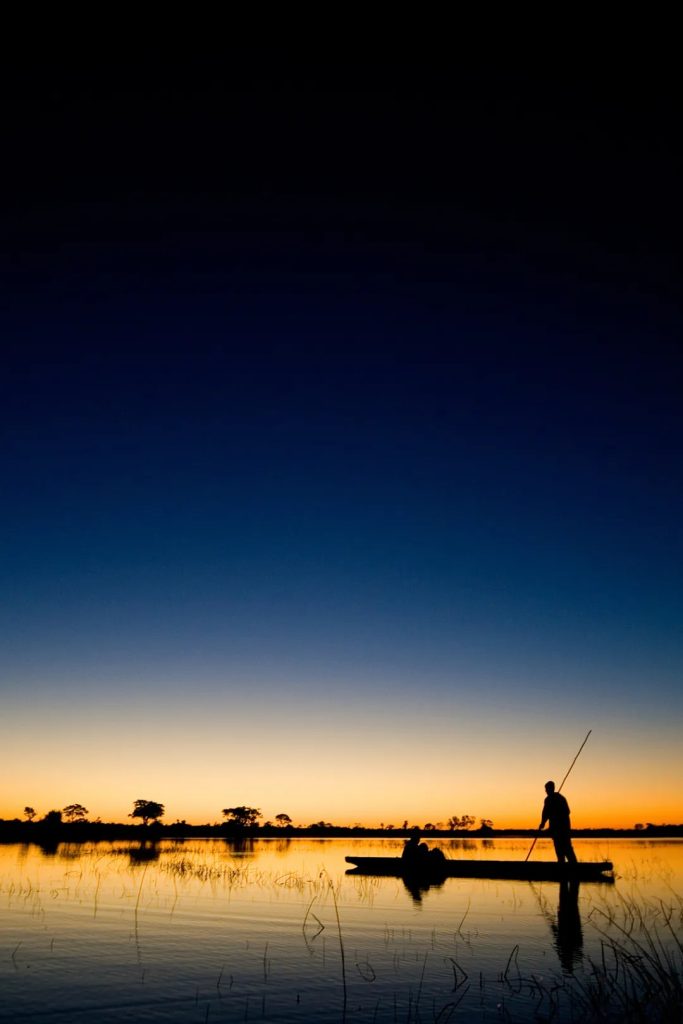

葦の間を音もなく滑空すると、カバやアンテロープから色とりどりの水鳥に至るまで、湿地の野生動物を間近で観察できます。この体験は平和で没入型で、自然と深く結びついています。
航空写真: デルタを空から観察しましょう
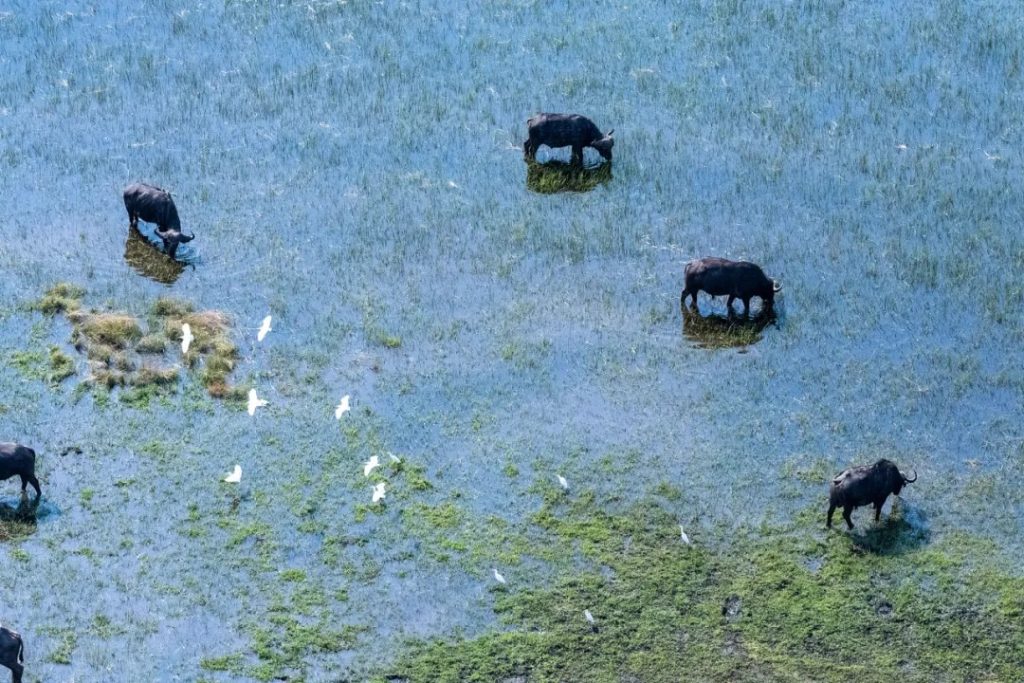
まったく異なる視点から見るために、多くの旅行者は次のように考えています。小型飛行機またはヘリコプターの飛行デルタの上。
空から見ると、水路、島々、氾濫原が複雑に絡み合った風景がその美しさを最大限に明らかにします。乾季には、陸地を横切るライフラインのような自然の水路に沿って移動する動物の群れを見ることもできます。

自然への敬意に基づいて構築されたサファリ
オカバンゴ デルタのアフリカの名声究極のサファリの目的地野生動物の豊かさだけが問題ではありません。それは保全にもつながります。
この地域の観光は次の厳格な原則に従っています。
- 来場者数制限あり過剰発達を防ぐために
- 野生動物の行動への干渉を最小限に抑える
- 地域社会と伝統的な生態学的知識を尊重する
これらの努力のおかげで、デルタ地帯は地球上に残された最も自然のままの自然地域の 1 つであり続けています。
ここでのサファリは、単に動物を観察するだけではありません。それは自然との力強い出会いとなり、野生の生命のありのままの美しさと回復力を明らかにする旅になります。